Physics Form 5 Syllabus
... State the properties of magnets Give an account of induced magnetism Distinguish between magnetic and nonmagnetic materials Describe an experiment to identify the pattern of field lines around a bar magnet Distinguish between the magnetic properties of iron and steel Distinguish between the design a ...
... State the properties of magnets Give an account of induced magnetism Distinguish between magnetic and nonmagnetic materials Describe an experiment to identify the pattern of field lines around a bar magnet Distinguish between the magnetic properties of iron and steel Distinguish between the design a ...
Magnetic Fields and Forces
... which has a value of 55mT at a particular location. When the proton moves eastward, the magnetic force is a maximum, and when it moves northward, no magnetic force acts upon it. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton? ...
... which has a value of 55mT at a particular location. When the proton moves eastward, the magnetic force is a maximum, and when it moves northward, no magnetic force acts upon it. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton? ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields
... AEP has followed worldwide scientific studies and developments related to EMF for decades. We have participated in EMF research through membership in trade associations and have communicated with customers and employees on the issue. ...
... AEP has followed worldwide scientific studies and developments related to EMF for decades. We have participated in EMF research through membership in trade associations and have communicated with customers and employees on the issue. ...
electromagnetism
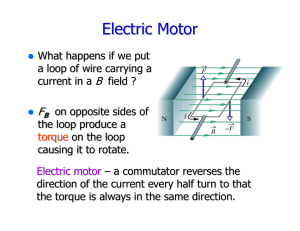
... direction of the current every half turn to that the torque is always in the same direction. ...
... direction of the current every half turn to that the torque is always in the same direction. ...
Magnets- a body having the property of attracting iron and
... Electromagnetism is also widely used in a hospital’s equipment and is vital for the survival of many people everyday. Electromagnetism is essential to so many functions of our everyday lives and to many industries livelihoods; it is now hard to think what life would be like without these forces. ...
... Electromagnetism is also widely used in a hospital’s equipment and is vital for the survival of many people everyday. Electromagnetism is essential to so many functions of our everyday lives and to many industries livelihoods; it is now hard to think what life would be like without these forces. ...
e-magnet lab day
... iron core. As a result, the field inside the solenoid with the iron core can be more than 1,000 times greater than the field inside the solenoid without the iron core. ...
... iron core. As a result, the field inside the solenoid with the iron core can be more than 1,000 times greater than the field inside the solenoid without the iron core. ...
Solutions to Period 16 Exercises
... d) have none of the above. E.1 = a E.2 You wish to design an electric motor. Which of the following motor designs will NOT work? a) An electromagnet is used to spin a permanent magnet. b) A permanent magnet is used to spin an electromagnet. c) ...
... d) have none of the above. E.1 = a E.2 You wish to design an electric motor. Which of the following motor designs will NOT work? a) An electromagnet is used to spin a permanent magnet. b) A permanent magnet is used to spin an electromagnet. c) ...
PPT - SLAC
... • At ultrafast speeds (< 1 ps) new ill-understood phenomena exist one approaches timescales of fundamental interactions between electrons, lattice and spin • Future experiments to explore the details using both H and E fields • In the future, e-beam “pump”/ laser “probe” experiments are of interest, ...
... • At ultrafast speeds (< 1 ps) new ill-understood phenomena exist one approaches timescales of fundamental interactions between electrons, lattice and spin • Future experiments to explore the details using both H and E fields • In the future, e-beam “pump”/ laser “probe” experiments are of interest, ...
What is magnetism?
... We have seen how electricity can produce a magnetic field, but a magnetic field can also produce electricity! How? What is electromagnetic induction? Moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field produces an electric current. This is electromagnetic induction. A generator is used to convert mechan ...
... We have seen how electricity can produce a magnetic field, but a magnetic field can also produce electricity! How? What is electromagnetic induction? Moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field produces an electric current. This is electromagnetic induction. A generator is used to convert mechan ...
Electricity Web Quest Report
... 1. A __________________________ attracts electrons and allows electricity to flow through. 2. Matter that doesn’t carry a current well is called an ______________. 3. _______________ _________________ discovered electricity through a lightning strike! 4. ______________ ___________________ discovered ...
... 1. A __________________________ attracts electrons and allows electricity to flow through. 2. Matter that doesn’t carry a current well is called an ______________. 3. _______________ _________________ discovered electricity through a lightning strike! 4. ______________ ___________________ discovered ...
Reading Guide CH 28KEYJWW
... What is magnetic domain? A magnetic domain is a small section of a ferromagnetic material in which the atoms in this section are magnetically aligned. Adjoining domains will tend to be aligned magnetically in the same way if the material is magnetized, but this tendency does not exist for domains in ...
... What is magnetic domain? A magnetic domain is a small section of a ferromagnetic material in which the atoms in this section are magnetically aligned. Adjoining domains will tend to be aligned magnetically in the same way if the material is magnetized, but this tendency does not exist for domains in ...
Lecture 10 - UConn Physics
... shape of an isosceles triangle as shown. A constant magnetic field exists in the -z direction. B – What is Fy, net force on the wire in the ydirection? ...
... shape of an isosceles triangle as shown. A constant magnetic field exists in the -z direction. B – What is Fy, net force on the wire in the ydirection? ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.