PCSD General Chemistry Pacing Guide
... Use heating curves to describe phase changes Use phase diagrams to predict the phase of a substance at certain temperatures and pressures ...
... Use heating curves to describe phase changes Use phase diagrams to predict the phase of a substance at certain temperatures and pressures ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Usually involve transition metals and common ligands (see below). Since many complex ion reactions occur with the addition of an excess of a substance containing the ligand, also watch for the terms excess and concentrated in the problem. Common complex ion metals (Lewis acids) are: Fe, Co, Ni, Cr, ...
... Usually involve transition metals and common ligands (see below). Since many complex ion reactions occur with the addition of an excess of a substance containing the ligand, also watch for the terms excess and concentrated in the problem. Common complex ion metals (Lewis acids) are: Fe, Co, Ni, Cr, ...
Chemistry A - Montgomery County Public Schools
... describe the characteristics of protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of location, charge and mass. illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, and charge to ident ...
... describe the characteristics of protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of location, charge and mass. illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, and charge to ident ...
February Homework Packet
... Matter can be a in the solid, liquid, or gas phase Chemistry is the study of the change in matter Physical changes are changes in matter in which the appearance of a substance changes but the identity of the compound remains the same Chemical changes are changes in matter in which the identi ...
... Matter can be a in the solid, liquid, or gas phase Chemistry is the study of the change in matter Physical changes are changes in matter in which the appearance of a substance changes but the identity of the compound remains the same Chemical changes are changes in matter in which the identi ...
Chemical Synthesis Using Earth-Abundant Metal
... therefore replace catalysts made of precious metals for at least certain chemical processes. It would be additionally beneficial if these catalysts also permitted energy-intensive processes to occur at lower temperature, thereby lowering the carbon footprint of the chemical industry as a whole. ...
... therefore replace catalysts made of precious metals for at least certain chemical processes. It would be additionally beneficial if these catalysts also permitted energy-intensive processes to occur at lower temperature, thereby lowering the carbon footprint of the chemical industry as a whole. ...
Spectra and Atomic Structure
... Absorption can boost an electron to the second (or higher) excited state Two ways to decay: 1. to ground state ...
... Absorption can boost an electron to the second (or higher) excited state Two ways to decay: 1. to ground state ...
Quantum Chemistry Predicts Multiply Bonded Diuranium
... relativistic effects. This was done using the second-order DouglasKroll-Hess (DKH) Hamiltonian. The scalar part of this Hamiltonian was used in the generation of the CASSCF/CASPT2 wave functions. Spin-orbit (SO) coupling was not included in the present study. It will have only a minor effects on the ...
... relativistic effects. This was done using the second-order DouglasKroll-Hess (DKH) Hamiltonian. The scalar part of this Hamiltonian was used in the generation of the CASSCF/CASPT2 wave functions. Spin-orbit (SO) coupling was not included in the present study. It will have only a minor effects on the ...
Atomic Structure PPQs 2
... Gallium chloride dissolves in water to form a solution containing ions. Suggest an experiment to show that the solution contains ions. State the result you would expect. Experiment ....................................................................................................... ...
... Gallium chloride dissolves in water to form a solution containing ions. Suggest an experiment to show that the solution contains ions. State the result you would expect. Experiment ....................................................................................................... ...
Exam 1 Review
... Questions that may appear on the exam: Calculate ΔH using: Hess’s Law, heats of formation, bond dissociation energies Given ΔH for a reaction, how much heat is released when 20 g of product is formed? (hint – use the balanced chemical equation to solve) Find heat needed to change water at 20 °C to s ...
... Questions that may appear on the exam: Calculate ΔH using: Hess’s Law, heats of formation, bond dissociation energies Given ΔH for a reaction, how much heat is released when 20 g of product is formed? (hint – use the balanced chemical equation to solve) Find heat needed to change water at 20 °C to s ...
IGCSE Revision Guide (Double Award) | PDF
... Say that electrolysis is the formation of new compounds when ionic compounds conduct electricity and be able to write chemical equations for these processes. Describe simple experiments for the electrolysis ...
... Say that electrolysis is the formation of new compounds when ionic compounds conduct electricity and be able to write chemical equations for these processes. Describe simple experiments for the electrolysis ...
KISS Notes
... From these 3 patterns of reaction, it seems there is a further, underlying pattern. Certain metals, like sodium, always seem to react readily and vigorously. Others, like copper, always react slowly or not at all. ...
... From these 3 patterns of reaction, it seems there is a further, underlying pattern. Certain metals, like sodium, always seem to react readily and vigorously. Others, like copper, always react slowly or not at all. ...
Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Which of the following molecules have a dipole moment? H2O, CO2, SO2, and CH4 ...
... Which of the following molecules have a dipole moment? H2O, CO2, SO2, and CH4 ...
