magnet and magnetism
... is strong enough to influence surrounding atoms. In iron, for example, four electrons are unpaired. These four electrons line up to form a strong atomic magnet. Under the influence of this atomic magnet adjacent atomic magnets line up in the same direction, and the fields of all the aligned atoms co ...
... is strong enough to influence surrounding atoms. In iron, for example, four electrons are unpaired. These four electrons line up to form a strong atomic magnet. Under the influence of this atomic magnet adjacent atomic magnets line up in the same direction, and the fields of all the aligned atoms co ...
Chapter 12 Review, pages 580–585
... the train that is repelled by the section of track immediately behind it, so it experiences a force horizontally forward, which pushes the train forward. 23. (a) Oersted aligned a conducting wire in an electric circuit with Earth’s magnetic field and held a compass near it. When the current was swit ...
... the train that is repelled by the section of track immediately behind it, so it experiences a force horizontally forward, which pushes the train forward. 23. (a) Oersted aligned a conducting wire in an electric circuit with Earth’s magnetic field and held a compass near it. When the current was swit ...
The first battery-powered flashlights were designed around 1899
... Equation for voltage generated by a change in the magnetic field (Lenz’s Law): N- number of turns for the wire coil BA- magnetic flux T- rate of change in time i.e.) Determine the change of rate in time for (turn “on” voltage for LED), 100 turns of wire, and magnetic flux of 5 Tesla. (Approxim ...
... Equation for voltage generated by a change in the magnetic field (Lenz’s Law): N- number of turns for the wire coil BA- magnetic flux T- rate of change in time i.e.) Determine the change of rate in time for (turn “on” voltage for LED), 100 turns of wire, and magnetic flux of 5 Tesla. (Approxim ...
Chapter III Description of Existing and Alternative Brakes
... shows that decay of the coil current and resulting torque has a dynamic response similar to engaging, except a rise (blip) in the current curve represent the armature plate separating from the friction surface. Kebco, which sells units ranging in maximum static torque capabilities of 0.4 Lbf-ft (0.5 ...
... shows that decay of the coil current and resulting torque has a dynamic response similar to engaging, except a rise (blip) in the current curve represent the armature plate separating from the friction surface. Kebco, which sells units ranging in maximum static torque capabilities of 0.4 Lbf-ft (0.5 ...
Microwave tunability in a GaAs-based multiferroic heterostructure: Co MnAl/GaAs/PMN-PT
... structure. Note, that the PMN-PT crystal has a thickness of 0.5 mm and was bonded to a 180 m thick GaAs substrate with a quick curing ethyl cyanoacrylate glue. Unlike previously reported multiferroic heterostructures,16 the bonding of the Co2MnAl magnetic film to the PMN-PT crystal is mediated by t ...
... structure. Note, that the PMN-PT crystal has a thickness of 0.5 mm and was bonded to a 180 m thick GaAs substrate with a quick curing ethyl cyanoacrylate glue. Unlike previously reported multiferroic heterostructures,16 the bonding of the Co2MnAl magnetic film to the PMN-PT crystal is mediated by t ...
Magnetism
... 2. interior of a solenoid contains an approximately uniform B-field if wire carries a steady I 3. closely-spaced turns can be approximated as circular loops, and the net magnetic field is the vector sum of fields from all turns. 4. interior field lines are parallel and closely-spaced indicating a un ...
... 2. interior of a solenoid contains an approximately uniform B-field if wire carries a steady I 3. closely-spaced turns can be approximated as circular loops, and the net magnetic field is the vector sum of fields from all turns. 4. interior field lines are parallel and closely-spaced indicating a un ...
CHAPTER- 1 : FUNDAMENTALS OF MAGETIC
... rises (or falls) taken in a specified direction in a closed magnetic circuit is zero. Parallel Magnetic Circuit : Consider a parallel magnetic circuit shown in figure 4. Coil carrying a current I produces flux in path EFAB. At point B. flux gets divided into two paths, and such that ...
... rises (or falls) taken in a specified direction in a closed magnetic circuit is zero. Parallel Magnetic Circuit : Consider a parallel magnetic circuit shown in figure 4. Coil carrying a current I produces flux in path EFAB. At point B. flux gets divided into two paths, and such that ...
Generation of electricity
... for electroplating processes, railway and tramway systems and other motor driven applications where a smooth and wide range of speed control is required. It is generally more economical to transmit and distribute electricity in alternating current (AC) form, therefore all electricity generated at
... for electroplating processes, railway and tramway systems and other motor driven applications where a smooth and wide range of speed control is required. It is generally more economical to transmit and distribute electricity in alternating current (AC) form, therefore all electricity generated at
GP2Y0D810Z0F
... reserves the right to make changes in the specifications, characteristics, data, materials, structure, and other contents described herein at any time without notice in order to improve design or reliability. Manufacturing locations are also subject to change without notice. · Observe the following ...
... reserves the right to make changes in the specifications, characteristics, data, materials, structure, and other contents described herein at any time without notice in order to improve design or reliability. Manufacturing locations are also subject to change without notice. · Observe the following ...
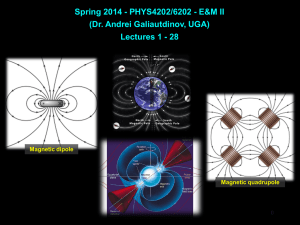
Spring 2014 - PHYS4202/6202 - E&M II (Dr. Andrei Galiautdinov, UGA) 0
... cross is sufficient to change the state; other cores will see only half the needed field ("half-selected"), or none at all. Driving the current through the wires magnetizes the core in one direction (“1”) or the other (“0”). ...
... cross is sufficient to change the state; other cores will see only half the needed field ("half-selected"), or none at all. Driving the current through the wires magnetizes the core in one direction (“1”) or the other (“0”). ...
Maxwell`s Equations, Part I: History
... voltaic pile through a wire that was placed parallel to a compass needle. The needle was deflected. Later experiments (especially by Ampère) demonstrated that with a strong enough current, a magnetized compass needle will orient itself perpendicular to the direction of the current. If the current wa ...
... voltaic pile through a wire that was placed parallel to a compass needle. The needle was deflected. Later experiments (especially by Ampère) demonstrated that with a strong enough current, a magnetized compass needle will orient itself perpendicular to the direction of the current. If the current wa ...
Optical and magneto-optical properties of UPtGe
... The crystal structure has been determined to be of the noncentrosymmetric EuAuGe type with two uranium sites with different magnetic moments [3]. The electrical and magnetic properties show a small anisotropy in the ac plane, while the electric and magnetic behavior along the b axis is distinct from ...
... The crystal structure has been determined to be of the noncentrosymmetric EuAuGe type with two uranium sites with different magnetic moments [3]. The electrical and magnetic properties show a small anisotropy in the ac plane, while the electric and magnetic behavior along the b axis is distinct from ...
Theme 2: The story of Magnets
... magnetic poles repel each other whereas unlike poles attract each other. Remember the force when you held two magnets close and felt them either attract (pull toward one another) or repel (push away)? One of the most amazing things about magnets is the way they can attract other magnets (or other ma ...
... magnetic poles repel each other whereas unlike poles attract each other. Remember the force when you held two magnets close and felt them either attract (pull toward one another) or repel (push away)? One of the most amazing things about magnets is the way they can attract other magnets (or other ma ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.