Chapter 2. Electrostatics
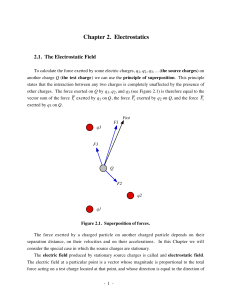
... The electric field generated by the source charges is thus equal to F 1 n qi E= = Â 2 rˆ Q 4pe 0 i =1 ri i In most applications the source charges are not discrete, but are distributed continuously over some region. The following three different distributions will be used in this course: 1. line cha ...
... The electric field generated by the source charges is thus equal to F 1 n qi E= = Â 2 rˆ Q 4pe 0 i =1 ri i In most applications the source charges are not discrete, but are distributed continuously over some region. The following three different distributions will be used in this course: 1. line cha ...
Magnetism and Static Electricity WebQuest
... http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/lsps07_int_theatom/ http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html http://www.tutorvista.com/content/chemistry/chemistry-i/atom/atomanimation.php http://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/Education/wmfield.html ...
... http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/lsps07_int_theatom/ http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html http://www.tutorvista.com/content/chemistry/chemistry-i/atom/atomanimation.php http://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/Education/wmfield.html ...
magnetism - Supercharged Science
... Goggles: These should be worn when working with chemicals, heat, fire, or projectiles. These protect your eyes from chemical splatter, explosions, and tiny fast-moving objects aimed at the eyes. If you wear glasses, you can find goggles that fit over them. Don’t substitute eyeglasses for goggles, be ...
... Goggles: These should be worn when working with chemicals, heat, fire, or projectiles. These protect your eyes from chemical splatter, explosions, and tiny fast-moving objects aimed at the eyes. If you wear glasses, you can find goggles that fit over them. Don’t substitute eyeglasses for goggles, be ...
Physics 217: Electricity and Magnetism I
... when you want a different explanation or example related to a concept you find troublesome. Many other books, at levels both higher and lower, will also serve as useful references. Here are the books that will be on reserve in the Physics, Optics and Astronomy Library. The titles of required textboo ...
... when you want a different explanation or example related to a concept you find troublesome. Many other books, at levels both higher and lower, will also serve as useful references. Here are the books that will be on reserve in the Physics, Optics and Astronomy Library. The titles of required textboo ...
Antennas and propagation
... very small, on the order of 1 ohm, most of which is loss resistance in the conductor making up the loop. The actual radiation resistance may be 0.5 ohms or less. Because the radiation resistance is small compared to the loss resistance, the small loop antenna is not an efficient antenna and cannot b ...
... very small, on the order of 1 ohm, most of which is loss resistance in the conductor making up the loop. The actual radiation resistance may be 0.5 ohms or less. Because the radiation resistance is small compared to the loss resistance, the small loop antenna is not an efficient antenna and cannot b ...
3 3-0
... (2) Determine the direction of the electric field, and a “Gaussian surface” on which the magnitude of the electric field is constant over portions of the surface. (3) Divide the space into different regions associated with the charge distribution. For each region, calculate qenc , the charge enclos ...
... (2) Determine the direction of the electric field, and a “Gaussian surface” on which the magnitude of the electric field is constant over portions of the surface. (3) Divide the space into different regions associated with the charge distribution. For each region, calculate qenc , the charge enclos ...
Magnetism and Static Electricity WebQuest
... http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html http://www.tutorvista.com/content/chemistry/chemistry-i/atom/atomanimation.php ...
... http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html http://www.tutorvista.com/content/chemistry/chemistry-i/atom/atomanimation.php ...
lec11 1.72 MB
... Compasses point north so earth has magnetic field. But compasses point from N to S! Because earth’s “north” pole is really magnetic S. ...
... Compasses point north so earth has magnetic field. But compasses point from N to S! Because earth’s “north” pole is really magnetic S. ...
Theory of Electromagnetic Fields
... Electromagnetic waves on boundaries: Fresnel’s equations The relationships between the amplitudes of the incident, transmitted and reflected waves can be summed up in a set of formulae, known as Fresnel’s equations. We do not go through the derivations, but present the results on the following slid ...
... Electromagnetic waves on boundaries: Fresnel’s equations The relationships between the amplitudes of the incident, transmitted and reflected waves can be summed up in a set of formulae, known as Fresnel’s equations. We do not go through the derivations, but present the results on the following slid ...