Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... (1868-1953) :excelled in his experimental designs and conclusions, in addition to research, he also spent much time preparing textbooks so that his student didn’t have to rely so much on lectures ...
... (1868-1953) :excelled in his experimental designs and conclusions, in addition to research, he also spent much time preparing textbooks so that his student didn’t have to rely so much on lectures ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... (1868-1953) :excelled in his experimental designs and conclusions, in addition to research, he also spent much time preparing textbooks so that his student didn’t have to rely so much on lectures ...
... (1868-1953) :excelled in his experimental designs and conclusions, in addition to research, he also spent much time preparing textbooks so that his student didn’t have to rely so much on lectures ...
CHAPTER 25 - CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
... Living or was once living Organic Chemistry - The chemistry of carbon compounds Carbon is well suited for life because it is the most versatile element in terms of bonding. ...
... Living or was once living Organic Chemistry - The chemistry of carbon compounds Carbon is well suited for life because it is the most versatile element in terms of bonding. ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... A. Who first arranged the periodic table by atomic mass? Dmitri Mendeleev B. What characteristics did Mendeleev use to place the elements in order when creating the periodic table? Rows - Increasing mass Columns – Similar properties C. What are valence electrons? Electrons in the highest occupied en ...
... A. Who first arranged the periodic table by atomic mass? Dmitri Mendeleev B. What characteristics did Mendeleev use to place the elements in order when creating the periodic table? Rows - Increasing mass Columns – Similar properties C. What are valence electrons? Electrons in the highest occupied en ...
Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
... P.W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry (broad discussion of the basics for the whole chemistry course). P.A. Cox, Introduction to Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure (Oxford Chemistry Primer – cheap and worth buying, more specialised coverage of much of the course at an easily understood level). W.G. Richa ...
... P.W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry (broad discussion of the basics for the whole chemistry course). P.A. Cox, Introduction to Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure (Oxford Chemistry Primer – cheap and worth buying, more specialised coverage of much of the course at an easily understood level). W.G. Richa ...
Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms and Ions
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds 5. Atoms are indivisible and can not be created or des ...
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds 5. Atoms are indivisible and can not be created or des ...
Chem 1a Review
... Fe2+ has 6 valence electrons, while CN– has a lone pair to donate so it gives 2 electrons; Thus 6 + 6(2) =18; Remember that you don't use the total charge this second method because you have already used the partial charges and these add up to the total charge. Groups that can contribute elect ...
... Fe2+ has 6 valence electrons, while CN– has a lone pair to donate so it gives 2 electrons; Thus 6 + 6(2) =18; Remember that you don't use the total charge this second method because you have already used the partial charges and these add up to the total charge. Groups that can contribute elect ...
Atomic Structure, Eelectronic Bonding, Periodicity, orbitals
... 1. Count the number of electrons brought to the party (element’s group number) 2. For ions we must adjust the number of electrons available. a. Add one e- for each negative charge. b. Subtract one e- for each positive charge. 3. Select a reasonable skeleton a. The least electronegative is the centra ...
... 1. Count the number of electrons brought to the party (element’s group number) 2. For ions we must adjust the number of electrons available. a. Add one e- for each negative charge. b. Subtract one e- for each positive charge. 3. Select a reasonable skeleton a. The least electronegative is the centra ...
Quantum Theory and Electrons as Waves
... If light could have particle-like behavior, then could matter have wave-like behavior? ...
... If light could have particle-like behavior, then could matter have wave-like behavior? ...
Chemistry Claims Unit 1: Alchemy: Matter, Atomic Structure, and
... Combinatino/exchange reactions are the most important/coolest type of chemical reaction. Every substance on the planet is a potential toxin. Most toxic substances have health benefits. There are different ways to compare amounts of a chemical. Fluorine/Iron is the most/least toxic element ...
... Combinatino/exchange reactions are the most important/coolest type of chemical reaction. Every substance on the planet is a potential toxin. Most toxic substances have health benefits. There are different ways to compare amounts of a chemical. Fluorine/Iron is the most/least toxic element ...
The Atomic Theory, and the Structure of Matter
... 4. Catalysts and Reaction Rates A Catalyst is defined as: A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction. Catalyst lower the energy required to break the bonds that hold substances together. Examples include: enzymes (biological catalysts), platinum ...
... 4. Catalysts and Reaction Rates A Catalyst is defined as: A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction. Catalyst lower the energy required to break the bonds that hold substances together. Examples include: enzymes (biological catalysts), platinum ...
a level chemistry - some definitions to learn
... The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The mass of an atom relative to that of the carbon 12 isotope having a value of 12.000 The simplest, whole number, ratio of elements in a compound The exact number of atoms of each element i ...
... The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The mass of an atom relative to that of the carbon 12 isotope having a value of 12.000 The simplest, whole number, ratio of elements in a compound The exact number of atoms of each element i ...
Modern Model of the Atom Student Notes and Assignment
... Each energy sublevel corresponds to an ATOMIC ORBITAL (often referred to as a cloud) ...
... Each energy sublevel corresponds to an ATOMIC ORBITAL (often referred to as a cloud) ...
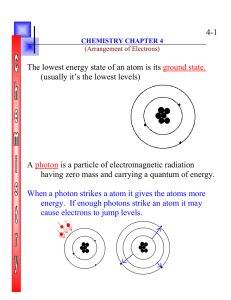
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... This section summarizes the development of atomic theory. It also explains the significance of quantized energies of electrons as they relate to the quan– tum mechanical model of the atom. ...
... This section summarizes the development of atomic theory. It also explains the significance of quantized energies of electrons as they relate to the quan– tum mechanical model of the atom. ...
04 Biochemistry
... • You can draw an atom by showing how electrons are arranged in each energy level. • Electrons move around the energy levels (aka “electron shells” or “electron orbitals”) outside the nucleus rapidly to form an electron cloud ...
... • You can draw an atom by showing how electrons are arranged in each energy level. • Electrons move around the energy levels (aka “electron shells” or “electron orbitals”) outside the nucleus rapidly to form an electron cloud ...
Sample Exam 1 Key
... c) aluminum d) boron 5. These two elements follow a “duet” rather than an octet rule. What are they? a) helium and neon b) hydrogen and helium c) sodium and chloride d) this is a trick question: all elements follow an octet rule. 6. Which of the following descriptions is true of ionic compounds? a) ...
... c) aluminum d) boron 5. These two elements follow a “duet” rather than an octet rule. What are they? a) helium and neon b) hydrogen and helium c) sodium and chloride d) this is a trick question: all elements follow an octet rule. 6. Which of the following descriptions is true of ionic compounds? a) ...
namimg compounds
... In the early days of chemistry, there was no system for the naming of compounds. Chemists used common names like bicarb of soda, quicklime, milk of magnesia, Epsom salts, spirits of salt, and laughing gas to describe compounds. As the number of named compounds increased it was obvious that if such c ...
... In the early days of chemistry, there was no system for the naming of compounds. Chemists used common names like bicarb of soda, quicklime, milk of magnesia, Epsom salts, spirits of salt, and laughing gas to describe compounds. As the number of named compounds increased it was obvious that if such c ...
The Atom Power point - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.