Chapter 3
... – how much reactant is consumed and how much product is formed – coefficients must be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. – i.e. chemical equation must be balanced ...
... – how much reactant is consumed and how much product is formed – coefficients must be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. – i.e. chemical equation must be balanced ...
Yao nl903302q
... using chemically sharpened tungsten nanoprobes, and Pt electrodes were deposited on the nanowire/nanoprobe junction to create mechanical and electrical connections. These electrodes were created by first injecting a cloud of organometallic molecules containing platinum ((MeCp)PtMe3). The focused ion ...
... using chemically sharpened tungsten nanoprobes, and Pt electrodes were deposited on the nanowire/nanoprobe junction to create mechanical and electrical connections. These electrodes were created by first injecting a cloud of organometallic molecules containing platinum ((MeCp)PtMe3). The focused ion ...
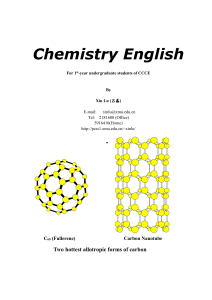
Chemistry English
... Atomic theory: if the matter were divided a sufficient number of times, it could eventually be reduced to the indivisible, indestructible particles called atom. The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in th ...
... Atomic theory: if the matter were divided a sufficient number of times, it could eventually be reduced to the indivisible, indestructible particles called atom. The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in th ...
astrochemistry_caselli
... The timescale on which almost all carbon becomes contained in CO (nO > nC) is at least equal to the timescale for one hydrogen molecule to be ionized for every C: nC/[ n(H2)] = 2 nC/[ nH] For = 610-17 s-1 and nC/nH = 10-4, the above expression gives a value of 105 yr. ...
... The timescale on which almost all carbon becomes contained in CO (nO > nC) is at least equal to the timescale for one hydrogen molecule to be ionized for every C: nC/[ n(H2)] = 2 nC/[ nH] For = 610-17 s-1 and nC/nH = 10-4, the above expression gives a value of 105 yr. ...
Glossary: Chemical bonds
... of isotopic masses found in a typical terrestrial sample of the element. Atom. Compare with molecule and ion. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Atoms are electrically neutral, with a positively charged nucleus that binds one or more e ...
... of isotopic masses found in a typical terrestrial sample of the element. Atom. Compare with molecule and ion. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Atoms are electrically neutral, with a positively charged nucleus that binds one or more e ...
Chem 11 Notes Booklet (pdf version)
... ◘ Note that the number given under the symbol is not the mass number of that particular atom. It is an averaged mass number called the atomic mass and will be used later. 4. Ions a) Creating Ions We know that atoms are electrically neutral because they have equal numbers of protons (p+) and electr ...
... ◘ Note that the number given under the symbol is not the mass number of that particular atom. It is an averaged mass number called the atomic mass and will be used later. 4. Ions a) Creating Ions We know that atoms are electrically neutral because they have equal numbers of protons (p+) and electr ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another ato ...
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another ato ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... Hund’s Rule- Each orbital is occupied before pairing begins. (orbital- probable location of each electron - at least 2 electrons per orbital - no electrons=no orbital) Quantum Numbers- a number that describes the properties of electrons and consists of 4 numbers (Quantum- a certain number) Pauli’s E ...
... Hund’s Rule- Each orbital is occupied before pairing begins. (orbital- probable location of each electron - at least 2 electrons per orbital - no electrons=no orbital) Quantum Numbers- a number that describes the properties of electrons and consists of 4 numbers (Quantum- a certain number) Pauli’s E ...
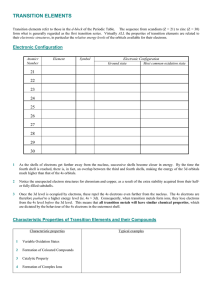
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... Formation of Coloured Compounds Most of the compounds and complexes of transition elements are coloured. The colour of these compounds can often be related to incompletely filled d-orbitals in the transition metal ion. The outer electronic orbitals of transition metal ions have only small energy dif ...
... Formation of Coloured Compounds Most of the compounds and complexes of transition elements are coloured. The colour of these compounds can often be related to incompletely filled d-orbitals in the transition metal ion. The outer electronic orbitals of transition metal ions have only small energy dif ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... In part I we have collected what we feel is the “canonical” contents of an introductory course in computational chemistry. This material is elementary and does not require special skills or prior knowle ...
... In part I we have collected what we feel is the “canonical” contents of an introductory course in computational chemistry. This material is elementary and does not require special skills or prior knowle ...
