Flux or flux linkage? - Institute of Physics
... and the distance between the wires is 1 m, then the force on each metre length of the wires will be 2 x 10-7 N. ...
... and the distance between the wires is 1 m, then the force on each metre length of the wires will be 2 x 10-7 N. ...
magnet
... The Cause of Magnetism • As electrons in atoms move around, a magnetic field is generated. • The atom will then have a north and south pole. • The atoms group together in areas called domains, which are like tiny magnets. • In most materials, the magnetic fields cancel each other out because the do ...
... The Cause of Magnetism • As electrons in atoms move around, a magnetic field is generated. • The atom will then have a north and south pole. • The atoms group together in areas called domains, which are like tiny magnets. • In most materials, the magnetic fields cancel each other out because the do ...
MAGNETISM MAGNETISM
... There is an inverse relationship between voltage and current Control of voltage and current is achieved by a process of Mutual Induction ...
... There is an inverse relationship between voltage and current Control of voltage and current is achieved by a process of Mutual Induction ...
North Magnetic Pole - Effingham County Schools
... electromagnetic induction – process by which an electric current is produced by moving a wire in a magnetic field ...
... electromagnetic induction – process by which an electric current is produced by moving a wire in a magnetic field ...
B . A = BA - RAJEEV Classes
... When a conductor is moved across a magnetic field , an electromagnetic force(emf) is produced in the conductor. Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force that results from the movement of a conductor through a magnetic field. An electromotive force also results from the c ...
... When a conductor is moved across a magnetic field , an electromagnetic force(emf) is produced in the conductor. Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force that results from the movement of a conductor through a magnetic field. An electromotive force also results from the c ...
- Physics
... electromagnetic induction – process by which an electric current is produced by moving a wire in a magnetic field ...
... electromagnetic induction – process by which an electric current is produced by moving a wire in a magnetic field ...
Magnetic Jeopardy
... 16. Two parallel conductors each of 0.50 m length, separated by 5.0 103 m and carrying 3.0 A in opposite directions, will experience what type and magnitude of mutual force? (magnetic permeability in empty space ...
... 16. Two parallel conductors each of 0.50 m length, separated by 5.0 103 m and carrying 3.0 A in opposite directions, will experience what type and magnitude of mutual force? (magnetic permeability in empty space ...
Teacher`s Notes - Electricity and Magnetism, Part 2 Electricity and
... to sort the objects in their materials bag. Predictions should be recorded in worksheet item 3. 4. Get students to propose how they would test the objects for magnetic behavior (see if the magnet will attract the object). Let them test the objects and record the results in their worksheets. Were the ...
... to sort the objects in their materials bag. Predictions should be recorded in worksheet item 3. 4. Get students to propose how they would test the objects for magnetic behavior (see if the magnet will attract the object). Let them test the objects and record the results in their worksheets. Were the ...
Teacher`s Notes
... to sort the objects in their materials bag. Predictions should be recorded in worksheet item 3. 4. Get students to propose how they would test the objects for magnetic behavior (see if the magnet will attract the object). Let them test the objects and record the results in their worksheets. Were the ...
... to sort the objects in their materials bag. Predictions should be recorded in worksheet item 3. 4. Get students to propose how they would test the objects for magnetic behavior (see if the magnet will attract the object). Let them test the objects and record the results in their worksheets. Were the ...
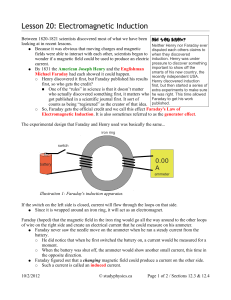
Faraday`s Law of Induction
... If the switch on the left side is closed, current will flow through the loops on that side. ● Since it is wrapped around an iron ring, it will act as an electromagnet. Faraday (hoped) that the magnetic field in the iron ring would go all the way around to the other loops of wire on the right side an ...
... If the switch on the left side is closed, current will flow through the loops on that side. ● Since it is wrapped around an iron ring, it will act as an electromagnet. Faraday (hoped) that the magnetic field in the iron ring would go all the way around to the other loops of wire on the right side an ...
ISNS3371_041907_bw
... The electron spins on its axis, giving rise to a electron current in the direction of rotation. The electron is like a magnetic dipole, a miniature magnet, with a north end and a south end. In most substances, electrons spin in random directions - magnetic fields cancel. For iron and other magnetic ...
... The electron spins on its axis, giving rise to a electron current in the direction of rotation. The electron is like a magnetic dipole, a miniature magnet, with a north end and a south end. In most substances, electrons spin in random directions - magnetic fields cancel. For iron and other magnetic ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.