DEMONSTRATION EXPERIMENTS IN PHYSICS
... (E-2 and3) are adequate. Other more sensitive types of electrostatic instrument are useful for experiments where voltages, minute charges, or ion currents must be measured. The electrostatic voltmeter (Braun) consists of an aluminum vane balanced in a vertical position near a fixed vertical metal ro ...
... (E-2 and3) are adequate. Other more sensitive types of electrostatic instrument are useful for experiments where voltages, minute charges, or ion currents must be measured. The electrostatic voltmeter (Braun) consists of an aluminum vane balanced in a vertical position near a fixed vertical metal ro ...
James Ruse Trial with Solutions
... competitors, Nikola Tesla and George Westinghouse, began to use transformers with their alternating current (AC) electric power systems. Why was Edison unable to use transformers in his direct current (DC) electric power systems? (A) Tesla and Westinghouse held the U.S. patent rights to transformers ...
... competitors, Nikola Tesla and George Westinghouse, began to use transformers with their alternating current (AC) electric power systems. Why was Edison unable to use transformers in his direct current (DC) electric power systems? (A) Tesla and Westinghouse held the U.S. patent rights to transformers ...
Ch. 24 Capacitance
... Capacitor • A device that stores electric charge • Used with resistors in timing circuits because it takes time for a capacitor to fill with charge • Used to smooth varying DC supplies by acting as a reservoir of charge • Used in filter circuits because capacitors easily pass AC (changing) signals ...
... Capacitor • A device that stores electric charge • Used with resistors in timing circuits because it takes time for a capacitor to fill with charge • Used to smooth varying DC supplies by acting as a reservoir of charge • Used in filter circuits because capacitors easily pass AC (changing) signals ...
Electric Forces and Fields
... As another example, consider rubbing an insulating rod (e.g., rubber, hard plastic glass) against a piece of silk. The act of rubbing these two insulating materials will physically force some charges to move from one object to the other. When charges are transferred to the insulating rod, they do no ...
... As another example, consider rubbing an insulating rod (e.g., rubber, hard plastic glass) against a piece of silk. The act of rubbing these two insulating materials will physically force some charges to move from one object to the other. When charges are transferred to the insulating rod, they do no ...
Magnetism and Electricity
... Roxana Cervantes, Eliana Postigo, Katie Vázquez, Sarah Wargaski—Project GLAD (January 2012) ...
... Roxana Cervantes, Eliana Postigo, Katie Vázquez, Sarah Wargaski—Project GLAD (January 2012) ...
Physical/Mathematical Background The Basics
... Bioengineering 6003 Cellular Electrophysiology & Biophysics ...
... Bioengineering 6003 Cellular Electrophysiology & Biophysics ...
Lesson 7 – Gauss`s Law and Electric Fields
... other. Furthermore, if charges +10 and −10 are both located inside the box, some field lines from the positive charge may go directly to the negative charge without ever leaving the box, and some field lines may leave the box from the positive charge and come back in to the negative charge. The one ...
... other. Furthermore, if charges +10 and −10 are both located inside the box, some field lines from the positive charge may go directly to the negative charge without ever leaving the box, and some field lines may leave the box from the positive charge and come back in to the negative charge. The one ...
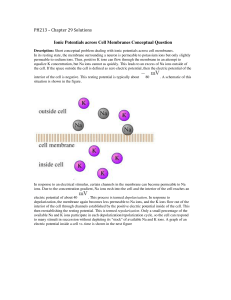
PH213 – Chapter 29 Solutions Ionic Potentials across Cell
... Because positive charges create positive electric potentials in their vicinity and negative charges create negative potentials in their vicinity, electric potential is sometimes visualized as a sort of "elevation." Positive charges represent mountain peaks and negative charges deep valleys. In this ...
... Because positive charges create positive electric potentials in their vicinity and negative charges create negative potentials in their vicinity, electric potential is sometimes visualized as a sort of "elevation." Positive charges represent mountain peaks and negative charges deep valleys. In this ...
Chapter 16: Electromagnetic Induction
... Working: When electric current is passed through the coil in the direction ABCD, it sets up a magnetic field which is at right angles to the plane of the coil and a mechanical force acts on its limbs in opposing direction. Therefore the coil begins to rotate about its axis. During the first half of ...
... Working: When electric current is passed through the coil in the direction ABCD, it sets up a magnetic field which is at right angles to the plane of the coil and a mechanical force acts on its limbs in opposing direction. Therefore the coil begins to rotate about its axis. During the first half of ...
Multipole Expansion of the Electrostatic Potential
... 2.1 Find the dipole moment of the system of four point charges q at (a, 0, 0), q at (0, a, 0), −q at (−a, 0, 0) and −q at (0, −a, 0). 2.2 Write the potential for the system of three point charges: two charges +q in the points (0, 0, a) and (0, 0, −a), and a charge −2q in the origin of the frame. Fin ...
... 2.1 Find the dipole moment of the system of four point charges q at (a, 0, 0), q at (0, a, 0), −q at (−a, 0, 0) and −q at (0, −a, 0). 2.2 Write the potential for the system of three point charges: two charges +q in the points (0, 0, a) and (0, 0, −a), and a charge −2q in the origin of the frame. Fin ...
Lesson 2 Flux and Gauss`s Law Charles Augustine de Coulomb
... point charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and the electric field surrounding an isolated charge therefore has, by definition, an identical inverse-square-law dependence. In our Gauss’s-law picture, the radial flux lines originating or terminating on an isolat ...
... point charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and the electric field surrounding an isolated charge therefore has, by definition, an identical inverse-square-law dependence. In our Gauss’s-law picture, the radial flux lines originating or terminating on an isolat ...
Physics - Belfast Royal Academy
... know that electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to travel through know that all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in air or vacuum know that all electromagnetic waves are transverse waves know that all electromagnetic waves carry energy or transfer energy be able to recall some ...
... know that electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to travel through know that all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in air or vacuum know that all electromagnetic waves are transverse waves know that all electromagnetic waves carry energy or transfer energy be able to recall some ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.