Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
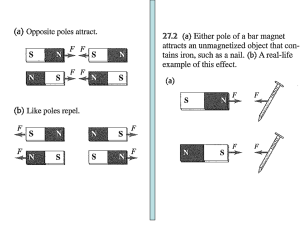
... magnet will always point north when allowed to swing freely such as in a compass. Magnets always have 2 poles. Magnetic effect is always strongest at the poles—North and South, Like poles repel. Opposite poles attract. This interaction is called magnetic force. ...
... magnet will always point north when allowed to swing freely such as in a compass. Magnets always have 2 poles. Magnetic effect is always strongest at the poles—North and South, Like poles repel. Opposite poles attract. This interaction is called magnetic force. ...
Magnetic field
... cobalt, or nickel can be made into permanent magnets by placing them in a strong magnetic field. ► This creates a magnetic field inside the material ► It can retain magnetic properties for a long time. ► Permanent magnets can lose their magnetism if heated or dropped. ► When a magnet is broken, each ...
... cobalt, or nickel can be made into permanent magnets by placing them in a strong magnetic field. ► This creates a magnetic field inside the material ► It can retain magnetic properties for a long time. ► Permanent magnets can lose their magnetism if heated or dropped. ► When a magnet is broken, each ...
electrom - studylib.net
... produced by such an electromagnet depends on the number of coils of wire, the magnitude of the current, and the magnetic permeability of the core material; a strong field can be produced from a small current if a large number of turns of wire are used. Unlike the materials from which permanent magne ...
... produced by such an electromagnet depends on the number of coils of wire, the magnitude of the current, and the magnetic permeability of the core material; a strong field can be produced from a small current if a large number of turns of wire are used. Unlike the materials from which permanent magne ...
Producing Electric Current
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... • An electric charge changes the properties of the space around it. – It is the source of an “electric field”. – It could be defined as the “force per unit charge”: ...
... • An electric charge changes the properties of the space around it. – It is the source of an “electric field”. – It could be defined as the “force per unit charge”: ...
Producing Electric Current
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
A fast, high-tech, low cost electric motor construction
... coiled wire and magnets. Since one expects something complex from something complicated, one is not more surprised by the possibility to make something moving from an inanimate object. One sees surprise and fascination, not only amongst experts when, before one's eyes, a motor is assembled in a few ...
... coiled wire and magnets. Since one expects something complex from something complicated, one is not more surprised by the possibility to make something moving from an inanimate object. One sees surprise and fascination, not only amongst experts when, before one's eyes, a motor is assembled in a few ...
fourth nine weeks
... mirrors, prisms, tuning forks, optical illusions, lights, color, musical instruments, common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz ...
... mirrors, prisms, tuning forks, optical illusions, lights, color, musical instruments, common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz ...