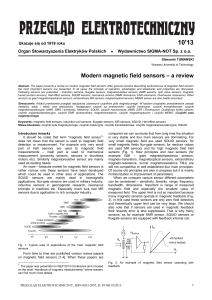
Modern magnetic field sensors – a review
... It is also possible to use other output circuit – known as self-integrating one. Fig. 8 presents frequency characteristic of the induction sensor. If the sensor is no loaded ( = 0) the output signal increased up to resonance frequency f0. But if we load the sensor with small resistance the plateau ...
... It is also possible to use other output circuit – known as self-integrating one. Fig. 8 presents frequency characteristic of the induction sensor. If the sensor is no loaded ( = 0) the output signal increased up to resonance frequency f0. But if we load the sensor with small resistance the plateau ...
PC_Chapter_14latest
... The magnitude of the buoyant force always equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object This is called Archimedes’s Principle Archimedes’s Principle does not refer to the makeup of the object experiencing the buoyant force The object’s composition is not a factor since the buoyant force i ...
... The magnitude of the buoyant force always equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object This is called Archimedes’s Principle Archimedes’s Principle does not refer to the makeup of the object experiencing the buoyant force The object’s composition is not a factor since the buoyant force i ...
Ch. 29 and 30 notes
... Direction of this force: Right Hand Rule #2” (RHR2) ν Point your right-hand fingers in the direction of I. ν Orient so your fingertips can curl naturally towards B. ν Stick out your thumb. It points in the direction of F. In the picture above, the force on the wire points out of the page: The wire i ...
... Direction of this force: Right Hand Rule #2” (RHR2) ν Point your right-hand fingers in the direction of I. ν Orient so your fingertips can curl naturally towards B. ν Stick out your thumb. It points in the direction of F. In the picture above, the force on the wire points out of the page: The wire i ...
The PDE`s of continuum physics - Niels Bohr Institutet – Niels Bohr
... time to arrive from even the farthest corners of space. But should the mass density vary with time, as it for example does in the solar system because of the motions of the planets, the Newtonian field of gravity must according to (4) respond instantaneously everywhere to reflect this variation7 . ...
... time to arrive from even the farthest corners of space. But should the mass density vary with time, as it for example does in the solar system because of the motions of the planets, the Newtonian field of gravity must according to (4) respond instantaneously everywhere to reflect this variation7 . ...
Energy flow and the speed of electric field in DC circuit
... the energy flowing into the wire from the field outside. Intuition would seem to tell us that the electrons get their energy from being pushed along the wire, so the energy should be flowing down (or up) along the wire. But the theory says that the electrons are really being pushed by an electric fi ...
... the energy flowing into the wire from the field outside. Intuition would seem to tell us that the electrons get their energy from being pushed along the wire, so the energy should be flowing down (or up) along the wire. But the theory says that the electrons are really being pushed by an electric fi ...
chapter- ii literature review
... It is a dimensionless quantity. Substance with a positive susceptibility is called paramagnets, while materials with negatives susceptibility are diamagnets. The ferromagnetic materials have a spontaneous magnetic moment, that is, a magnetic moment exists even when the applied magnetic field is zero ...
... It is a dimensionless quantity. Substance with a positive susceptibility is called paramagnets, while materials with negatives susceptibility are diamagnets. The ferromagnetic materials have a spontaneous magnetic moment, that is, a magnetic moment exists even when the applied magnetic field is zero ...
electromagnetism guide
... 67. Electric current created by a changing magnetic field is called an induced current. 68. When an induced current is created, it does not matter whether the magnetic field moves, as seen here, or… 69. ...whether the circuit moves. 70. In each case, an electric current is produced when a circuit ex ...
... 67. Electric current created by a changing magnetic field is called an induced current. 68. When an induced current is created, it does not matter whether the magnetic field moves, as seen here, or… 69. ...whether the circuit moves. 70. In each case, an electric current is produced when a circuit ex ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.