IB Definitions
... An exothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall negative enthalpy change (heat is evolved) An endothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall postive enthalpy change (heat is absorbed) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change when one mole of reactants is ...
... An exothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall negative enthalpy change (heat is evolved) An endothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall postive enthalpy change (heat is absorbed) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change when one mole of reactants is ...
The physical characteristics of the atom of an element are called
... 4. Mendeleev's Periodic Table:When mendeleev started his work, 63 elements were known at that time. He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are very reactive and formed compounds with most elements. Mendeleev's periodic table contains vertical columns called groups and horizontal rows called periods ...
... 4. Mendeleev's Periodic Table:When mendeleev started his work, 63 elements were known at that time. He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are very reactive and formed compounds with most elements. Mendeleev's periodic table contains vertical columns called groups and horizontal rows called periods ...
June review January 2012 part A
... 37 Which compound is formed from its elements by an exothermic reaction at 298 K and 101.3 kPa? (HINT: This is a table I question) ...
... 37 Which compound is formed from its elements by an exothermic reaction at 298 K and 101.3 kPa? (HINT: This is a table I question) ...
Bohr`s Theory of the Atom
... As described earlier, elements give off an emission spectrum when energized. The light emitted is visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-ray energy (all are part of the electromagnetic spectrum). In 1913, Henry Moseley studied the X-ray part of the emission spectra of elements, and noted that a cha ...
... As described earlier, elements give off an emission spectrum when energized. The light emitted is visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-ray energy (all are part of the electromagnetic spectrum). In 1913, Henry Moseley studied the X-ray part of the emission spectra of elements, and noted that a cha ...
The Atom
... He observed that the mass of reactants before the reaction was equal to the mass of the products after the reaction He concluded that when an chemical reaction occurs, matter is neither created nor destroyed but only changed This idea became known as the Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter ...
... He observed that the mass of reactants before the reaction was equal to the mass of the products after the reaction He concluded that when an chemical reaction occurs, matter is neither created nor destroyed but only changed This idea became known as the Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter ...
IPC – First Semester Exam Review Be able to classify an example
... Element- 1 kind of atom (all the atoms are alike), pure substance, organized on Periodic Table OF ELEMENTS, identified by the atomic ‘protomic’ number ...
... Element- 1 kind of atom (all the atoms are alike), pure substance, organized on Periodic Table OF ELEMENTS, identified by the atomic ‘protomic’ number ...
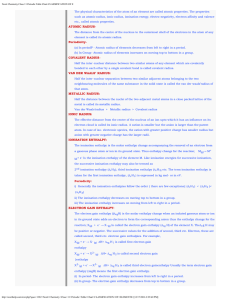
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... Actinides – the bottom row of which only Ac, Th, Pa, and U occur naturally on earth Most of the actinides are synthetic elements formed in particle accelerators Mixed group metals – metals found in the bottom left corner of the p block The most familiar of these metals are Al, Sn, and Pb Pb was used ...
... Actinides – the bottom row of which only Ac, Th, Pa, and U occur naturally on earth Most of the actinides are synthetic elements formed in particle accelerators Mixed group metals – metals found in the bottom left corner of the p block The most familiar of these metals are Al, Sn, and Pb Pb was used ...
Atoms- Building Blocks TG quark.qxd
... holds the atom together. There are different types of atoms with different numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons. They are called elements. An electrically neutral atom has the same number of protons and electrons. Usually an atom has the same number of protons and neutrons but when it has mor ...
... holds the atom together. There are different types of atoms with different numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons. They are called elements. An electrically neutral atom has the same number of protons and electrons. Usually an atom has the same number of protons and neutrons but when it has mor ...
All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons but
... • The nucleus contains most of the mass of the atom because protons and neutrons are far more massive than electrons. • The mass of a proton is about the same as that of a neutron. And the mass of each is about 1,800 times greater than the mass of the electron. • The unit of measurement used for ato ...
... • The nucleus contains most of the mass of the atom because protons and neutrons are far more massive than electrons. • The mass of a proton is about the same as that of a neutron. And the mass of each is about 1,800 times greater than the mass of the electron. • The unit of measurement used for ato ...
Powerpoint slides
... Within each subshell, electrons are grouped into orbitals, regions of space within an atom where the specific electrons are most likely to be found. An s subshell has 1 orbital, a p has 3 orbitals, a d has 5 orbitals, and an f has 7 orbitals. Each orbital holds two electrons which differ in a proper ...
