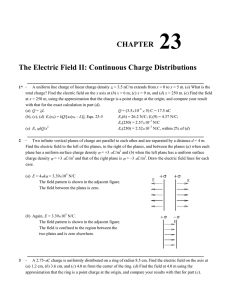
Answers
... directly proportional to the magnitude of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The force acts along the line joining the two charges. Consider two point charges q1 and q2 at rest in vacuum. Let r be the separation between them . According to Coulomb’s law, t ...
... directly proportional to the magnitude of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The force acts along the line joining the two charges. Consider two point charges q1 and q2 at rest in vacuum. Let r be the separation between them . According to Coulomb’s law, t ...
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units
... exactly equal to the charge enclosed there are no extra prefactors needin that surface, and the electric field lessly cluttering an already messy of a point charge on a fictitious sphere equation. The prefactors in SI of radius r is simply the average sur- present no new meaning and simply face char ...
... exactly equal to the charge enclosed there are no extra prefactors needin that surface, and the electric field lessly cluttering an already messy of a point charge on a fictitious sphere equation. The prefactors in SI of radius r is simply the average sur- present no new meaning and simply face char ...
preview as pdf - Pearson Higher Education
... n physics, an important tool for simplifying problems is the symmetry properties of systems. Many physical systems have symmetry; for example, a cylindrical body doesn’t look any different after you’ve rotated it around its axis, and a charged metal sphere looks just the same after you’ve turned it ...
... n physics, an important tool for simplifying problems is the symmetry properties of systems. Many physical systems have symmetry; for example, a cylindrical body doesn’t look any different after you’ve rotated it around its axis, and a charged metal sphere looks just the same after you’ve turned it ...
who was james clerk maxwell and what was/is
... In 1855, he published the first-part of his paper On Faraday’s Lines of Force [1, pp. 337375, 5, pp. 155-229], where he used fluid flow as an analogy for lines of force shaped in his exposition based on physical geometry. His objective was to find a physical analogy which would help the mind to gras ...
... In 1855, he published the first-part of his paper On Faraday’s Lines of Force [1, pp. 337375, 5, pp. 155-229], where he used fluid flow as an analogy for lines of force shaped in his exposition based on physical geometry. His objective was to find a physical analogy which would help the mind to gras ...
Electric Charge - University of Hawaii
... 3. Electrons are much freer to move than protons. If the students can understand those principles, they should be able to understand what is going on in electricity. The material is presented in two parts. First are stations. Second is an activity where they prove that opposites attract and likes re ...
... 3. Electrons are much freer to move than protons. If the students can understand those principles, they should be able to understand what is going on in electricity. The material is presented in two parts. First are stations. Second is an activity where they prove that opposites attract and likes re ...
Magnetism and Electricity
... Electromagnetic forces can attract or repel. Opposite charges attract each other, and like charges repel each other. Electric current is the flow of electrons. A complete, continuous path of current is called an electric circuit. Conductors are materials that allow energy to flow and carry out curre ...
... Electromagnetic forces can attract or repel. Opposite charges attract each other, and like charges repel each other. Electric current is the flow of electrons. A complete, continuous path of current is called an electric circuit. Conductors are materials that allow energy to flow and carry out curre ...
MRI SAFETY JEOPARDY (NONTechnologist Edition) Questions
... magnetic field. The longer an object is (the less spherical), the greater that rotational force will be. Also, the rotational force increases as you approach the magnet. ...
... magnetic field. The longer an object is (the less spherical), the greater that rotational force will be. Also, the rotational force increases as you approach the magnet. ...
21 Electric Fields - mrphysicsportal.net
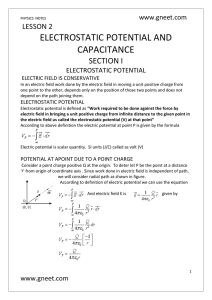
... It is easy to state that a charge produces an electric field. But how can the field be detected and measured? We will describe a method that can be used to measure the field produced by an electric charge q. You must measure the field at a specific location, for example, point A. An electrical field ...
... It is easy to state that a charge produces an electric field. But how can the field be detected and measured? We will describe a method that can be used to measure the field produced by an electric charge q. You must measure the field at a specific location, for example, point A. An electrical field ...
Unit 13 - Magnetism
... 3.3 Current: The Source of All Magnetism An electromagnet creates magnetism with an electric current. In later sections we explore this more quantitatively, nding the strength and direction of magnetic elds created by various currents. But what about ferromagnets? Figure 3.7 shows models of how el ...
... 3.3 Current: The Source of All Magnetism An electromagnet creates magnetism with an electric current. In later sections we explore this more quantitatively, nding the strength and direction of magnetic elds created by various currents. But what about ferromagnets? Figure 3.7 shows models of how el ...
Electric Charge - University of Hawaii System
... You’ll need to move electrons from one object to another. Check the list of charge-transferring materials in the student reading. You’ll need materials to make charge imbalances, both – and +. Wool works well to move both negative and positive charge, depending on the material you rub it with. A pie ...
... You’ll need to move electrons from one object to another. Check the list of charge-transferring materials in the student reading. You’ll need materials to make charge imbalances, both – and +. Wool works well to move both negative and positive charge, depending on the material you rub it with. A pie ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.