Document
... By removing H+ ions from the solution, this reaction causes more CH3COOH molecules to ionize, producing more H+ to react with more NH3 and so on. Soon all the CH3COOH molecules ionize, and the neutralization goes to completion: ...
... By removing H+ ions from the solution, this reaction causes more CH3COOH molecules to ionize, producing more H+ to react with more NH3 and so on. Soon all the CH3COOH molecules ionize, and the neutralization goes to completion: ...
the Language of Chemistry
... Basic radical: The radical carrying positive charge is called basic radical. It is also called electropositive radical or cation. The radicals having a unit positive (+) charge are called monovalent basic radicals. The radicals having two units of positive (2+) charge are called divalent radicals. ...
... Basic radical: The radical carrying positive charge is called basic radical. It is also called electropositive radical or cation. The radicals having a unit positive (+) charge are called monovalent basic radicals. The radicals having two units of positive (2+) charge are called divalent radicals. ...
Electron Dynamics on Surfaces and Nanostructures November 05
... alternative [1,2] to the standard silicon-based cells. The development of these devices relies on the latest advances in materials science, which ultimately require in-depth knowledge of the interaction of atoms and molecules deposited on surfaces when they are exposed to the interaction with light: ...
... alternative [1,2] to the standard silicon-based cells. The development of these devices relies on the latest advances in materials science, which ultimately require in-depth knowledge of the interaction of atoms and molecules deposited on surfaces when they are exposed to the interaction with light: ...
DEVELOPMENT, IMPLEMENTATION AND APPLICATION OF ELECTRONIC STRUCTURAL DESCRIPTORS TO THE
... At the outset of the 21st century, theoretical and computational chemistry has arrived at a position of central importance in chemistry.1 The algorithms of calculation are being improved, making calculations that were prohibitive feasible and with accuracies sometimes competing with experimental one ...
... At the outset of the 21st century, theoretical and computational chemistry has arrived at a position of central importance in chemistry.1 The algorithms of calculation are being improved, making calculations that were prohibitive feasible and with accuracies sometimes competing with experimental one ...
Final Exam Review Packet
... 5. - The molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule of a compound. - The formula weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a formula unit. - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quanti ...
... 5. - The molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule of a compound. - The formula weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a formula unit. - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quanti ...
POGIL.CH7B.Tro
... INSTRUCTIONS: Complete the worksheet with your group using a black or blue pen or pencil. Be prepared to share your answers. When answered are shared with the rest of the class, use only a red pen. 1. What are the characteristic shapes of s, p, and d orbitals that distinguish them from each other? 2 ...
... INSTRUCTIONS: Complete the worksheet with your group using a black or blue pen or pencil. Be prepared to share your answers. When answered are shared with the rest of the class, use only a red pen. 1. What are the characteristic shapes of s, p, and d orbitals that distinguish them from each other? 2 ...
Types of Aqueous Reactions
... Group 1A salts are all soluble. All salts containing nitrates, ammonium, chlorate, perchlorate, and acetate are soluble. All Cl, Br, I salts are soluble EXCEPT for Ag, Pb, and Hg22+ salts All sulfates are soluble EXCEPT Pb, Ca, Ag, Sr, Hg22+ and Ba Metal hydroxides are INSOLUBLE except for those of ...
... Group 1A salts are all soluble. All salts containing nitrates, ammonium, chlorate, perchlorate, and acetate are soluble. All Cl, Br, I salts are soluble EXCEPT for Ag, Pb, and Hg22+ salts All sulfates are soluble EXCEPT Pb, Ca, Ag, Sr, Hg22+ and Ba Metal hydroxides are INSOLUBLE except for those of ...
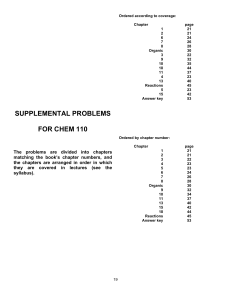
SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEMS FOR CHEM 110
... 0.0100 mole of dry, solid KClO3 is added to 50.0 g of water at 20.10°C in a coffee–cup calorimeter. The temperature is observed to drop to 18.10°C. ΔH of hydration for one mole of KClO3 is (within 2%) [Heat capacity of water = 4.18 J/°C g] A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 0.0100 mole of dry, solid KClO3 is added to 50.0 g of water at 20.10°C in a coffee–cup calorimeter. The temperature is observed to drop to 18.10°C. ΔH of hydration for one mole of KClO3 is (within 2%) [Heat capacity of water = 4.18 J/°C g] A. B. C. D. E. ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are technically defined as any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of the participating atom, ion, or molecule of a chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynth ...
... Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are technically defined as any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of the participating atom, ion, or molecule of a chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynth ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Composition
... • One amu is one-twelfth of the mass of a 12C atom • One amu is close to the mass of one proton or one neutron. • One amu is a very small mass – 1.66 x 10-24 g • One mole is 6.022 x 1023 units of anything • One mole (of atoms) of an element will have a mass in grams equal to the mass in amu of one a ...
