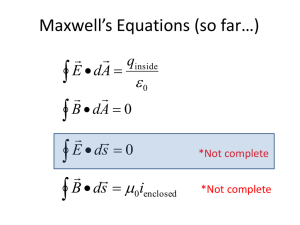Ch. 15: Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... 4. On an irregularly shaped conductor, the charge tends to accumulate at locations where the radius of curvature of the surface is smallest, that is, at sharp points. The first property is true since if the electric field is not zero inside a conductor, then some of the sea of mobile charges inside ...
... 4. On an irregularly shaped conductor, the charge tends to accumulate at locations where the radius of curvature of the surface is smallest, that is, at sharp points. The first property is true since if the electric field is not zero inside a conductor, then some of the sea of mobile charges inside ...
What are electric and magnetic fields?
... body. At the levels encountered in everyday life, these are too small to have any effects. In fields of several kV/m, sensitive individuals might feel minute vibrations of skin, hair or clothing. Some people may experience small shocks when touching large ungrounded objects (eg, a large bus) in thes ...
... body. At the levels encountered in everyday life, these are too small to have any effects. In fields of several kV/m, sensitive individuals might feel minute vibrations of skin, hair or clothing. Some people may experience small shocks when touching large ungrounded objects (eg, a large bus) in thes ...
The birth of the electric machines: a commentary on Faraday (1832
... Ørsted’s original interpretation was that the magnetic effects produced by the current through the wire radiated outwards in the same way that heat or light does. But after further experimentation he showed that in fact the produced magnetic field circled around the wire (although of course no one w ...
... Ørsted’s original interpretation was that the magnetic effects produced by the current through the wire radiated outwards in the same way that heat or light does. But after further experimentation he showed that in fact the produced magnetic field circled around the wire (although of course no one w ...
Types of Relays Types of Electromagnets
... weaken. The power of the release spring will become stronger than the magnetic attraction, so the armature will release and the relay will be in a relaxed state. When the armature has released, there will be almost no residual magnetic flux in the semi-hard magnetic material. Note: In contrast to th ...
... weaken. The power of the release spring will become stronger than the magnetic attraction, so the armature will release and the relay will be in a relaxed state. When the armature has released, there will be almost no residual magnetic flux in the semi-hard magnetic material. Note: In contrast to th ...
EMF
... We call the curly electric fields Non-Coulomb electric fields ENC They are related to magnetic fields that are changing in time: ...
... We call the curly electric fields Non-Coulomb electric fields ENC They are related to magnetic fields that are changing in time: ...
lecture1423813661
... The Co-ordinate Systems, Rectangular, Cylindrical, and Spherical Co-ordinate System. Coordinate transformation. Gradient of a Scalar field, Divergence of a vector field and curl of a vector field. Their Physical interpretation. The Laplacian. Divergence Theorem, Stokes Theorem. Useful vector identif ...
... The Co-ordinate Systems, Rectangular, Cylindrical, and Spherical Co-ordinate System. Coordinate transformation. Gradient of a Scalar field, Divergence of a vector field and curl of a vector field. Their Physical interpretation. The Laplacian. Divergence Theorem, Stokes Theorem. Useful vector identif ...
Faraday and the Electromagnetic Theory of Light
... of field and field lines, moving away from the mechanistic explanation of natural phenomena like Newton’s actions-at-a-distance. Faraday’s introduction of the concept of field into physics is perhaps his most important contribution and was described by Einstein as the great change in physics because ...
... of field and field lines, moving away from the mechanistic explanation of natural phenomena like Newton’s actions-at-a-distance. Faraday’s introduction of the concept of field into physics is perhaps his most important contribution and was described by Einstein as the great change in physics because ...
2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Science SMART Teacher`s
... Science SMART Teacher’s Guide Grade 4 Chapter 6 Lesson Plans ...
... Science SMART Teacher’s Guide Grade 4 Chapter 6 Lesson Plans ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.