Electricity - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... current from size of its magnetic field • Coil of wire wrapped around an iron core becomes an electromagnet that rotates in field of a permanent magnet • This rotation moves a pointer on a scale ...
... current from size of its magnetic field • Coil of wire wrapped around an iron core becomes an electromagnet that rotates in field of a permanent magnet • This rotation moves a pointer on a scale ...
Energy of the Universe
... extra galactic energy density should affect subsequent galaxy formation. This possibly explains why the large extra galactic mass of gas in both clusters and the walls has not subsequently formed further galaxies. Also the reconnection of this magnetic field during a Hubble time provides enough ener ...
... extra galactic energy density should affect subsequent galaxy formation. This possibly explains why the large extra galactic mass of gas in both clusters and the walls has not subsequently formed further galaxies. Also the reconnection of this magnetic field during a Hubble time provides enough ener ...
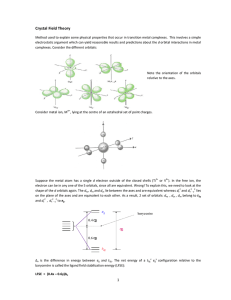
Crystal Field Theory
... Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
... Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... magnetic force. • We call one end of a permanent magnet “N” or North, and the other end of a permanent magnet “S” or South • The N and S are called magnetic poles – ...
... magnetic force. • We call one end of a permanent magnet “N” or North, and the other end of a permanent magnet “S” or South • The N and S are called magnetic poles – ...
Chapter 21: Magnetism
... Movement of electrons around the nucleus and “spinbehavior mathematically resemble a spinning object” of electrons causes them to act like magnets. In materials electrons usually are paired with other electrons which have an opposite spin. Magnetic fields mostly cancel out; material has weak magneti ...
... Movement of electrons around the nucleus and “spinbehavior mathematically resemble a spinning object” of electrons causes them to act like magnets. In materials electrons usually are paired with other electrons which have an opposite spin. Magnetic fields mostly cancel out; material has weak magneti ...
Why do things move? - Utah State University
... The direction of the induced current (generated by changing magnetic flux) is such that it produces a magnetic field that opposes the change in original flux. E.g. If field increases with time the field produced by induced current will be opposite in direction to original external field (and vice ...
... The direction of the induced current (generated by changing magnetic flux) is such that it produces a magnetic field that opposes the change in original flux. E.g. If field increases with time the field produced by induced current will be opposite in direction to original external field (and vice ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.