Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... a. Draw Lewis structure of the compound. a. Count # of bonding pairs (central atom / terminal atoms). a. Count # of lone pairs (nonbonding); (around the central atoms ONLY) a. Look at the tables 10.1 and 10.2 (pages 369 and 375, respectively) in the textbook and figure out the electron bonding pair ...
... a. Draw Lewis structure of the compound. a. Count # of bonding pairs (central atom / terminal atoms). a. Count # of lone pairs (nonbonding); (around the central atoms ONLY) a. Look at the tables 10.1 and 10.2 (pages 369 and 375, respectively) in the textbook and figure out the electron bonding pair ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii) Unit IV: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond: bond parameters. Lewis structure ...
... anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii) Unit IV: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond: bond parameters. Lewis structure ...
Chem 105 Final Exam
... Your answer:______________ 39. The correct order of increasing electronegativity is ______________ . a) As < Ga < K < Cs b) Cs < K < Ga < As c) Ga < As < K < Cs d) K < Ga < As < Cs Your answer:______________ 40. List the following atoms and ions in an order of increasing atomic size: K+, Cl-, Ar, Ca ...
... Your answer:______________ 39. The correct order of increasing electronegativity is ______________ . a) As < Ga < K < Cs b) Cs < K < Ga < As c) Ga < As < K < Cs d) K < Ga < As < Cs Your answer:______________ 40. List the following atoms and ions in an order of increasing atomic size: K+, Cl-, Ar, Ca ...
Textbook Answer Keys - Mr. Massey`s Chemistry Pages
... 7. B; the series of lines found in the visible region of the spectrum is called the Balmer series; they are associated with electronic transitions from upper energy levels down to the n = 2 energy level; 8. D; the line emission spectrum of hydrogen provides evidence for the existence of electron in ...
... 7. B; the series of lines found in the visible region of the spectrum is called the Balmer series; they are associated with electronic transitions from upper energy levels down to the n = 2 energy level; 8. D; the line emission spectrum of hydrogen provides evidence for the existence of electron in ...
Electronic Structure and Exchange Integrals of Low
... The essential di erence between all these cuprates composed of copper-oxygen plaquettes is the varying connection between the plaquettes. Corresponding to the connection, these compounds can be classi ed as zero-, one-, two- and threedimensional systems with respect to the electronic structure (see ...
... The essential di erence between all these cuprates composed of copper-oxygen plaquettes is the varying connection between the plaquettes. Corresponding to the connection, these compounds can be classi ed as zero-, one-, two- and threedimensional systems with respect to the electronic structure (see ...
class XI CHEMISTRY - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Harni Road
... should contain equal number of molecules. Dalton's Atomic Theory All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and otherproperties. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atom is the smallest u ...
... should contain equal number of molecules. Dalton's Atomic Theory All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and otherproperties. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atom is the smallest u ...
class XI CHEMISTRY - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Ichhanath Surat
... should contain equal number of molecules. Dalton's Atomic Theory All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and otherproperties. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atom is the smallest u ...
... should contain equal number of molecules. Dalton's Atomic Theory All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and otherproperties. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atom is the smallest u ...
Building Geometrical Models for Biological Molecules
... translation, a rotation, or a combination of both. So let R3 be a group of translations and SO(3) = {A ∈ R3×3 | AT A = I and detA = 1} be the set of rotation matrices where AT denotes the transpose of a matrix A. It is easy to check that SO(3) is a group. Also note that for A ∈ SO(3), AT A = AAT = I ...
... translation, a rotation, or a combination of both. So let R3 be a group of translations and SO(3) = {A ∈ R3×3 | AT A = I and detA = 1} be the set of rotation matrices where AT denotes the transpose of a matrix A. It is easy to check that SO(3) is a group. Also note that for A ∈ SO(3), AT A = AAT = I ...
Chem 150 Unit 2 - Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
... single bonds. • Every carbon atom participates in 4 single bonds, either to another carbon or to a hydrogen. • Every hydrogen atom is bonded to a carbon by a single bond. ...
... single bonds. • Every carbon atom participates in 4 single bonds, either to another carbon or to a hydrogen. • Every hydrogen atom is bonded to a carbon by a single bond. ...
Here
... (e) Gibbs free energy, G = H − TS, combines enthalpy and entropy to give a quantity which must decrease for any processes that actually happens. (f) Lewisite is a chlorinate alkyl arsenic compound which was produced as a chemical weapon causing blisters and lung irritation. (g) A Lewis base ...
... (e) Gibbs free energy, G = H − TS, combines enthalpy and entropy to give a quantity which must decrease for any processes that actually happens. (f) Lewisite is a chlorinate alkyl arsenic compound which was produced as a chemical weapon causing blisters and lung irritation. (g) A Lewis base ...
the chemistry of life: organic and biological chemistry
... The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Although biological systems are almost unimaginably complex, they are nevertheless constructed of molecules of quite modest size, put together in nature to form a host of complex, interacting structures. The example of phenylalanine and PKU ill ...
... The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Although biological systems are almost unimaginably complex, they are nevertheless constructed of molecules of quite modest size, put together in nature to form a host of complex, interacting structures. The example of phenylalanine and PKU ill ...
REVIEW and answers
... melting point (bottom right hand side of transition metals). As electrons become less delocalized the metals become harder, more brittle and conduct less well, but their melting and boiling points increase (top left hand side of transition metals). ...
