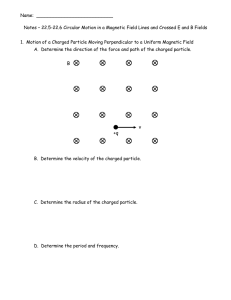
Name: Notes – 22.5-22.6 Circular Motion in a Magnetic Field Lines
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
3-8 electricity1 - Worth County Schools
... Clouds get their charges as water and ice particles move and interact. Smaller, positively charged particles rise to the top of the cloud and larger, negatively charged particles gather at the bottom. When the buildup of charge is great enough, the oppositely charged particles attract and discharge ...
... Clouds get their charges as water and ice particles move and interact. Smaller, positively charged particles rise to the top of the cloud and larger, negatively charged particles gather at the bottom. When the buildup of charge is great enough, the oppositely charged particles attract and discharge ...
Magnets and Magnetic Field
... • All moving charges cause a magnetic field – All of the electrons within an object moving create their own small magnetic fields – The movement of protons within the nucleus of the atom creates a small magnetic field – The “electron spin” also produces a tiny magnetic field ...
... • All moving charges cause a magnetic field – All of the electrons within an object moving create their own small magnetic fields – The movement of protons within the nucleus of the atom creates a small magnetic field – The “electron spin” also produces a tiny magnetic field ...
Magnets Review
... are affected by magnetic fields. • In these materials, small groups of atoms band together in areas called domains. – The electrons of the atoms in a domain are all in the same magnetic orientation. • The electrons are all oriented in the same way! ...
... are affected by magnetic fields. • In these materials, small groups of atoms band together in areas called domains. – The electrons of the atoms in a domain are all in the same magnetic orientation. • The electrons are all oriented in the same way! ...
Chapter 6 Part1: Multiple choices
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
magnetic fields
... Any magnet, no matter what its shape, has two ends called poles. A pole is the area of a magnet where the magnetic effect is strongest. One pole of a magnet points towards magnetic north of the earth and is labeled north. The other pole is labeled south. Although magnetic forces are strongest at the ...
... Any magnet, no matter what its shape, has two ends called poles. A pole is the area of a magnet where the magnetic effect is strongest. One pole of a magnet points towards magnetic north of the earth and is labeled north. The other pole is labeled south. Although magnetic forces are strongest at the ...
21-5M How are Electricity
... 5. DESCRIBE: What determines the direction of electric current in a wire when a magnet is moved around the wire? ...
... 5. DESCRIBE: What determines the direction of electric current in a wire when a magnet is moved around the wire? ...
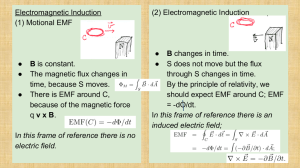
Electromagnetic Induction (2) Electromagnetic Induction (1) Motional EMF ●
... S does not move but the flux through S changes in time. ● By the principle of relativity, we should expect EMF around C; EMF = -dO/dt. In this frame of reference there is an induced electric field; ...
... S does not move but the flux through S changes in time. ● By the principle of relativity, we should expect EMF around C; EMF = -dO/dt. In this frame of reference there is an induced electric field; ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.