chapter-2 - HCC Learning Web
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons ...
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons ...
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy must be released. b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ...
... 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy must be released. b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ...
Science Olympiad
... (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ionization energy increases due to an increase in atomic radius. ______ ...
... (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ionization energy increases due to an increase in atomic radius. ______ ...
Unit 1
... Special bond—very weak Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule ...
... Special bond—very weak Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule ...
Unit 1
... Special bond—very weak Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule ...
... Special bond—very weak Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule ...
PSI AP Chemistry Name Unit 4: Chemical Bonding MC Review Part
... 78. The liquefied hydrogen halides have the normal boiling points given below. The relatively high boiling point of HF can be correctly explained by which of the following? (A) HF gas is more ideal. (B) HF is the strongest acid. (C) HF molecules have a smaller dipole moment. (D) HF is much less solu ...
... 78. The liquefied hydrogen halides have the normal boiling points given below. The relatively high boiling point of HF can be correctly explained by which of the following? (A) HF gas is more ideal. (B) HF is the strongest acid. (C) HF molecules have a smaller dipole moment. (D) HF is much less solu ...
Chem 121 QU 78 Due in lecture
... →__________________________________________________________________________ Write the electron configuration diagram on the above blank↑ → n = _______ l = _______ Write the 2 quantum numbers for an electron indicated by the above arrow. ...
... →__________________________________________________________________________ Write the electron configuration diagram on the above blank↑ → n = _______ l = _______ Write the 2 quantum numbers for an electron indicated by the above arrow. ...
Atomic Structure. Chemical Bonds.
... Outer shells lack 1 electron tendency to pick up such an electron through the strong attraction of the poorly shielded nuclear charge. Metals and Nonmetals: Metals have 1 or several electrons outside the closed shells combine chemically by losing these electrons to nonmetals Nonmetals lack 1 or ...
... Outer shells lack 1 electron tendency to pick up such an electron through the strong attraction of the poorly shielded nuclear charge. Metals and Nonmetals: Metals have 1 or several electrons outside the closed shells combine chemically by losing these electrons to nonmetals Nonmetals lack 1 or ...
Lecture 2 - MyCourses
... (a) 2D-electron density distribution of Kr atom. (b) Colouring of the electron density distribution of a Kr atom with the values of ELF (colour bar see Fig. 1d). ( c) Full electron 2D-electron density distribution of an ethane molecule. (d) Colouring of the electron density distribution in Fig. 1c w ...
... (a) 2D-electron density distribution of Kr atom. (b) Colouring of the electron density distribution of a Kr atom with the values of ELF (colour bar see Fig. 1d). ( c) Full electron 2D-electron density distribution of an ethane molecule. (d) Colouring of the electron density distribution in Fig. 1c w ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Define what is meant by the term chemical reaction. In the following chemical equation, identify the reactants and the products. 3Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaC2H3O2(aq) In the above chemical equation, what do the symbols (aq) and (s) stand for? What would the symbols (l) ...
... Define what is meant by the term chemical reaction. In the following chemical equation, identify the reactants and the products. 3Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaC2H3O2(aq) In the above chemical equation, what do the symbols (aq) and (s) stand for? What would the symbols (l) ...
Zn + HCl → ZnCl 2 + H2 NaOH + H3PO4 → Na3PO4 + H2O N2 +
... 1) Write all the reactant and product formulas on the left and right side of the equation, respectively. Make sure you have all and that you have written the formulas correctly. Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equat ...
... 1) Write all the reactant and product formulas on the left and right side of the equation, respectively. Make sure you have all and that you have written the formulas correctly. Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equat ...
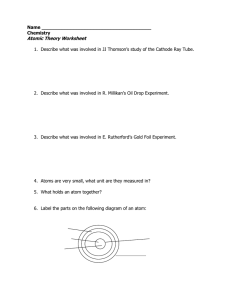
Atomic Theory Worksheet
... 4. Atoms are very small, what unit are they measured in? 5. What holds an atom together? 6. Label the parts on the following diagram of an atom: ...
