C. - Taylor County Schools
... • Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 that light has a dual nature. • Einstein suggested a beam of light has wavelike and particlelike properties. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy. ...
... • Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 that light has a dual nature. • Einstein suggested a beam of light has wavelike and particlelike properties. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy. ...
Calculations and Chemical Equations Atomic mass: Mass of an
... Chemical Reaction: Interaction between substances that results in one or more new substances being produced ...
... Chemical Reaction: Interaction between substances that results in one or more new substances being produced ...
Chapter 1 The Periodic Table - Beck-Shop
... When main group metals, such as potassium and calcium, are compared with transition metals in the same period, such as iron and copper, which of the following is correct? A. B. C. D. ...
... When main group metals, such as potassium and calcium, are compared with transition metals in the same period, such as iron and copper, which of the following is correct? A. B. C. D. ...
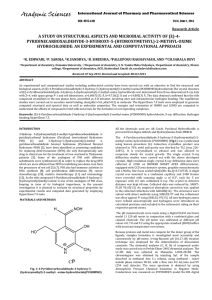
A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ASPECTS AND MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF (E)-4- PYRIDINECARBOXALDEHYDE-3-HYDROXY-5-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-2-METHYL-OXIME
... Log(1- n A)/ n A, Vs pH (Fig.7 and 8). The results indicated the presence of two dissociable protons corresponding to ring NH + proton (pKa1=5.0) and phenolic OH group of PCHHMMO (pKa2=8.2). The titration curves clearly indicated the release of dissociable protons more easily in presence of metal io ...
... Log(1- n A)/ n A, Vs pH (Fig.7 and 8). The results indicated the presence of two dissociable protons corresponding to ring NH + proton (pKa1=5.0) and phenolic OH group of PCHHMMO (pKa2=8.2). The titration curves clearly indicated the release of dissociable protons more easily in presence of metal io ...
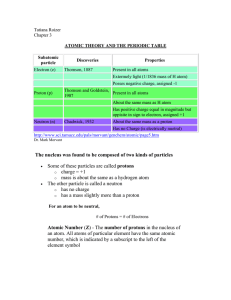
atomic theory and the periodic table
... can hold up to two electrons. (Encarta) When the a planet moves around the sun, you can plot a definite path for it which is called an orbit. A simple view of the atom looks similar and you may have pictured the electrons as orbiting around the nucleus. The truth is different, and electrons in fact ...
... can hold up to two electrons. (Encarta) When the a planet moves around the sun, you can plot a definite path for it which is called an orbit. A simple view of the atom looks similar and you may have pictured the electrons as orbiting around the nucleus. The truth is different, and electrons in fact ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts Answer Key
... bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one polar molecule attracts the less electronegative end of another polar molecule) and London Dispersio ...
... bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces (when the H of one polar molecule attracts the N, O or F of another polar molecule), followed by dipole (where the more electronegative end of one polar molecule attracts the less electronegative end of another polar molecule) and London Dispersio ...
Section 7: Free electron model
... confined to a length L by infinite potential barriers. The wavefunction ψ n ( x) of the electron is a solution of the Schrödinger equation Hψ n ( x) = Enψ n ( x) , where En is the energy of electron orbital. Since w can assume that the potential lies at zero, the Hamiltonian H includes only the kine ...
... confined to a length L by infinite potential barriers. The wavefunction ψ n ( x) of the electron is a solution of the Schrödinger equation Hψ n ( x) = Enψ n ( x) , where En is the energy of electron orbital. Since w can assume that the potential lies at zero, the Hamiltonian H includes only the kine ...
POGIL - Basic Skills Supplement - The Mole-1
... 3. There are an equal number of nitrogen atoms in one mole of NH3 and one mole of N2. 4. The number of Cu atoms in 100 grams of pure copper metal is the same as the number of atoms in 100 grams of cupric oxide. 5. The number of Ni atoms in 100 moles of pure nickel metal is the same as the number of ...
... 3. There are an equal number of nitrogen atoms in one mole of NH3 and one mole of N2. 4. The number of Cu atoms in 100 grams of pure copper metal is the same as the number of atoms in 100 grams of cupric oxide. 5. The number of Ni atoms in 100 moles of pure nickel metal is the same as the number of ...
Some Success Applications for Local
... bonding electron moves between the two hydrogen nuclei, no superluminal interaction—the extranuclear electron is local. If the bonding electron between the two nuclei is the phase trajectory ring, the relationship between each particle is the exact causation, and this extranuclear electron must be i ...
... bonding electron moves between the two hydrogen nuclei, no superluminal interaction—the extranuclear electron is local. If the bonding electron between the two nuclei is the phase trajectory ring, the relationship between each particle is the exact causation, and this extranuclear electron must be i ...
CHM 629: Principles of Physical Chemistry
... and programming language Mathematica. It has many good mathematical tips too. 3. http:/www.mathworks.com/MATLAB: Another mathematical software and an associated programming language. Grading System 1. Homework Assignments: (25 marks total) : These will consist of 5 assignments. You have one week to ...
... and programming language Mathematica. It has many good mathematical tips too. 3. http:/www.mathworks.com/MATLAB: Another mathematical software and an associated programming language. Grading System 1. Homework Assignments: (25 marks total) : These will consist of 5 assignments. You have one week to ...