... melting point (bottom right hand side of transition metals). As electrons become less delocalized the metals become harder, more brittle and conduct less well, but their melting and boiling points increase (top left hand side of transition metals). ...
Contributions to Function in Blue Copper Proteins
... photoelectron experiment should be done on relevant active site model complexes rather than the complete protein system. There are two regions of focus in variable energy photoelectron spectroscopy (VEPES) experiments. One involves ionization of core electrons (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, XPS) ...
... photoelectron experiment should be done on relevant active site model complexes rather than the complete protein system. There are two regions of focus in variable energy photoelectron spectroscopy (VEPES) experiments. One involves ionization of core electrons (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, XPS) ...
1.9 M - Thierry Karsenti
... 1. A pure substance: A substance with a definite chemical composition. 2. Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the identify and properties of the element and can take part in a chemical change. 3. Atomic number (symbol Z): the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. 4. Compo ...
... 1. A pure substance: A substance with a definite chemical composition. 2. Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the identify and properties of the element and can take part in a chemical change. 3. Atomic number (symbol Z): the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. 4. Compo ...
CHAPTER I
... The configuration of Be 1s2 2s2.All elements of Group 2A have electron configurations [electrons of preceding rare gas + ns2], where n is the period in which the element is found in the periodic table. At boron (Group ЗА) you first encounter an element in the block of elements on the right side of t ...
... The configuration of Be 1s2 2s2.All elements of Group 2A have electron configurations [electrons of preceding rare gas + ns2], where n is the period in which the element is found in the periodic table. At boron (Group ЗА) you first encounter an element in the block of elements on the right side of t ...
Class-XII, Summer assignment
... 20. What is the basicity of H3PO4? Ans: Three P–OH groups are present in the molecule of H3PO4. Therefore, its basicity is three. 21. Phosphorous in solid state is ionic, why? Ans: In the solid state it exists as an ionic solid, [PCl4]+[PCl6]– in which the cation, [PCl4]+ is tetrahedral and the anio ...
... 20. What is the basicity of H3PO4? Ans: Three P–OH groups are present in the molecule of H3PO4. Therefore, its basicity is three. 21. Phosphorous in solid state is ionic, why? Ans: In the solid state it exists as an ionic solid, [PCl4]+[PCl6]– in which the cation, [PCl4]+ is tetrahedral and the anio ...
Peter Ertl - American Chemical Society
... monovalent, 34% bivalent, 18% trivalent, and 13% have more than 3 connection points. When constructing molecules by combining these “elementary” fragments, one can easily get more than 10100 structures, but most of them would be nonrealistic (not stable, or synthetically inaccessible, at least by cu ...
... monovalent, 34% bivalent, 18% trivalent, and 13% have more than 3 connection points. When constructing molecules by combining these “elementary” fragments, one can easily get more than 10100 structures, but most of them would be nonrealistic (not stable, or synthetically inaccessible, at least by cu ...
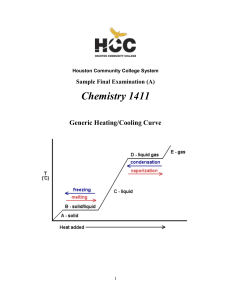
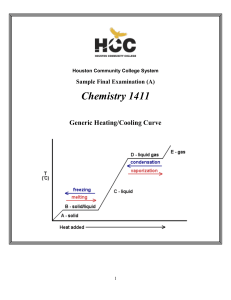
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electrons), but not sp, sp2, or sp3. Furthermore, to form a -bond, we must have unhybridized p-orbitals on the sulfur and oxygen atoms. This p orbital will not be present if the hybridization is sp3, sp3d, or sp3d2. For simp ...
... an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electrons), but not sp, sp2, or sp3. Furthermore, to form a -bond, we must have unhybridized p-orbitals on the sulfur and oxygen atoms. This p orbital will not be present if the hybridization is sp3, sp3d, or sp3d2. For simp ...
Bent's rule

Bent's rule describes and explains the relationship between the isovalent hybridization of central atoms in molecules and the electronegativities of substituents. The rule was stated by Henry Bent as follows: ""Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed toward electropositive substituents"".The chemical structure of a molecule is intimately related to its properties and reactivity. Valence bond theory proposes that molecular structures are due to covalent bonds between the atoms and that each bond consists of two overlapping and typically hybridised atomic orbitals. Traditionally, p-block elements in molecules are assumed to hybridise strictly as spn, where n is either 1, 2, or 3. In addition, the hybrid orbitals are all assumed to be equivalent (i.e. the n+1 spn orbitals have the same p character). Results from this approach are usually good, but they can be improved upon by allowing hybridised orbitals with noninteger and unequal p character. Bent's rule provides a qualitative estimate as to how these hybridised orbitals should be constructed. Bent's rule is that in a molecule, a central atom bonded to multiple groups will hybridise so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards electropositive groups, while orbitals with more p character will be directed towards groups that are more electronegative. By removing the assumption that all hybrid orbitals are equivalent spn orbitals, better predictions and explanations of properties such as molecular geometry and bond strength can be obtained.Bent's rule can be generalized to d-block elements as well. The hybridisation of a metal center is arranged so that orbitals with more s character are directed towards ligands that form bonds with more covalent character. Equivalently, orbitals with more d character are directed towards groups that form bonds of greater ionic character.