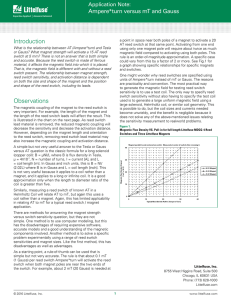
x a a = 3.0 cm B = 0.04 T I = 5 A y I 60° 30° C B A
... )(π r 2 ) = =(1.60 × 10−19 ) × (2.184 × 106 ) × (5.3 × 10−11 ) / 2 =9.26 × 10−24 A m 2 2π r ...
... )(π r 2 ) = =(1.60 × 10−19 ) × (2.184 × 106 ) × (5.3 × 10−11 ) / 2 =9.26 × 10−24 A m 2 2π r ...
Magnetism - Iroquois Central School District / Home Page
... Pole do not coincide. The magnetic pole is about 1500 km (930 mi) south of the geographic North Pole and it wanders. A compass actually indicates the direction of magnetic north, not true north. Therefore a navigator must need to know the magnetic declination for a specific area. This is the angular ...
... Pole do not coincide. The magnetic pole is about 1500 km (930 mi) south of the geographic North Pole and it wanders. A compass actually indicates the direction of magnetic north, not true north. Therefore a navigator must need to know the magnetic declination for a specific area. This is the angular ...
vgp302
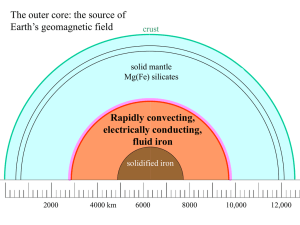
... lines are drawn out to two Earth radii. Magnetic field is wrapped around the "tangent cylinder" due to the shear of the zonal fluid flow. ...
... lines are drawn out to two Earth radii. Magnetic field is wrapped around the "tangent cylinder" due to the shear of the zonal fluid flow. ...
Electricity and Magnetism - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Correct answers without adequate explanations will not receive full credit. Make sure your work is legible and clear The points assigned to each part of each question are clearly indicated ...
... Correct answers without adequate explanations will not receive full credit. Make sure your work is legible and clear The points assigned to each part of each question are clearly indicated ...
spin-orbit coupling
... • It can not be explained by Coulomb interaction between the nucleus and the electrons. It results from a magnetic interaction between the orbital magnetic moment and spin magnetic moment of the electron, called spin-orbit coupling. ...
... • It can not be explained by Coulomb interaction between the nucleus and the electrons. It results from a magnetic interaction between the orbital magnetic moment and spin magnetic moment of the electron, called spin-orbit coupling. ...
File
... Heart and brain are the two main organs in our body where this magnetic field is quite significant. The magnetic field in our body enables us to obtain the images of its different parts by using a technique called MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). On analysing the images obtained through MRI, we are ...
... Heart and brain are the two main organs in our body where this magnetic field is quite significant. The magnetic field in our body enables us to obtain the images of its different parts by using a technique called MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). On analysing the images obtained through MRI, we are ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.