... Within each subshell, electrons are grouped into orbitals, regions of space within an atom where the specific electrons are most likely to be found. An s subshell has 1 orbital, a p has 3 orbitals, a d has 5 orbitals, and an f has 7 orbitals. Each orbital holds two electrons which differ in a proper ...
Text Related to Segment 7.01 ©2002 Claude E. Wintner To make a
... vibrational potential energy vs. nuclear separation, and used as a model for bond strength vs. nuclear separation ...
... vibrational potential energy vs. nuclear separation, and used as a model for bond strength vs. nuclear separation ...
Naming Inorganic Compounds
... • How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of 197Au? • Hydrogen has three isotopes, with mass numbers 1, 2, and 3. Write the complete chemical symbol for each of them. ...
... • How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of 197Au? • Hydrogen has three isotopes, with mass numbers 1, 2, and 3. Write the complete chemical symbol for each of them. ...
CHAPTER 2. THE ELEMENTS: BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF …
... protons in its nucleus • Atomic number Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and, therefore, different masses • Isotopes are represented by special symbols: Mass number ...
... protons in its nucleus • Atomic number Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and, therefore, different masses • Isotopes are represented by special symbols: Mass number ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _C__ 36) Which of the following pairs of elements is most likely to form an ionic compound? a. chlorine and oxygen c. aluminum and chlorine (ionic is metal and nonmetal) ...
... _C__ 36) Which of the following pairs of elements is most likely to form an ionic compound? a. chlorine and oxygen c. aluminum and chlorine (ionic is metal and nonmetal) ...
sample
... Candles and mice Around the same time as Brand’s discovery of phosphorus, John Mayow was experimenting with air. He published his results in 1668. In one experiment, Mayow put a lighted candle in a dish of water and covered it with an upturned jar. The flame eventually went out, and water rose a lit ...
... Candles and mice Around the same time as Brand’s discovery of phosphorus, John Mayow was experimenting with air. He published his results in 1668. In one experiment, Mayow put a lighted candle in a dish of water and covered it with an upturned jar. The flame eventually went out, and water rose a lit ...
15.2 Electrons and Chemical Bonds
... Hydrogen is Because of its single electron, hydrogen can also have 0 valence special electrons! Zero is a magic number for hydrogen, as well as 2. This ...
... Hydrogen is Because of its single electron, hydrogen can also have 0 valence special electrons! Zero is a magic number for hydrogen, as well as 2. This ...
ch14
... Zeff increases for the larger 3A elements due to poor shielding by d and f electrons. The larger 3A elements have smaller atomic radii and larger ionization energies than electronegativities than expected. These properties influence the physical and chemical behavior of these elements. ...
... Zeff increases for the larger 3A elements due to poor shielding by d and f electrons. The larger 3A elements have smaller atomic radii and larger ionization energies than electronegativities than expected. These properties influence the physical and chemical behavior of these elements. ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... o A nucleus – a central region that is positively charged and contains most of the mass - protons are heavy positive particles within the nucleus o Electrons – particles with a negative charge and are very light (compared to protons). - Electrons circle around the nucleus o Empty space surrounding t ...
... o A nucleus – a central region that is positively charged and contains most of the mass - protons are heavy positive particles within the nucleus o Electrons – particles with a negative charge and are very light (compared to protons). - Electrons circle around the nucleus o Empty space surrounding t ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... Molecular elements: elements that naturally occur in combinations of 2-3 atoms. Ex: H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, P4, S8 Compound: when two or more elements are chemically combined together. o They can’t be separated by ordinary physical means o Fixed ratio of elements/never change o e.g., water (H2O) an ...
... Molecular elements: elements that naturally occur in combinations of 2-3 atoms. Ex: H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, P4, S8 Compound: when two or more elements are chemically combined together. o They can’t be separated by ordinary physical means o Fixed ratio of elements/never change o e.g., water (H2O) an ...
Developing the atomic model worksheet (student)
... This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. ...
... This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. ...
Alpha Decay Alpha decay can most simply be described like this: 1
... Gamma radiation ( ) is the emission of high energy photons in the range of 10-10 m, with no matter associated with it. Gamma rays are normally the by-products of other alpha or beta emissions. Gamma rays have no effect on either mass or charge, gamma rays only stabilize the nucleus by releasing some ...
... Gamma radiation ( ) is the emission of high energy photons in the range of 10-10 m, with no matter associated with it. Gamma rays are normally the by-products of other alpha or beta emissions. Gamma rays have no effect on either mass or charge, gamma rays only stabilize the nucleus by releasing some ...