ECON3120/4120 Mathematics 2, autumn 2005 Problem
... (For practical reasons some of the solutions may include problem parts that are not on the problem list for this seminar.) EMEA, 15.7.3 (= LA, 2.1.5) Using the definitions of vector addition and multiplication of a vector by a real number, we get 3(x, y, z) + 5(−1, 2, 3) = (4, 1, 3) ⇐⇒ (3x − 5, 3y + ...
... (For practical reasons some of the solutions may include problem parts that are not on the problem list for this seminar.) EMEA, 15.7.3 (= LA, 2.1.5) Using the definitions of vector addition and multiplication of a vector by a real number, we get 3(x, y, z) + 5(−1, 2, 3) = (4, 1, 3) ⇐⇒ (3x − 5, 3y + ...
Curriculum plan of Dr . Rachana Kumar For even session 2015-16
... Curriculum plan of Dr . Rachana Kumar For even session 2015-16 B.Sc I (PS) PHYSICS-DSC 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2 periods per week Allocation of Lectures ...
... Curriculum plan of Dr . Rachana Kumar For even session 2015-16 B.Sc I (PS) PHYSICS-DSC 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2 periods per week Allocation of Lectures ...
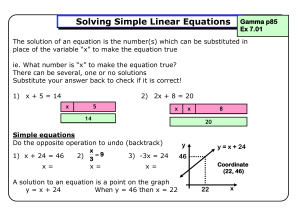
Practical Algebra A/I and B/II Curriculum Crawford Central School
... Reference Problem #24 on page 239 from Keystone Coach Algebra 1. Edit to have one of the sides of the rectangle be a constant to avoid a polynomial expression. Use and/or identify an algebraic property to justify any step in an equationsolving process ...
... Reference Problem #24 on page 239 from Keystone Coach Algebra 1. Edit to have one of the sides of the rectangle be a constant to avoid a polynomial expression. Use and/or identify an algebraic property to justify any step in an equationsolving process ...
Chapters 7 and 8 Slides
... • The graph of the quadratic function defined by f(x) = a(x-h)2 + k, a not 0, is a parabola with vertex (h,k) and the vertical line x = h as axis of symmetry • The graph opens up if a is positive and down if a is negative • The graph is wide if |a|<1 and narrow if |a|>1 compared to y = x2 ...
... • The graph of the quadratic function defined by f(x) = a(x-h)2 + k, a not 0, is a parabola with vertex (h,k) and the vertical line x = h as axis of symmetry • The graph opens up if a is positive and down if a is negative • The graph is wide if |a|<1 and narrow if |a|>1 compared to y = x2 ...
EP-307 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
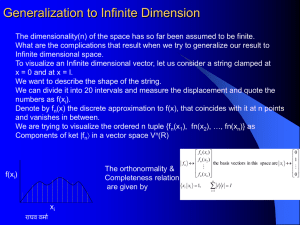
... infinite set of basis vectors. A point charge in a macroscopic problem in electrostatics is in actuality a charge concentrated on a small region in space as compared to the dimensions of the problem. The point charge is mathematically convenient limit that allows two things ...
... infinite set of basis vectors. A point charge in a macroscopic problem in electrostatics is in actuality a charge concentrated on a small region in space as compared to the dimensions of the problem. The point charge is mathematically convenient limit that allows two things ...
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning vector spaces and linear mappings between such spaces. It includes the study of lines, planes, and subspaces, but is also concerned with properties common to all vector spaces.The set of points with coordinates that satisfy a linear equation forms a hyperplane in an n-dimensional space. The conditions under which a set of n hyperplanes intersect in a single point is an important focus of study in linear algebra. Such an investigation is initially motivated by a system of linear equations containing several unknowns. Such equations are naturally represented using the formalism of matrices and vectors.Linear algebra is central to both pure and applied mathematics. For instance, abstract algebra arises by relaxing the axioms of a vector space, leading to a number of generalizations. Functional analysis studies the infinite-dimensional version of the theory of vector spaces. Combined with calculus, linear algebra facilitates the solution of linear systems of differential equations.Techniques from linear algebra are also used in analytic geometry, engineering, physics, natural sciences, computer science, computer animation, and the social sciences (particularly in economics). Because linear algebra is such a well-developed theory, nonlinear mathematical models are sometimes approximated by linear models.