Abstract Submitted for the Graduate Seminar Meeting of
... Anomalous Magnetic Moment of Muon and g-2 Experiment JAEHYUNG CHOI, SUNY at Stony Brook, NY — The magnetic moment of a particle is one of the physical quantities which can be measured by the experiment and be testified by the theory. Especially, the magnetic moment of electron is precisely measured ...
... Anomalous Magnetic Moment of Muon and g-2 Experiment JAEHYUNG CHOI, SUNY at Stony Brook, NY — The magnetic moment of a particle is one of the physical quantities which can be measured by the experiment and be testified by the theory. Especially, the magnetic moment of electron is precisely measured ...
Document
... Cool Temperature➱ Electrons reconbine with other particles (Ions) and the photons can be easily absorbed. This decreases the radiative conductivity and increases the temperature gradient. Where this occurs a volume of material moved upward will be warmer than its surroundings and will continue to ri ...
... Cool Temperature➱ Electrons reconbine with other particles (Ions) and the photons can be easily absorbed. This decreases the radiative conductivity and increases the temperature gradient. Where this occurs a volume of material moved upward will be warmer than its surroundings and will continue to ri ...
Electromagnetic Rules
... produced if the velocity and the direction of the field are parallel to each other. When the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field the EMF will be produced that is perpendicular to both. The directions are determined by the “right hand rule” where the right hand thumb points in the directi ...
... produced if the velocity and the direction of the field are parallel to each other. When the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field the EMF will be produced that is perpendicular to both. The directions are determined by the “right hand rule” where the right hand thumb points in the directi ...
24-1 Magnets: permanent & temporary
... When there is an electric current in a coil wire, the field acts like a permanent magnet Electromagnet Strength of the field is proportional to the current in the coil ...
... When there is an electric current in a coil wire, the field acts like a permanent magnet Electromagnet Strength of the field is proportional to the current in the coil ...
adan (1)
... Electromagnetism Electromagnetism is responsible for interactions between charged particles that occur because of their charge and for the emission and absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). The phenomena of electricity and magnetism are consequences of this force, and the relationships ...
... Electromagnetism Electromagnetism is responsible for interactions between charged particles that occur because of their charge and for the emission and absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). The phenomena of electricity and magnetism are consequences of this force, and the relationships ...
Word
... c. The auroras are caused by charged particles entering the Earth’s magnetic field where they Paths of follow helical paths along the field lines either charged north or south. The light observed as auroras is due particles to ionization of atoms in the atmosphere when they collide with high speed c ...
... c. The auroras are caused by charged particles entering the Earth’s magnetic field where they Paths of follow helical paths along the field lines either charged north or south. The light observed as auroras is due particles to ionization of atoms in the atmosphere when they collide with high speed c ...
Electrical & Electronic Principles
... • Only powers of ten (I, X, C, M) can be repeated. • Do not repeat any letter more than three times in a row. • Because of the preceding rule, certain numbers must be written using subtraction. In this case, a letter with a smaller value precedes one with a larger value and the value of the smaller ...
... • Only powers of ten (I, X, C, M) can be repeated. • Do not repeat any letter more than three times in a row. • Because of the preceding rule, certain numbers must be written using subtraction. In this case, a letter with a smaller value precedes one with a larger value and the value of the smaller ...
ElectroMagnet - Arbor Scientific
... screws and clip the Genecon leads into the plastic covers), students can turn the crank and create enough current to induce magnetism. Have students hang weights from the hook and determine how much force they are creating. What happens when they stop cranking? 2. Batteries work even better in creat ...
... screws and clip the Genecon leads into the plastic covers), students can turn the crank and create enough current to induce magnetism. Have students hang weights from the hook and determine how much force they are creating. What happens when they stop cranking? 2. Batteries work even better in creat ...
Lesson 18 - Magnetic Sources
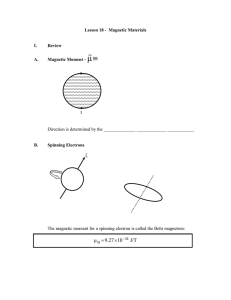
... zero. However, the outer (valence) electrons may produce a net magnetic moment since the shell isn't filled!! ...
... zero. However, the outer (valence) electrons may produce a net magnetic moment since the shell isn't filled!! ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
Ch 29 Magnetic Fields due to Currents
... Fig. 29-19 Application of Ampere’s law to a section of a long ideal solenoid carrying a current i. The Amperian loop is the rectangle abcda. ...
... Fig. 29-19 Application of Ampere’s law to a section of a long ideal solenoid carrying a current i. The Amperian loop is the rectangle abcda. ...
Lesson 7 Magnets
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
File
... A magnet has two ends which are called _________. The two poles are called North and South, and the magnetic field that is produced is directed from the North to the South. The magnetic field interacts with other magnetic fields in a similar way that the electric field interacts with other electric ...
... A magnet has two ends which are called _________. The two poles are called North and South, and the magnetic field that is produced is directed from the North to the South. The magnetic field interacts with other magnetic fields in a similar way that the electric field interacts with other electric ...
Magnetism.
... They line up in the direction in which a piece of iron would move if put there (field lines). They gather most thickly where the force on the iron would be the greatest (larger field line density). ...
... They line up in the direction in which a piece of iron would move if put there (field lines). They gather most thickly where the force on the iron would be the greatest (larger field line density). ...
ECE 341: Electromagnetic Fields I Concepts: Maxwell’s Equations
... Understands basics of electricity and magnetism Can use Coulomb's law and Biot-Savart law to compute electric and magnetic fields due to simple charge and current distributions Can use Gauss’ law and Ampère’s law in integral form to solve simple electric and magnetic static field problems Has comman ...
... Understands basics of electricity and magnetism Can use Coulomb's law and Biot-Savart law to compute electric and magnetic fields due to simple charge and current distributions Can use Gauss’ law and Ampère’s law in integral form to solve simple electric and magnetic static field problems Has comman ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.