Lecture 1 ppt version
... electrons are bound to nearby atoms and none can move freely. These materials are called insulators. In many materials, such as copper and other metals, some of the electrons are free to move about the entire material. Such materials are called conductors. ...
... electrons are bound to nearby atoms and none can move freely. These materials are called insulators. In many materials, such as copper and other metals, some of the electrons are free to move about the entire material. Such materials are called conductors. ...
Define and Explain Electromagnetic Induction
... Imagine a simple circuit of a switch, a coil, and a battery. When the switch is closed, the current through the coil sets up a magnetic field. As the current is increasing, the magnetic flux through the coil is also changing. This changing magnetic flux generates an emf opposing that of the battery. ...
... Imagine a simple circuit of a switch, a coil, and a battery. When the switch is closed, the current through the coil sets up a magnetic field. As the current is increasing, the magnetic flux through the coil is also changing. This changing magnetic flux generates an emf opposing that of the battery. ...
8. electromagnetic waves
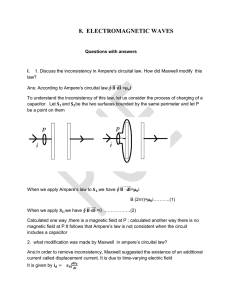
... 2. what modification was made by Maxwell in ampere’s circuital law? Ans:In order to remove inconsistency, Maxwell suggested the existence of an additional current called displacement current. It is due to time-varying electric field It is given by ...
... 2. what modification was made by Maxwell in ampere’s circuital law? Ans:In order to remove inconsistency, Maxwell suggested the existence of an additional current called displacement current. It is due to time-varying electric field It is given by ...
R-Electrostatics-Unit
... • Charging Objects (friction, contact and induction) For all methods of charging neutral objects, one object/system ends up with a surplus of positive charge and the other object/system ends up with the same amount of surplus of negative charge. This supports the law of conservation of charge that s ...
... • Charging Objects (friction, contact and induction) For all methods of charging neutral objects, one object/system ends up with a surplus of positive charge and the other object/system ends up with the same amount of surplus of negative charge. This supports the law of conservation of charge that s ...
Document
... 3) Find the force required to pull the loop at a constant velocity. 4) Explain why such force is required. ...
... 3) Find the force required to pull the loop at a constant velocity. 4) Explain why such force is required. ...
Electrostatics
... Q19. A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has a capacitance of 8 pF . The separation between the plates is now reduced by half and the space between them is filled with a medium of dielectric constant 5. Calculate the value of capacitance of parallel plate capacitor in second case ...
... Q19. A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has a capacitance of 8 pF . The separation between the plates is now reduced by half and the space between them is filled with a medium of dielectric constant 5. Calculate the value of capacitance of parallel plate capacitor in second case ...
The Titanic and the Wireless
... connection between electricity and magnetism. Electric currents could produce magnetic fields and changing magnetic fields could result in electric currents. In 1864 James Clerk Maxwell combined the mathematical connections among charges, currents and electric and magnetic fields into four equations ...
... connection between electricity and magnetism. Electric currents could produce magnetic fields and changing magnetic fields could result in electric currents. In 1864 James Clerk Maxwell combined the mathematical connections among charges, currents and electric and magnetic fields into four equations ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.