Electrostatic - Portal UniMAP
... Neutrons and most materials have a net charge of zero or neutral. When certain types of objects are rubbed together, electrons from one object may be transferred to an object with a greater affinity for the electrons. When this happens, the object that gave up the electrons is positive, whereas the ...
... Neutrons and most materials have a net charge of zero or neutral. When certain types of objects are rubbed together, electrons from one object may be transferred to an object with a greater affinity for the electrons. When this happens, the object that gave up the electrons is positive, whereas the ...
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... This course, aiming at students in Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Science and Technology programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws of electricity and magnetism, and applications of electromagnetism in modern science and technology. This course consists of five parts: electrost ...
... This course, aiming at students in Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Science and Technology programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws of electricity and magnetism, and applications of electromagnetism in modern science and technology. This course consists of five parts: electrost ...
Chapter 16: Electromagnets and Induction
... As the rotor spins, the three plates come into contact with the positive and negative brushes. ...
... As the rotor spins, the three plates come into contact with the positive and negative brushes. ...
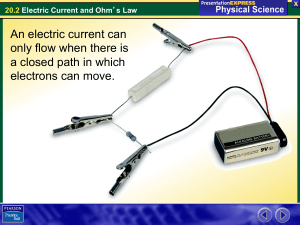
20.2 Electric Current and Ohm
... • Charge flows only in one direction in direct current (DC). A flashlight and most other battery-operated devices use direct current. • Alternating current (AC) is a flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction. Electric current in your home and school is mostly alternating curren ...
... • Charge flows only in one direction in direct current (DC). A flashlight and most other battery-operated devices use direct current. • Alternating current (AC) is a flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction. Electric current in your home and school is mostly alternating curren ...
Make an electric motor
... wire when the wire is connected in a circuit from one battery terminal to the other. The negatively charged electrons in the wire move away from the negative terminal of the battery towards the positive terminal. The movement of electrons through a conductor is called an electric current. A magnet i ...
... wire when the wire is connected in a circuit from one battery terminal to the other. The negatively charged electrons in the wire move away from the negative terminal of the battery towards the positive terminal. The movement of electrons through a conductor is called an electric current. A magnet i ...
9.6 - iupac
... Mobilities are sometimes expressed with a negative sign, because migration of the solutes or particles generally occurs in the direction opposite to the electrophoretic field (which is taken as reference for the direction). ...
... Mobilities are sometimes expressed with a negative sign, because migration of the solutes or particles generally occurs in the direction opposite to the electrophoretic field (which is taken as reference for the direction). ...
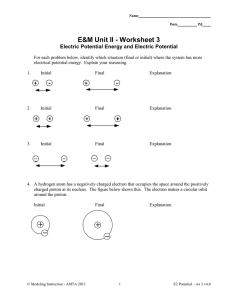
Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... 4. A hydrogen atom has a negatively charged electron that occupies the space around the positively charged proton at its nucleus. The figure below shows this. The electron makes a circular orbit around the proton. ...
... 4. A hydrogen atom has a negatively charged electron that occupies the space around the positively charged proton at its nucleus. The figure below shows this. The electron makes a circular orbit around the proton. ...
Ενότητα 9: Electric Meters
... through this shunt resistance, but the small current flowing through the meter is still proportional to the total current. By taking advantage of this proportionality, a galvanometer can be used to measure currents of hundreds of amperes. Galvanometers are usually named according to the magnitude o ...
... through this shunt resistance, but the small current flowing through the meter is still proportional to the total current. By taking advantage of this proportionality, a galvanometer can be used to measure currents of hundreds of amperes. Galvanometers are usually named according to the magnitude o ...
Chapter 7: Magnetism and Its Uses
... As the alternating current passes through the primary coil the core becomes an electromagnet Because the current is changing direction many times each second, the magnetic field of the iron core changes direction. The changing magnetic field induces an alternating current in the secondary coil ...
... As the alternating current passes through the primary coil the core becomes an electromagnet Because the current is changing direction many times each second, the magnetic field of the iron core changes direction. The changing magnetic field induces an alternating current in the secondary coil ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.