MICHAEL FARADAY, EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCHES IN
... round one part of this ring, each containing about twenty-four feet of copper wire onetwentieth of an inch thick; they were insulated from the iron and each other, and superposed in the manner before described (6), 6 occupying about nine inches in length upon the ring. They could be used separately ...
... round one part of this ring, each containing about twenty-four feet of copper wire onetwentieth of an inch thick; they were insulated from the iron and each other, and superposed in the manner before described (6), 6 occupying about nine inches in length upon the ring. They could be used separately ...
Document
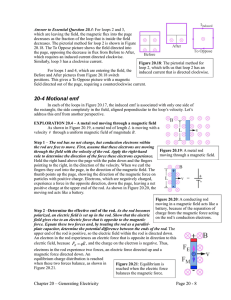
... the sides of the stream. We can use a paddlewheel as a tool to measure the curl. The air stream at the left exhibits no curl. Insert the paddlewheel into that air stream and it doesn’t turn. Insert the paddlewheel into the air stream at the right and it will turn, except in the dead center. To eith ...
... the sides of the stream. We can use a paddlewheel as a tool to measure the curl. The air stream at the left exhibits no curl. Insert the paddlewheel into that air stream and it doesn’t turn. Insert the paddlewheel into the air stream at the right and it will turn, except in the dead center. To eith ...
magnet - UniMAP Portal
... an induced magnetic field is set up around the primary coil. The current increases from zero to some value over a short period of time. The changing electrical current produced a changing magnetic field which is the cause of the induced current. • When the switch is opened, the current decreases whi ...
... an induced magnetic field is set up around the primary coil. The current increases from zero to some value over a short period of time. The changing electrical current produced a changing magnetic field which is the cause of the induced current. • When the switch is opened, the current decreases whi ...
Magnets - Max-Planck
... harmful solvents, instead of the energy-intensive conditions of high pressure and high temperature. With this in mind, Faivre wants to understand how nature manages to produce the uniform magnetic particles. “Nature shapes material down to the smallest detail, literally down to the smallest unit, th ...
... harmful solvents, instead of the energy-intensive conditions of high pressure and high temperature. With this in mind, Faivre wants to understand how nature manages to produce the uniform magnetic particles. “Nature shapes material down to the smallest detail, literally down to the smallest unit, th ...
electromagnets - School Science
... It is possible to use a plotting compass to show the shape of the magnetic field around an electromagnet, in the same way as for a permanent magnet. At the same time, you can see the effect of changing the current; a compass will line up more stubbornly in a stronger field. From straight wire to elect ...
... It is possible to use a plotting compass to show the shape of the magnetic field around an electromagnet, in the same way as for a permanent magnet. At the same time, you can see the effect of changing the current; a compass will line up more stubbornly in a stronger field. From straight wire to elect ...
Supplement 1: Complete set of magneto static data
... In general, the composites show magnetoelectric relaxation at low bias fields. Details of the relaxation behavior between systems were not investigated. The magnetization as a function of the applied electric voltage shows magnetoelectric relaxation at a low magnetic field of 10G. At 3000G the magne ...
... In general, the composites show magnetoelectric relaxation at low bias fields. Details of the relaxation behavior between systems were not investigated. The magnetization as a function of the applied electric voltage shows magnetoelectric relaxation at a low magnetic field of 10G. At 3000G the magne ...
Lecture19
... Faraday's Law (integral form) relates voltage, v(t), induced in a loop of wire to the time derivative of the total flux passing through the winding: d φ (t ) v(t ) = − ('sign' is given by Lenz's law.) dt Ampere's Law (integral form) relates magnetomotive force, M (t), induced in magnetic core to the ...
... Faraday's Law (integral form) relates voltage, v(t), induced in a loop of wire to the time derivative of the total flux passing through the winding: d φ (t ) v(t ) = − ('sign' is given by Lenz's law.) dt Ampere's Law (integral form) relates magnetomotive force, M (t), induced in magnetic core to the ...
path to electron - FSU High Energy Physics
... “Experimental researches in electricity” (1844-1845) “Experimental researches in chemistry and physics” ...
... “Experimental researches in electricity” (1844-1845) “Experimental researches in chemistry and physics” ...
Rotational States of Magnetic Molecules
... Crystals of high-spin magnetic molecules came to the attention of physicists after Sessoli et al. [1] discovered that they behave as regular arrays of identical superparamagnetic particles [2]. The remarkable property of magnetic molecules is that their spin can tunnel between up and down directions ...
... Crystals of high-spin magnetic molecules came to the attention of physicists after Sessoli et al. [1] discovered that they behave as regular arrays of identical superparamagnetic particles [2]. The remarkable property of magnetic molecules is that their spin can tunnel between up and down directions ...
Chapter 14: Magnets and Electromagnetism 1. Electrons flow
... B. The current in the solenoid is flowing clockwise as seen from the bar magnet. C. The current in the solenoid increases. D. The current in the solenoid is decreases. E. The direction of the current in the solenoid alternates with a constant frequency. Answer: B 17. Bar A has one end painted green ...
... B. The current in the solenoid is flowing clockwise as seen from the bar magnet. C. The current in the solenoid increases. D. The current in the solenoid is decreases. E. The direction of the current in the solenoid alternates with a constant frequency. Answer: B 17. Bar A has one end painted green ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.