Transformers and Generators - juan
... • A transformer can change electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. • It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to one coil, the var ...
... • A transformer can change electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. • It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to one coil, the var ...
5) – z (into page)
... below carry the same current, either into or out of the page. In which case is the magnetic field at the center of the square greatest? ...
... below carry the same current, either into or out of the page. In which case is the magnetic field at the center of the square greatest? ...
aurora_meeting - School of GeoSciences
... (angle from North) and inclination, I (angle from vertical), where magnetization strength is sufficiently high for the angles to be well determined. T marks Tyhrrhena Patera, shown in more detail in Figure 3. The solid line is the dichotomy. ...
... (angle from North) and inclination, I (angle from vertical), where magnetization strength is sufficiently high for the angles to be well determined. T marks Tyhrrhena Patera, shown in more detail in Figure 3. The solid line is the dichotomy. ...
Quantum Locking
... quantized packets through points in the magnet known as flux tubes, but at extremely low temperatures these flux tubes are locked into place to conserve energy causing Quantum Locking ...
... quantized packets through points in the magnet known as flux tubes, but at extremely low temperatures these flux tubes are locked into place to conserve energy causing Quantum Locking ...
Class Notes
... We would have to work on the current loop in order rotate the loop so that its magnetic field was no longer aligned with the external magnetic field. If we release the current loop, the external magnetic field will do work on our current loop to realign the fields. Thus, magnetic potential energy wa ...
... We would have to work on the current loop in order rotate the loop so that its magnetic field was no longer aligned with the external magnetic field. If we release the current loop, the external magnetic field will do work on our current loop to realign the fields. Thus, magnetic potential energy wa ...
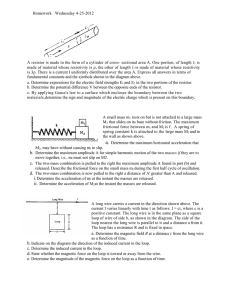
Homework Wednesday 4-25-2012 A resistor is made in the form of a
... materials,determine the sign and magnitude of the electric charge which is present on this boundary. ...
... materials,determine the sign and magnitude of the electric charge which is present on this boundary. ...
5) – z (into page)
... below carry the same current, either into or out of the page. In which case is the magnetic field at the center of the square greatest? ...
... below carry the same current, either into or out of the page. In which case is the magnetic field at the center of the square greatest? ...
Physics 102 Introduction to Physics
... Also similar to electrostatics … the space between 2 magnetic poles is filled by a MAGNETIC FIELD. You can visualize the magnetic field by sprinkling iron filings around a magnet. The direction of the field is from the North pole to the South both inside and outside of the magnet. Outside the magnet ...
... Also similar to electrostatics … the space between 2 magnetic poles is filled by a MAGNETIC FIELD. You can visualize the magnetic field by sprinkling iron filings around a magnet. The direction of the field is from the North pole to the South both inside and outside of the magnet. Outside the magnet ...
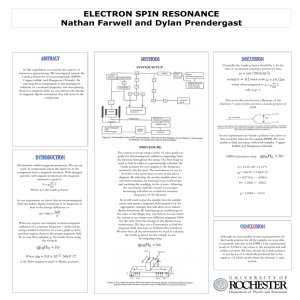
Poster: ESR
... Copper sulfide, and Manganese Chloride). By exposing these compounds to electromagnetic radiation of a constant frequency and then placing them in a magnetic field, we can observe the change in magnetic dipole orientation that will occur in the compound. ...
... Copper sulfide, and Manganese Chloride). By exposing these compounds to electromagnetic radiation of a constant frequency and then placing them in a magnetic field, we can observe the change in magnetic dipole orientation that will occur in the compound. ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... A segment of a closed loop of wire moves through a magnetic field. Note that the wire must be perpendicular to the magnetic field in order for current and emf to be induced. ...
... A segment of a closed loop of wire moves through a magnetic field. Note that the wire must be perpendicular to the magnetic field in order for current and emf to be induced. ...
Using Magnetism to Induce an Electric Current
... A segment of a closed loop of wire moves through a magnetic field. Note that the wire must be perpendicular to the magnetic field in order for current and emf to be induced. ...
... A segment of a closed loop of wire moves through a magnetic field. Note that the wire must be perpendicular to the magnetic field in order for current and emf to be induced. ...
Section 11: GRAPHIC STIMULUS
... 16. An important event in the history of magnets _________ when a Danish chemist discovered that magnets could be made using electrical currents. ...
... 16. An important event in the history of magnets _________ when a Danish chemist discovered that magnets could be made using electrical currents. ...
Magnetism - SchoolRack
... of its atoms, particularly its electrons. • A magnet is an object that exhibits a strong magnetic field and will attract materials, like iron, to it. • Magnets have two poles, called the north (N) and south (S) poles. Two magnets will be attracted by their opposite poles, and each will repel the lik ...
... of its atoms, particularly its electrons. • A magnet is an object that exhibits a strong magnetic field and will attract materials, like iron, to it. • Magnets have two poles, called the north (N) and south (S) poles. Two magnets will be attracted by their opposite poles, and each will repel the lik ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.