Problem 1 and is oriented in such a y E
... Problem 4. Non-relativistic particle with charge q and mass m is placed in electric field described by the potential ϕ(x, y, z) = k(x2 − y 2 ) (electrostatic lens). Magnetic field is absent. At the moment of time t = 0 the particle has zero velocity and is located at r0 = (x0 , y0 , z0 ). Find r(t) ...
... Problem 4. Non-relativistic particle with charge q and mass m is placed in electric field described by the potential ϕ(x, y, z) = k(x2 − y 2 ) (electrostatic lens). Magnetic field is absent. At the moment of time t = 0 the particle has zero velocity and is located at r0 = (x0 , y0 , z0 ). Find r(t) ...
AC Circuits
... Gauss's Law - calculation of the magnitude of the electric field caused by continuous distributions of charge starting with Gauss's Law and completing all the steps including evaluation of the integrals. Ampere's Law - calculation of the magnitude of the magnetic field caused by electric currents us ...
... Gauss's Law - calculation of the magnitude of the electric field caused by continuous distributions of charge starting with Gauss's Law and completing all the steps including evaluation of the integrals. Ampere's Law - calculation of the magnitude of the magnetic field caused by electric currents us ...
Part I (50 points)
... (b) For a function f (r ) which satisfies the Laplace equation 2 f (r) 0 , the value of f (r ) at any point is equal to the average of the function over the surface of any sphere centered on that point. (10 points) [Hint: Green’s theorem ...
... (b) For a function f (r ) which satisfies the Laplace equation 2 f (r) 0 , the value of f (r ) at any point is equal to the average of the function over the surface of any sphere centered on that point. (10 points) [Hint: Green’s theorem ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
... At the atomic level, there are protons (+ charge) & neutrons (neutral charge) in the nucleus, and electrons (- charge) spinning in orbits around the nucleus. The moving electron acts as a mini electrical charge and therefore has a magnetic field associated w/ it. In ferrous materials clusters of ato ...
... At the atomic level, there are protons (+ charge) & neutrons (neutral charge) in the nucleus, and electrons (- charge) spinning in orbits around the nucleus. The moving electron acts as a mini electrical charge and therefore has a magnetic field associated w/ it. In ferrous materials clusters of ato ...
Electromagnetic induction
... •Faraday’s law and the Ampere-Maxwell law are symmetrical in that the line integrals of E and B around a closed path are related to the rate of change of the respective fluxes ...
... •Faraday’s law and the Ampere-Maxwell law are symmetrical in that the line integrals of E and B around a closed path are related to the rate of change of the respective fluxes ...
document
... • Implication - the system is attempting to stay still: once a change is found in magnetic flux, an electric field is excited in such a way that it tries to cancel out the magnetic flux change by generating a new magnetic flux against the original one; i.e., ...
... • Implication - the system is attempting to stay still: once a change is found in magnetic flux, an electric field is excited in such a way that it tries to cancel out the magnetic flux change by generating a new magnetic flux against the original one; i.e., ...
MAGNETIC FIELDS
... • The voltage produced by a battery to move energy around a wire • It is not a force—it was named this because it was originally thought charges were being “forced” to move around a wire • Units: Volts ...
... • The voltage produced by a battery to move energy around a wire • It is not a force—it was named this because it was originally thought charges were being “forced” to move around a wire • Units: Volts ...
Al-Balqa Applied University
... Exams. Two in-class exams will be given. Each will cover about 40% of lectures Final Exam: The final exam will cover all the class material. Allocation of Marks Exam I Exam II Participation and activities Final Exam ...
... Exams. Two in-class exams will be given. Each will cover about 40% of lectures Final Exam: The final exam will cover all the class material. Allocation of Marks Exam I Exam II Participation and activities Final Exam ...
MAGNETISM
... One of the best ways is to heat the material (like the magma from the mid-atlantic ridge) and then pass it through a magnetic field. When the material cools, its domains will have settled in an aligned ...
... One of the best ways is to heat the material (like the magma from the mid-atlantic ridge) and then pass it through a magnetic field. When the material cools, its domains will have settled in an aligned ...
Generators and Motors
... 16. When there is relative motion between the wire and a nearby magnet, we have created an _____________ current. 17. This connection between magnetism and electricity was used to develop ____________, ________________, and other electrical technology. What’s in a Generator? 18. Define AC – alternat ...
... 16. When there is relative motion between the wire and a nearby magnet, we have created an _____________ current. 17. This connection between magnetism and electricity was used to develop ____________, ________________, and other electrical technology. What’s in a Generator? 18. Define AC – alternat ...
Time Varying Electric and Magnetic Fields
... Faraday’s law states that, the total emf induced in a closed circuit is equal to the time rate of decrease of the total magnetic flux linking the circuit. ...
... Faraday’s law states that, the total emf induced in a closed circuit is equal to the time rate of decrease of the total magnetic flux linking the circuit. ...
Section 2 notes--Electromagnetism
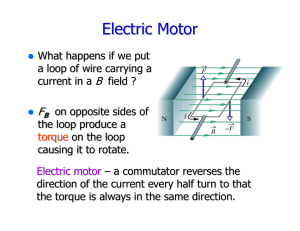
... Electric Motors • An electric motor is a device that changes electrical energy into mechanical energy Electric motors contain electromagnets that are free to rotate between the poles of a permanent, fixed magnet The coil in the electromagnet is connected to a source of electric current ...
... Electric Motors • An electric motor is a device that changes electrical energy into mechanical energy Electric motors contain electromagnets that are free to rotate between the poles of a permanent, fixed magnet The coil in the electromagnet is connected to a source of electric current ...
Pretest 13 (EMF) - University of Colorado Boulder
... On which part of the wing will the positive charge accumulate? Please select ALL that apply. a) Top b) Bottom c) Front d) Rear e) Other f) Not enough information Please explain your answers to the previous 2 questions briefly but clearly: ...
... On which part of the wing will the positive charge accumulate? Please select ALL that apply. a) Top b) Bottom c) Front d) Rear e) Other f) Not enough information Please explain your answers to the previous 2 questions briefly but clearly: ...
fourth nine weeks
... common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz ...
... common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.