Detailed characterization of anodic bonding process between glass
... nents from damage, the bonding performance of the thinfilm coated Si substrates at lower voltages is also given in Table 2. 3.4. Effect of glass properties The TCE of Fisher slide is very different from that of Si. So when they were bonded at high temperature Ž3008C., in spite of similar bonding tim ...
... nents from damage, the bonding performance of the thinfilm coated Si substrates at lower voltages is also given in Table 2. 3.4. Effect of glass properties The TCE of Fisher slide is very different from that of Si. So when they were bonded at high temperature Ž3008C., in spite of similar bonding tim ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... The numbering system for groups in the periodic table is shown in the Chemistry data booklet. Students should also be aware of the position of the transition elements in the periodic table. Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table u ...
... The numbering system for groups in the periodic table is shown in the Chemistry data booklet. Students should also be aware of the position of the transition elements in the periodic table. Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table u ...
mark scheme - A-Level Chemistry
... * when checking for best fit, candidate’s line must go through the origin ± one square. Extend candidate’s line if necessary ...
... * when checking for best fit, candidate’s line must go through the origin ± one square. Extend candidate’s line if necessary ...
Answer Key
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
Naming Binary Inorganic Compounds
... Naming of Compounds that contain Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions are ___________ molecules. The atoms within a polyatomic ion are usually very tightly bound together, so the ion retains its identity within ionic compounds and over the course of many chemical reactions. o o o o ...
... Naming of Compounds that contain Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions are ___________ molecules. The atoms within a polyatomic ion are usually very tightly bound together, so the ion retains its identity within ionic compounds and over the course of many chemical reactions. o o o o ...
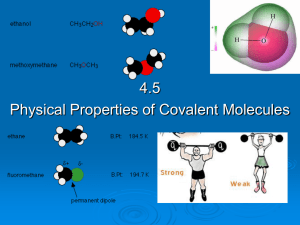
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... decreases. E.g. Individual amino acids are soluble in water but large protein polymers are generally insoluble. As the non-polar hydrocarbon chain of a polar molecule increases, the solubility of the molecule decreases because the non-polar carbon chain outweighs the polar part. E.g. ethanol (CH3CH2 ...
... decreases. E.g. Individual amino acids are soluble in water but large protein polymers are generally insoluble. As the non-polar hydrocarbon chain of a polar molecule increases, the solubility of the molecule decreases because the non-polar carbon chain outweighs the polar part. E.g. ethanol (CH3CH2 ...
Chemistry Final Test 1999-2000 - Nashoba Valley Technical High
... 18) The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Which of the following lists these types of radiation from lest dangerous to most dangerous? A. alpha, gamma, beta B. beta, alpha, gamma C. alpha, beta, gamma D. gamma, beta, alpha 19) Which of the following statements correct ...
... 18) The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Which of the following lists these types of radiation from lest dangerous to most dangerous? A. alpha, gamma, beta B. beta, alpha, gamma C. alpha, beta, gamma D. gamma, beta, alpha 19) Which of the following statements correct ...
Matter - tompkinsmath
... a) Elements – substances composed of only one kind of atom which cannot be broken down using heat or electricity. Ex. Na, Br, O2, S8 b) Compounds – substances composed of 2 or more kinds of atoms and can be decomposed using heat or electricity. Ex. H2O, NaCl, C12H22O11 Mixtures – mixtures of pure su ...
... a) Elements – substances composed of only one kind of atom which cannot be broken down using heat or electricity. Ex. Na, Br, O2, S8 b) Compounds – substances composed of 2 or more kinds of atoms and can be decomposed using heat or electricity. Ex. H2O, NaCl, C12H22O11 Mixtures – mixtures of pure su ...
Chapter 2
... • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
... • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
Week 8 - Day 3 (End of Chapter 6)
... Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but it does not give good numerical predictions. ...
... Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but it does not give good numerical predictions. ...
Redox Introduction
... In burning, oxygen unites rapidly with carbon to form CO2. Observation of these reactions gave rise to the terms "slow" and "rapid" oxidation. Chemists recognize, however, that other nonmetallic elements unite with substances in a manner similar to that of oxygen. – Hydrogen, antimony, and sodium al ...
... In burning, oxygen unites rapidly with carbon to form CO2. Observation of these reactions gave rise to the terms "slow" and "rapid" oxidation. Chemists recognize, however, that other nonmetallic elements unite with substances in a manner similar to that of oxygen. – Hydrogen, antimony, and sodium al ...
Chapter 2 PPT - Richsingiser.com
... empirical formula that uses the smallest whole number subscripts to express the relative numbers of ions. • The relative numbers of ions in the empirical formula balances the charges to zero. • The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, because the 1+ ions have to be present in a 1:1 ...
... empirical formula that uses the smallest whole number subscripts to express the relative numbers of ions. • The relative numbers of ions in the empirical formula balances the charges to zero. • The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, because the 1+ ions have to be present in a 1:1 ...