Section 8.10 Lewis Structures
... • Property of a molecule whose charge distribution can be represented by a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge. • Use an arrow to represent a dipole moment. Point to the negative charge center with the tail of the arrow indicating the positive center of charge. ...
... • Property of a molecule whose charge distribution can be represented by a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge. • Use an arrow to represent a dipole moment. Point to the negative charge center with the tail of the arrow indicating the positive center of charge. ...
Periodic table Periodic Trends
... Based on Bohr’s model of the atom, we would be able to easily measure the radius of an element. • However, Bohr’s model of an atom was too simplistic and electrons are not fixed in orbit around nucleus. • They are found in orbitals (regions of space) where there is a high probability of finding an e ...
... Based on Bohr’s model of the atom, we would be able to easily measure the radius of an element. • However, Bohr’s model of an atom was too simplistic and electrons are not fixed in orbit around nucleus. • They are found in orbitals (regions of space) where there is a high probability of finding an e ...
Chemical Equations
... Balancing Chemical Equations • Write a word equation for the reaction. • Write the correct formulas for all reactants and products. • Determine the coefficients that make the equation balance. ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations • Write a word equation for the reaction. • Write the correct formulas for all reactants and products. • Determine the coefficients that make the equation balance. ...
The Physics of Metal Clusters - Nano
... shows a comparison between the experimental abundance spectrum and ∆2 for Na clusters. The peaks in ∆2 coincide with the discontinuities in the mass spectra. This result represented the first confirmation of cluster shell structure and of the appropriateness of the jellium approach. The jellium mode ...
... shows a comparison between the experimental abundance spectrum and ∆2 for Na clusters. The peaks in ∆2 coincide with the discontinuities in the mass spectra. This result represented the first confirmation of cluster shell structure and of the appropriateness of the jellium approach. The jellium mode ...
Atomic Theory - Relativistic quantum dynamics of ions and beams
... 1.2. Atomic theory Covers a very wide range of many-body methods and techniques, from the simple shell model of the atom to various semi-empirical method to mean-field approaches ... and up to ab-initio and quantum-field theories. The aim of ab-initio atomic structure and collision theory is to descri ...
... 1.2. Atomic theory Covers a very wide range of many-body methods and techniques, from the simple shell model of the atom to various semi-empirical method to mean-field approaches ... and up to ab-initio and quantum-field theories. The aim of ab-initio atomic structure and collision theory is to descri ...
mark scheme - A-Level Chemistry
... – the ideas are expressed with reasonable clarity but with a few errors of grammar, punctuation and spelling – valid points but not clearly linked to an argument structure – limited use of information or ideas about chemistry ...
... – the ideas are expressed with reasonable clarity but with a few errors of grammar, punctuation and spelling – valid points but not clearly linked to an argument structure – limited use of information or ideas about chemistry ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
... solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
Chapter 2a
... (a) Formation of four single covalent bonds: carbon shares four electron pairs with four hydrogen atoms. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... (a) Formation of four single covalent bonds: carbon shares four electron pairs with four hydrogen atoms. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Inserting Two Atoms into a Single Optical Micropotential
... different potential wells, radiative escape is not possible and the atoms remain trapped [18]. Detecting the absence of the pair of atoms after the optical molasses stage thus confirms the successful joining of the two atoms in one potential well of the HDT. In order to independently examine the dyn ...
... different potential wells, radiative escape is not possible and the atoms remain trapped [18]. Detecting the absence of the pair of atoms after the optical molasses stage thus confirms the successful joining of the two atoms in one potential well of the HDT. In order to independently examine the dyn ...
Using Models - Pleasant Valley School District
... anot aproducts. molecule substance. towritten produce of the of chlorine gas. (Coefficients reactants ofare one and are the out.) 1 Na is bonded (Subscripts They Two tomolecules determine reactants 1 Cl of to one make of and the are sodium asubstance products. not molecule written chloride. itself. ...
