Ferrites and accessories - ETD 39/20/13 - Core and
... certain areas of application. These statements are based on our knowledge of typical requirements that are often placed on our products in the areas of application concerned. We nevertheless expressly point out that such statements cannot be regarded as binding statements about the suitability of ou ...
... certain areas of application. These statements are based on our knowledge of typical requirements that are often placed on our products in the areas of application concerned. We nevertheless expressly point out that such statements cannot be regarded as binding statements about the suitability of ou ...
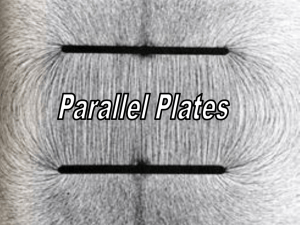
Electrostatics Problems 4 – Electric Fields due to a
... *What is the strength of the electric field produced a distance of 8 E-8 m from a nucleus* containing 10 protons? [Hint: what is the charge of this nucleus? Recall there are always Zero electrons in a nucleus.] ...
... *What is the strength of the electric field produced a distance of 8 E-8 m from a nucleus* containing 10 protons? [Hint: what is the charge of this nucleus? Recall there are always Zero electrons in a nucleus.] ...
phys1444-spring06-032006
... producing the field. The top portion of the wire loop is free of the field. The loop hangs from a balance which measures a downward force ( in addition to the gravitational force) of F=3.48x10-2N when the wire carries a current I=0.245A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the center of ...
... producing the field. The top portion of the wire loop is free of the field. The loop hangs from a balance which measures a downward force ( in addition to the gravitational force) of F=3.48x10-2N when the wire carries a current I=0.245A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the center of ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.