... 4. Atoms are very small, what unit are they measured in? 5. What holds an atom together? 6. Label the parts on the following diagram of an atom: ...
2014MSC(ORGANIC(CHEMISTRY!
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... 11. Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20; chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17. a. The number of electrons in the outer shell of calcium is ______________. b. The number of electrons in the outer shell of chlorine is ______________. c. In a chemical reaction between these two atoms, _________ ...
... 11. Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20; chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17. a. The number of electrons in the outer shell of calcium is ______________. b. The number of electrons in the outer shell of chlorine is ______________. c. In a chemical reaction between these two atoms, _________ ...
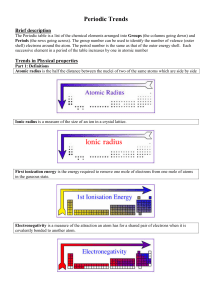
Topic 3 Periodicity notes SL - Chemical Minds
... i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus and the negative electrons in the electron shells orbiting the nucleus and ii) the valence electrons are shielded by the inner electron shells Shielding means that there is an increase in electron-elec ...
... i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus and the negative electrons in the electron shells orbiting the nucleus and ii) the valence electrons are shielded by the inner electron shells Shielding means that there is an increase in electron-elec ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... ions; the giant nature of ionic structures (e.g. the cubic lattice of NaCl and MgO). Unless otherwise stated, outer shells only need to be drawn. Usually only the electrons on the product ions need to be shown, but the use of dots and crosses to show which electrons have been transferred from metal ...
... ions; the giant nature of ionic structures (e.g. the cubic lattice of NaCl and MgO). Unless otherwise stated, outer shells only need to be drawn. Usually only the electrons on the product ions need to be shown, but the use of dots and crosses to show which electrons have been transferred from metal ...
2011 Chem Facts Key
... 33. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom when forming a bond with it. Which substance exhibits ionic bonding rather than covalent bonding? CO2 , N2O4, SiO2 , CaBr2 , C6H12O6 34. Lewis Dot Diagrams may be used to represent the formation of polyatomic ions or covalent m ...
... 33. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom when forming a bond with it. Which substance exhibits ionic bonding rather than covalent bonding? CO2 , N2O4, SiO2 , CaBr2 , C6H12O6 34. Lewis Dot Diagrams may be used to represent the formation of polyatomic ions or covalent m ...
CHEMISTRY 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... 3.) What is the total number of atoms in one molecule of C6Hl2O6? 4.) What types of elements when combined would be most likely to form an ionic compound? 5.) What is the ionic charge on the chromium ion in the ionic compound that has the formula Cr2O3? 6.) In a polyatomic ion the -ite ending indica ...
... 3.) What is the total number of atoms in one molecule of C6Hl2O6? 4.) What types of elements when combined would be most likely to form an ionic compound? 5.) What is the ionic charge on the chromium ion in the ionic compound that has the formula Cr2O3? 6.) In a polyatomic ion the -ite ending indica ...
Intermolecular Attractions
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
Take silver atoms with an electron that has a moment of µz = −g e(e
... should have different total spins and then they should respond differently to magnetic fields. In the Stern-Gerlach experiment they send these atoms in the x direction between magnets one above the other, where z is the up/down direction and the magnets have length l (not to be mixed up with the qua ...
... should have different total spins and then they should respond differently to magnetic fields. In the Stern-Gerlach experiment they send these atoms in the x direction between magnets one above the other, where z is the up/down direction and the magnets have length l (not to be mixed up with the qua ...
Chemistry 1 Practice Final Exam - Tutor
... b) A hydrogen atom in the ground state (n = 1) absorbs a 102.6 nm photon. What is the principal quantum number, n, of the excited state after this transition? The energy levels of the H atoms are given by: ...
... b) A hydrogen atom in the ground state (n = 1) absorbs a 102.6 nm photon. What is the principal quantum number, n, of the excited state after this transition? The energy levels of the H atoms are given by: ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.