... • One amu is one-twelfth of the mass of a 12C atom • One amu is close to the mass of one proton or one neutron. • One amu is a very small mass – 1.66 x 10-24 g • One mole is 6.022 x 1023 units of anything • One mole (of atoms) of an element will have a mass in grams equal to the mass in amu of one a ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Elements of Chemical Change
... b. Write the correct formulas for any compounds and check for diatomic molecules. (Some elements never exist as single atoms but only as diatomic molecules. These elements can be identified from their names, which end in -gen or -ine. The common diatomic molecules are hydrogen (H2), nitrogen (N2), o ...
... b. Write the correct formulas for any compounds and check for diatomic molecules. (Some elements never exist as single atoms but only as diatomic molecules. These elements can be identified from their names, which end in -gen or -ine. The common diatomic molecules are hydrogen (H2), nitrogen (N2), o ...
Document
... Check for Understanding Aqueous potassium nitrate and a precipitate of barium chromate are formed when aqueous solutions of barium nitrate and potassium chromate are mixed. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) ...
... Check for Understanding Aqueous potassium nitrate and a precipitate of barium chromate are formed when aqueous solutions of barium nitrate and potassium chromate are mixed. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) ...
Chapter 9
... close to the fluorine. • The electron pair is not shared equally. • This causes the fluorine atom to have a slight excess of negative charge and leaves the hydrogen atom partially positive. • This is exactly the bond polarity observed for HF. ...
... close to the fluorine. • The electron pair is not shared equally. • This causes the fluorine atom to have a slight excess of negative charge and leaves the hydrogen atom partially positive. • This is exactly the bond polarity observed for HF. ...
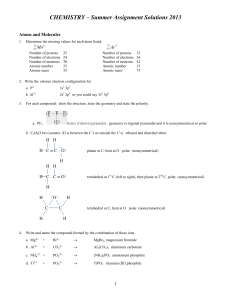
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... Wrote the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass and similar properties. Left gaps where necessary in order to line-up families with similar properties. Predicted products of missing elements that, when discovered, would fill-in the gaps ...
... Wrote the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass and similar properties. Left gaps where necessary in order to line-up families with similar properties. Predicted products of missing elements that, when discovered, would fill-in the gaps ...
Slide 1
... When gasoline burns these atoms react with oxygen atoms in air to form carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O). The original atoms of gasoline are not destroyed but become rearranged. ...
... When gasoline burns these atoms react with oxygen atoms in air to form carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O). The original atoms of gasoline are not destroyed but become rearranged. ...
Electron spectroscopy of atoms and molecules using synchrotron
... Electron spectroscopy analyzes the electrons emitted or scattered by the studied sample when bombarded using excitation beams (electron or photon) and it is based on two physical phenomena, the photoelectric effect and the Auger process. Both phenomena where discovered in the early 20th century, when ...
... Electron spectroscopy analyzes the electrons emitted or scattered by the studied sample when bombarded using excitation beams (electron or photon) and it is based on two physical phenomena, the photoelectric effect and the Auger process. Both phenomena where discovered in the early 20th century, when ...
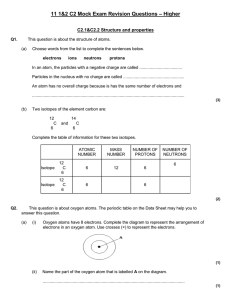
Atomic Structure
... In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe a method for making pure crystals of magnesium chloride from magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. In your method you should name the apparatus you wil ...
... In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe a method for making pure crystals of magnesium chloride from magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. In your method you should name the apparatus you wil ...
92, 054101 (2004)
... condensed and noncondensed atoms change dramatically. In Fig. 5, we plot the temporal evolution of the density distributions of condensed atoms as well as noncondensed atoms. In the stable regime, the condensate density oscillates regularly with time and shows a clear beating pattern [Fig. 5(a)], wh ...
... condensed and noncondensed atoms change dramatically. In Fig. 5, we plot the temporal evolution of the density distributions of condensed atoms as well as noncondensed atoms. In the stable regime, the condensate density oscillates regularly with time and shows a clear beating pattern [Fig. 5(a)], wh ...
Simulations of prompt many-body ionization in a frozen Rydberg gas Robicheaux
... In Fig. 1, we plot the fraction of atoms ionized versus the separation of atoms for different number of atoms. The solid line is for a pair of atoms. We can compare this result to that reported in Ref. [2] by multiplying the curve in Fig. 1 by a factor of 2 because the fraction of trajectories leadi ...
... In Fig. 1, we plot the fraction of atoms ionized versus the separation of atoms for different number of atoms. The solid line is for a pair of atoms. We can compare this result to that reported in Ref. [2] by multiplying the curve in Fig. 1 by a factor of 2 because the fraction of trajectories leadi ...
One-dimensional Substances
... During the past twenty or thirty years many physicists, chemists, and materials scientists have been excited by low-dimensional solids. One of the motivations was certainly the quest for high-temperature superconductors. In 1964 W. A. Little [1] suggested synthesizing an organic superconductor by ap ...
... During the past twenty or thirty years many physicists, chemists, and materials scientists have been excited by low-dimensional solids. One of the motivations was certainly the quest for high-temperature superconductors. In 1964 W. A. Little [1] suggested synthesizing an organic superconductor by ap ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.