Goals for solving equations: 1. Isolate the variable 2. Keep the
... Lesson number: Lesson Title: Solving Linear Equations Learning Target: Find the value of x in a linear equation Success Criteria: ...
... Lesson number: Lesson Title: Solving Linear Equations Learning Target: Find the value of x in a linear equation Success Criteria: ...
3-1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
... *A linear system in three variables is an equation in the form ax + by + cz = d where a, b, and c are not all zero. A solution of such a system is an ordered __________________ (x, y, z) whose coordinates make each equation true. The graph is a plane in three-dimensional space. See page 178 for exam ...
... *A linear system in three variables is an equation in the form ax + by + cz = d where a, b, and c are not all zero. A solution of such a system is an ordered __________________ (x, y, z) whose coordinates make each equation true. The graph is a plane in three-dimensional space. See page 178 for exam ...
Get Ready for the Chapter
... Step 3 Follow along a horizontal line to the y-axis. The y-coordinate is 2. ...
... Step 3 Follow along a horizontal line to the y-axis. The y-coordinate is 2. ...
11 Linear dependence and independence
... are linearly dependent because 2x1 + x2 − x3 = 0. 2. Any set containing the vector 0 is linearly dependent, because for any c 6= 0, c0 = 0. 3. In the definition, we require that not all of the scalars c1 , . . . , cn are 0. The reason for this is that otherwise, any set of vectors would be linearly ...
... are linearly dependent because 2x1 + x2 − x3 = 0. 2. Any set containing the vector 0 is linearly dependent, because for any c 6= 0, c0 = 0. 3. In the definition, we require that not all of the scalars c1 , . . . , cn are 0. The reason for this is that otherwise, any set of vectors would be linearly ...
Solving Absolute Value Equations
... An absolute value equation is an equation that contains an absolute value expression. You can solve these types of equations by solving two related linear equations. To solve ∣ ax + b ∣ = c when c ≥ 0, solve the related linear equations ax + b = c ...
... An absolute value equation is an equation that contains an absolute value expression. You can solve these types of equations by solving two related linear equations. To solve ∣ ax + b ∣ = c when c ≥ 0, solve the related linear equations ax + b = c ...
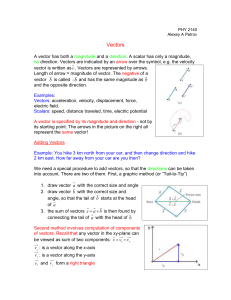
vectors
... Vectors: acceleration, velocity, displacement, force, electric field. Scalars: speed, distance traveled, time, electric potential A vector is specified by its magnitude and direction - not by its starting point. The arrows in the picture on the right all represent the same vector! Adding Vectors Exa ...
... Vectors: acceleration, velocity, displacement, force, electric field. Scalars: speed, distance traveled, time, electric potential A vector is specified by its magnitude and direction - not by its starting point. The arrows in the picture on the right all represent the same vector! Adding Vectors Exa ...
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning vector spaces and linear mappings between such spaces. It includes the study of lines, planes, and subspaces, but is also concerned with properties common to all vector spaces.The set of points with coordinates that satisfy a linear equation forms a hyperplane in an n-dimensional space. The conditions under which a set of n hyperplanes intersect in a single point is an important focus of study in linear algebra. Such an investigation is initially motivated by a system of linear equations containing several unknowns. Such equations are naturally represented using the formalism of matrices and vectors.Linear algebra is central to both pure and applied mathematics. For instance, abstract algebra arises by relaxing the axioms of a vector space, leading to a number of generalizations. Functional analysis studies the infinite-dimensional version of the theory of vector spaces. Combined with calculus, linear algebra facilitates the solution of linear systems of differential equations.Techniques from linear algebra are also used in analytic geometry, engineering, physics, natural sciences, computer science, computer animation, and the social sciences (particularly in economics). Because linear algebra is such a well-developed theory, nonlinear mathematical models are sometimes approximated by linear models.















![10 Questions & Answers[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008474122_1-913b0bc5b28ab2d292606c5c2aed9267-300x300.png)