AP CHEMISTRY - An Incomplete List of Topics
... Example: When Na2CO3(s) is heated, it will decompose to form CO2(g). Solid Na2O will also be formed as the remainder of the original compound. The Na2O(s) will slowly re-absorb CO2(g) from the air and convert back into Na2CO3(s). Other carbonates follow this same pattern, as seen in the reaction of ...
... Example: When Na2CO3(s) is heated, it will decompose to form CO2(g). Solid Na2O will also be formed as the remainder of the original compound. The Na2O(s) will slowly re-absorb CO2(g) from the air and convert back into Na2CO3(s). Other carbonates follow this same pattern, as seen in the reaction of ...
chemistry
... 73 Compared to atoms of metals, atoms of nonmetals generally (1) have higher electronegativities (2) have lower first ionization energies (3) conduct electricity more readily (4) lose electrons more readily 74 Aqueous solutions of compounds containing element X are blue. Element X could be (1) carbo ...
... 73 Compared to atoms of metals, atoms of nonmetals generally (1) have higher electronegativities (2) have lower first ionization energies (3) conduct electricity more readily (4) lose electrons more readily 74 Aqueous solutions of compounds containing element X are blue. Element X could be (1) carbo ...
Lecture 6 - TCD Chemistry
... How Molecular Oribital Theory enhances our understanding of the chemistry of transition metal complexes ...
... How Molecular Oribital Theory enhances our understanding of the chemistry of transition metal complexes ...
THE STRUCTURE OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
... The potential energy, EP or (when there is no fear of confusion with the symbol for volume) V, of a body is the energy it possesses as a result of its position. The zero of potential energy is arbitrary. For example, the gravitational potential energy of a body is often set to zero at the surface of ...
... The potential energy, EP or (when there is no fear of confusion with the symbol for volume) V, of a body is the energy it possesses as a result of its position. The zero of potential energy is arbitrary. For example, the gravitational potential energy of a body is often set to zero at the surface of ...
TDDFT as a tool in chemistry
... Variational (give an upper bound to the exact energy). Size consistent (especially important in chemical reactions). Correct ordering of the excited states energies. Energies and wavefunction (density) should possibly be analytically differentiable with respect to external parameters (for instance n ...
... Variational (give an upper bound to the exact energy). Size consistent (especially important in chemical reactions). Correct ordering of the excited states energies. Energies and wavefunction (density) should possibly be analytically differentiable with respect to external parameters (for instance n ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another ato ...
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another ato ...
Slide 1 ______
... Compound— When a molecule containing two or more different atoms forms Have characteristics different than the original atoms. ...
... Compound— When a molecule containing two or more different atoms forms Have characteristics different than the original atoms. ...
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 9th Edition
... by symbols, using the initial letter of the name in capital form, starting by the old known elements, so Carbon is represented by the letter C, but Calcium is represented by the symbol Ca and Cobalt by the symbol Co, ……, Nitrogen is represented by the symbol N and Nickel by the symbol Ni, etc…. In g ...
... by symbols, using the initial letter of the name in capital form, starting by the old known elements, so Carbon is represented by the letter C, but Calcium is represented by the symbol Ca and Cobalt by the symbol Co, ……, Nitrogen is represented by the symbol N and Nickel by the symbol Ni, etc…. In g ...
Document
... In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable ...
... In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 2. You need to master the formulas, charges, and names of the common ions. On the first week of the school year, you will be given a quiz on these ions. You will be asked to: • write the names of these ions when given the formula and charge • write the formula and charge when given the names I have ...
... 2. You need to master the formulas, charges, and names of the common ions. On the first week of the school year, you will be given a quiz on these ions. You will be asked to: • write the names of these ions when given the formula and charge • write the formula and charge when given the names I have ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... Ex- sodium has 11 electrons. How many are in it’s outermost level? ...
... Ex- sodium has 11 electrons. How many are in it’s outermost level? ...
Chemistry-5th-Edition-Brady-Solution-Manual
... Nonmetals are more frequently found in compounds because of the large variety of ways they may combine. A particularly illustrative example is the combination of carbon, a nonmetal, with other elements. So many compounds are possible that there is one entire area of chemistry devoted to the study of ...
... Nonmetals are more frequently found in compounds because of the large variety of ways they may combine. A particularly illustrative example is the combination of carbon, a nonmetal, with other elements. So many compounds are possible that there is one entire area of chemistry devoted to the study of ...
Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another ato ...
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another ato ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.