... anot aproducts. molecule substance. towritten produce of the of chlorine gas. (Coefficients reactants ofare one and are the out.) 1 Na is bonded (Subscripts They Two tomolecules determine reactants 1 Cl of to one make of and the are sodium asubstance products. not molecule written chloride. itself. ...
Atoms - York University
... solar system with the nucleus as the “sun” and the electrons as “planets.” Problem: If so, why did the electrons not all spiral into the nucleus and radiate energy continuously? ...
... solar system with the nucleus as the “sun” and the electrons as “planets.” Problem: If so, why did the electrons not all spiral into the nucleus and radiate energy continuously? ...
Time-Dependent Electron Interactions in Double
... During autoionization, energy is transferred from one electron to the other, creating free electrons and tightly bound Rydberg ions which do not undergo FI to Ba2þ . The principal goal of the experiments is to determine at what time(s), for different initial DRW configurations, energy transfer occur ...
... During autoionization, energy is transferred from one electron to the other, creating free electrons and tightly bound Rydberg ions which do not undergo FI to Ba2þ . The principal goal of the experiments is to determine at what time(s), for different initial DRW configurations, energy transfer occur ...
Chapter 4 - Colby College Wiki
... of a hydrobromic acid solution with an unknown concentration. If it takes 17.8 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition ...
... of a hydrobromic acid solution with an unknown concentration. If it takes 17.8 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition ...
When did atoms begin to do any explanatory work in
... the law of constant proportions, and came into its own with the discovery of isomerism in the third decade of the 19th century. But they must take account of the fact that even at the end of the century, several prominent scientists maintained the antiatomist stance, and it seems to me that Pierre D ...
... the law of constant proportions, and came into its own with the discovery of isomerism in the third decade of the 19th century. But they must take account of the fact that even at the end of the century, several prominent scientists maintained the antiatomist stance, and it seems to me that Pierre D ...
physical setting chemistry
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
Electron-pair center-of-mass-motion densities of atoms in position
... momentum space, however, it has been shown @4# that major contributions to the intracule density h̄( v ) come from pairs of valence spin orbitals. Equation ~13b! appears more often for these spin-orbital pairs, and therefore we expect that in momentum space the behaviors of the extracule d̄( P) and ...
... momentum space, however, it has been shown @4# that major contributions to the intracule density h̄( v ) come from pairs of valence spin orbitals. Equation ~13b! appears more often for these spin-orbital pairs, and therefore we expect that in momentum space the behaviors of the extracule d̄( P) and ...
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... The smaller spaces between colored lines, however, suggested that there were enough. The many-electron problem called for a new model to explain smaller energy differences within energy levels. It was fairly straightforward modify Bohr’s model to include theanother idea spectra of all types of atoms ...
... The smaller spaces between colored lines, however, suggested that there were enough. The many-electron problem called for a new model to explain smaller energy differences within energy levels. It was fairly straightforward modify Bohr’s model to include theanother idea spectra of all types of atoms ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... shown in the table at the end of this work sheet. There is no easy way to figure these out. If you know the charges on the ions comprising an ionic compound you can predict the empirical formula by taking the smallest number of cations and anions that would add to a charge of zero. For example, the ...
... shown in the table at the end of this work sheet. There is no easy way to figure these out. If you know the charges on the ions comprising an ionic compound you can predict the empirical formula by taking the smallest number of cations and anions that would add to a charge of zero. For example, the ...
Q1. This question is about the structure of atoms. (a) Choose words
... Apart from the gases normally in the atmosphere, which two gases would be at X? ..................................................... and ........................................................... ...
... Apart from the gases normally in the atmosphere, which two gases would be at X? ..................................................... and ........................................................... ...
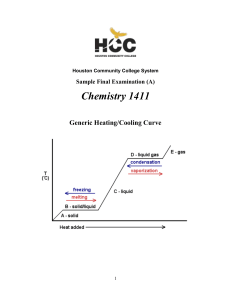
1411FINALSAMPLEs and Key
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.