Magnets - Delta Education
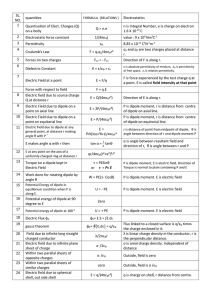
... magnet can attract magnetic materials; each magnet is surrounded by an invisible force, called its magnetic field, which can act on a magnetic object from a distance; every magnet has two poles that are equal in strength; a magnet’s force is strongest at its poles; and like poles repel and unlike po ...
... magnet can attract magnetic materials; each magnet is surrounded by an invisible force, called its magnetic field, which can act on a magnetic object from a distance; every magnet has two poles that are equal in strength; a magnet’s force is strongest at its poles; and like poles repel and unlike po ...
Chapter 15
... – If there were a parallel component to E, charges would experience a force and accelerate along the surface and it would not be in equilibrium The net flux through the surface is through only the flat face outside the conductor The field here is perpendicular to the surface Applying Gauss’s l ...
... – If there were a parallel component to E, charges would experience a force and accelerate along the surface and it would not be in equilibrium The net flux through the surface is through only the flat face outside the conductor The field here is perpendicular to the surface Applying Gauss’s l ...
Electric Potential Energy
... the cavity, the electric field inside the cavity must be zero, regardless of the charge distribution on the outside surface of the conductor. Furthermore, the field in the cavity is zero even if an electric field exists outside the conductor. To prove this, we can think of at least 2 points inside t ...
... the cavity, the electric field inside the cavity must be zero, regardless of the charge distribution on the outside surface of the conductor. Furthermore, the field in the cavity is zero even if an electric field exists outside the conductor. To prove this, we can think of at least 2 points inside t ...
r - Purdue Physics
... in electrostatic equilibrium all of this metal is an equipotential; i.e., it is all at the same voltage ...
... in electrostatic equilibrium all of this metal is an equipotential; i.e., it is all at the same voltage ...
File S1.
... Note S10 - Alleviating directionality - Dendritic excitation. A different approach to the problem would be the direct excitation of dendrites in the culture by applying pulses with durations of the order of 1 ms. As opposed to axons, which usually project a long stretch at a single direction from th ...
... Note S10 - Alleviating directionality - Dendritic excitation. A different approach to the problem would be the direct excitation of dendrites in the culture by applying pulses with durations of the order of 1 ms. As opposed to axons, which usually project a long stretch at a single direction from th ...
PowerPoint
... uniform volume charge density spread throughout shell. Note: if a conductor is in electrostatic equilibrium, any excess charge must lie on its surface (we will study this in more detail next time), so for the charge to be uniformly distributed throughout the volume, the object must be an insulator ...
... uniform volume charge density spread throughout shell. Note: if a conductor is in electrostatic equilibrium, any excess charge must lie on its surface (we will study this in more detail next time), so for the charge to be uniformly distributed throughout the volume, the object must be an insulator ...
OVERVIEW: Electromagnetism
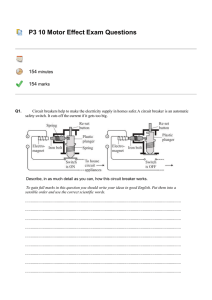
... generator varies in time. Using the same set of axes show how the potential difference would vary if the rotational speed of the generator was doubled. ...
... generator varies in time. Using the same set of axes show how the potential difference would vary if the rotational speed of the generator was doubled. ...
Bound charges and currents
... charges is original and has not been, by and large, adopted in modern textbooks. This is probably because his derivation assumes a linear response of the material, is written in the Gaussian system of units, and unfolds piece-wise within a much broader discussion (see chapter 10 of Ref. 1). Yet, as ...
... charges is original and has not been, by and large, adopted in modern textbooks. This is probably because his derivation assumes a linear response of the material, is written in the Gaussian system of units, and unfolds piece-wise within a much broader discussion (see chapter 10 of Ref. 1). Yet, as ...
Presentation - Copernicus.org
... GR equations then made the problem impossible by assigning zero (‘infinitesimal’) volume to that bit of space! • We now know that’s wrong; they do have space inside them in which to develop the external property. ...
... GR equations then made the problem impossible by assigning zero (‘infinitesimal’) volume to that bit of space! • We now know that’s wrong; they do have space inside them in which to develop the external property. ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.