the effect of a magnetic field on the her, the ph
... The electrodeposition of less noble metals is usually overlapped by the reduction of hydrogen ions. This leads to an increase of the pH value in front of the electrode surface which can result in spontaneous formation of hydroxides. This changes the deposition behaviour, the morphology and the prope ...
... The electrodeposition of less noble metals is usually overlapped by the reduction of hydrogen ions. This leads to an increase of the pH value in front of the electrode surface which can result in spontaneous formation of hydroxides. This changes the deposition behaviour, the morphology and the prope ...
Equation sheet #1
... September 29, 2004 12:10 to 1:10 pm Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one el ...
... September 29, 2004 12:10 to 1:10 pm Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one el ...
File
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. magnet d. electromagnetism b. magnetic pole e. electric motor c. magnetic force f. electromagnetic induction ...
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. magnet d. electromagnetism b. magnetic pole e. electric motor c. magnetic force f. electromagnetic induction ...
Magnetism Magnets Magnetic Poles - mrkearsley.com
... is much stronger by thousands of times. The more loops of wire, the stronger the magnet. A great advantage of an electromagnet is the ability to turn it on or off magnetism as needed. ...
... is much stronger by thousands of times. The more loops of wire, the stronger the magnet. A great advantage of an electromagnet is the ability to turn it on or off magnetism as needed. ...
(magnetic fields and forces) (PPT - 5.9MB)
... A galvanometer is a type of an electric current meter. It is an analog electromechanical transducer that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current flowing through its coil. Ampere invented the galvanometer. Schweigger used a coil (1821). Nobili improved on ...
... A galvanometer is a type of an electric current meter. It is an analog electromechanical transducer that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current flowing through its coil. Ampere invented the galvanometer. Schweigger used a coil (1821). Nobili improved on ...
TAP 411-2: Brush up on magnetism
... Use some permanent magnets and a current-carrying coil to review your knowledge of the nature and behaviour of magnetic fields. The purpose of this sheet is to help you to brush up your knowledge of magnets before you learn how magnetism is used with trains. ...
... Use some permanent magnets and a current-carrying coil to review your knowledge of the nature and behaviour of magnetic fields. The purpose of this sheet is to help you to brush up your knowledge of magnets before you learn how magnetism is used with trains. ...
Cathode ray tube - Oxford Physics
... A magnetic field will cause a force to act on the electrons which is perpendicular to both their direction of travel and the magnetic field. This causes a charged particle in a magnetic field to follow a circular path. The faster the motion of the particle, the larger the circle traced out for a giv ...
... A magnetic field will cause a force to act on the electrons which is perpendicular to both their direction of travel and the magnetic field. This causes a charged particle in a magnetic field to follow a circular path. The faster the motion of the particle, the larger the circle traced out for a giv ...
Lecture 2 - Purdue Physics
... Electron current is a number of electrons per second entering a section of a conductor. Conventional current (Coulombs/second) is opposite in direction to the electron current, and is assumed to be due to positively charged particles. The superposition principle can be applied to calculate the ...
... Electron current is a number of electrons per second entering a section of a conductor. Conventional current (Coulombs/second) is opposite in direction to the electron current, and is assumed to be due to positively charged particles. The superposition principle can be applied to calculate the ...
End of chapter exercises
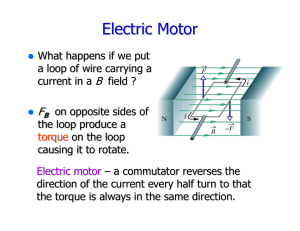
... connected to the load via brushes. In an AC generator the two ends of the coil are each attached to a slip ring that makes contact with brushes as the coil turns. The direction of the current changes with every half turn of the coil. As one side of the loop moves to the other pole of the magnetic fi ...
... connected to the load via brushes. In an AC generator the two ends of the coil are each attached to a slip ring that makes contact with brushes as the coil turns. The direction of the current changes with every half turn of the coil. As one side of the loop moves to the other pole of the magnetic fi ...
A Brief Outline of the History of Electromagnetism
... experiments. In effect, he showed that two parallel conductors carrying electricity in the same direction attract each other, whereas if the currents are in opposite directions, the conductors repel one another. From the experiments he claimed: • Outside its body, a permanent magnet is exactly equiv ...
... experiments. In effect, he showed that two parallel conductors carrying electricity in the same direction attract each other, whereas if the currents are in opposite directions, the conductors repel one another. From the experiments he claimed: • Outside its body, a permanent magnet is exactly equiv ...
Magnetism - Coach Ed Science
... • A magnetic domain is when all magnetic fields are lined up in the same way. ...
... • A magnetic domain is when all magnetic fields are lined up in the same way. ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.