AP Chemistry - Chagrin Falls Schools
... nuclear charge, electron configurations, relationship between configurations and periodicity. Student Conducted Lab Experiences Flame tests of various metals (instructor created lab) Unit 5: Periodic Properties Topics Electron shells vs. atomic radius, periodic properties including: ionization energ ...
... nuclear charge, electron configurations, relationship between configurations and periodicity. Student Conducted Lab Experiences Flame tests of various metals (instructor created lab) Unit 5: Periodic Properties Topics Electron shells vs. atomic radius, periodic properties including: ionization energ ...
Free electrons
... 3. Electron experiences a collision with a probability per unit time 1/ τ. The time τ − an average time between the two consecutive scattering events - known as, the collision time (relaxation time). The relaxation time τ is taken to be independent of electron's position and velocity. 4. Electrons a ...
... 3. Electron experiences a collision with a probability per unit time 1/ τ. The time τ − an average time between the two consecutive scattering events - known as, the collision time (relaxation time). The relaxation time τ is taken to be independent of electron's position and velocity. 4. Electrons a ...
chem1a_ch02_lecture - Santa Rosa Junior College
... (a) Iodine is a nonmetal in Group 17. It gains one electron to have the same number of electrons as 54Xe. The ion is I(b) Calcium is a metal in Group 2. It loses two electrons to have the same number of electrons as 18Ar. The ion is Ca2+ (c) Aluminum is a metal in Group 13. It loses three electrons ...
... (a) Iodine is a nonmetal in Group 17. It gains one electron to have the same number of electrons as 54Xe. The ion is I(b) Calcium is a metal in Group 2. It loses two electrons to have the same number of electrons as 18Ar. The ion is Ca2+ (c) Aluminum is a metal in Group 13. It loses three electrons ...
Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 073002
... The formation of ultracold molecules is currently one of the most actively pursued topics in atomic and molecular physics. Recently, spectacular progress in this field has been achieved by using adiabatic sweeps over Feshbach resonances to produce quantum gases of a variety of alkali dimers [1–6] cu ...
... The formation of ultracold molecules is currently one of the most actively pursued topics in atomic and molecular physics. Recently, spectacular progress in this field has been achieved by using adiabatic sweeps over Feshbach resonances to produce quantum gases of a variety of alkali dimers [1–6] cu ...
chem1a_ch02_lecture - Santa Rosa Junior College
... (a) Iodine is a nonmetal in Group 17. It gains one electron to have the same number of electrons as 54Xe. The ion is I(b) Calcium is a metal in Group 2. It loses two electrons to have the same number of electrons as 18Ar. The ion is Ca2+ (c) Aluminum is a metal in Group 13. It loses three electrons ...
... (a) Iodine is a nonmetal in Group 17. It gains one electron to have the same number of electrons as 54Xe. The ion is I(b) Calcium is a metal in Group 2. It loses two electrons to have the same number of electrons as 18Ar. The ion is Ca2+ (c) Aluminum is a metal in Group 13. It loses three electrons ...
Chemistry Handout 08 - (Redox)
... gain electrons and have an increase in oxidation number lose electrons and have an increase in oxidation number gain electrons and have a decrease in oxidation number lose electrons and have a decrease in oxidation number ...
... gain electrons and have an increase in oxidation number lose electrons and have an increase in oxidation number gain electrons and have a decrease in oxidation number lose electrons and have a decrease in oxidation number ...
Atoms: Some Basics
... which has been discovered in atoms has been discovered in hydrogen (but Na and other alkalis have taken over since tunable lasers arrived). In this chapter we shall use the phrase “one electron atom” to include not only atoms which are isoelectronic with H (e.g. He+ , Li++ ... etc.) but also atoms w ...
... which has been discovered in atoms has been discovered in hydrogen (but Na and other alkalis have taken over since tunable lasers arrived). In this chapter we shall use the phrase “one electron atom” to include not only atoms which are isoelectronic with H (e.g. He+ , Li++ ... etc.) but also atoms w ...
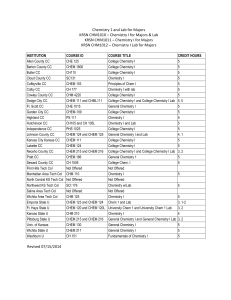
Chemistry 1 and Lab for Majors KRSN CHM1010 – Chemistry I for
... c. Describe the behavior of photons and electrons during electronic transitions between principle quantum levels and calculate the wavelength and frequency of light involved in these transitions. d. Using the Aufbau principle, write the electron configuration of many electron atoms and monatomic ion ...
... c. Describe the behavior of photons and electrons during electronic transitions between principle quantum levels and calculate the wavelength and frequency of light involved in these transitions. d. Using the Aufbau principle, write the electron configuration of many electron atoms and monatomic ion ...
Chemistry 30 Review of Basic Chemistry 20
... named, use brackets to keep that complex ion as a group. ...
... named, use brackets to keep that complex ion as a group. ...
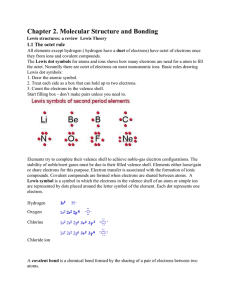
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.