Examination
... the instructions from the proctor for completing the student information on your answer sheet. Record your answers to the Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure ...
... the instructions from the proctor for completing the student information on your answer sheet. Record your answers to the Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure ...
Balancing Chemical Equations – A Primer
... Recall, the elements in the “far right” column (Family 18) have a stable electron configuration (i.e., a full outer or valence shell of electrons). All other elements seek to have this stable configuration. In some reactions, elements will give or take electrons from other elements to achieve stabil ...
... Recall, the elements in the “far right” column (Family 18) have a stable electron configuration (i.e., a full outer or valence shell of electrons). All other elements seek to have this stable configuration. In some reactions, elements will give or take electrons from other elements to achieve stabil ...
Section 8.10 Lewis Structures
... given molecule or ion must equal the overall charge on that species. ...
... given molecule or ion must equal the overall charge on that species. ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... stereoisomers of an organic molecule, given its molecular formula. Describe the different types of covalent bond fission: ...
... stereoisomers of an organic molecule, given its molecular formula. Describe the different types of covalent bond fission: ...
Chem 173: Final Exam Review Short Answer and Problems 1
... Limestone is composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) as well as other compounds. In an analysis, a chemist takes a sample of limestone which has a mass of 413 mg and treats it with oxalic acid (H2C 2O4). A chemical reaction occurs between the calcium carbonate and the acid producing calcium oxalate an ...
... Limestone is composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) as well as other compounds. In an analysis, a chemist takes a sample of limestone which has a mass of 413 mg and treats it with oxalic acid (H2C 2O4). A chemical reaction occurs between the calcium carbonate and the acid producing calcium oxalate an ...
reactions taking place within cells
... Specific heat capacity (c)(Jg–1 °C–1) Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K Temperature Measurement of KE of particles(independent of the amount) Heat Measurement of total energy in a substance(dependent on the amount) Calorimetry Measurement of heat transferred t ...
... Specific heat capacity (c)(Jg–1 °C–1) Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K Temperature Measurement of KE of particles(independent of the amount) Heat Measurement of total energy in a substance(dependent on the amount) Calorimetry Measurement of heat transferred t ...
Notes-C12-121
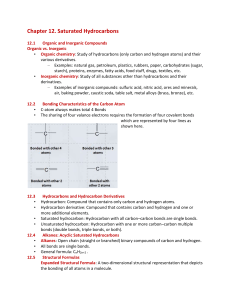
... All bonds are single bonds. General formula: CnH2n+2 . Structural Formulas Expanded Structural Formula: A two-dimensional structural representation that depicts the bonding of all atoms in a molecule. ...
... All bonds are single bonds. General formula: CnH2n+2 . Structural Formulas Expanded Structural Formula: A two-dimensional structural representation that depicts the bonding of all atoms in a molecule. ...
Review 1
... The figurine could be pure silver but hollow. It also might be an alloy of silver and another, less dense metal. ...
... The figurine could be pure silver but hollow. It also might be an alloy of silver and another, less dense metal. ...
Answers to Selected Exercises
... its kinetic energy) drops to zero. Most of the kinetic energy is transferred to the sand, which deforms when the ball lands. Some energy is released as heat through friction between the ball and the sand. 4.11 The energy source of a 100-watt light bulb is electrical current from household wiring. En ...
... its kinetic energy) drops to zero. Most of the kinetic energy is transferred to the sand, which deforms when the ball lands. Some energy is released as heat through friction between the ball and the sand. 4.11 The energy source of a 100-watt light bulb is electrical current from household wiring. En ...
1)A neutral atom has no overall charge, and ion is a
... 5)a)Create graph, will be gone over in class. b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attractio ...
... 5)a)Create graph, will be gone over in class. b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attractio ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... Explain how potential energy changes as distances between atoms change to form a covalent bond Be able to use electronegativity difference to classify the type of bond between two atoms. Understand that ionic bonding and covalent bonding are at two ends of a sliding scale of bond type Draw electron- ...
... Explain how potential energy changes as distances between atoms change to form a covalent bond Be able to use electronegativity difference to classify the type of bond between two atoms. Understand that ionic bonding and covalent bonding are at two ends of a sliding scale of bond type Draw electron- ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... In a covalent bond, therefore, bonding electron pairs are localized in the region between the bonded atoms. In metals valence electrons are not localized to individual atoms but are free to move to temporarily occupy vacant orbitals on adjacent metal atoms. For this reason metals conduct electricity ...
... In a covalent bond, therefore, bonding electron pairs are localized in the region between the bonded atoms. In metals valence electrons are not localized to individual atoms but are free to move to temporarily occupy vacant orbitals on adjacent metal atoms. For this reason metals conduct electricity ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
IB Chemistry Review. Unit I. Topics 2
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... Come to tutoring to use the study guide to find additional facts! ...
... Come to tutoring to use the study guide to find additional facts! ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Complete Notes
... Refer to the Periodic Chart of Ions for a list of ions. The charge for polyatomic ions is for the whole group of atoms not just for the atom written last. DO NOT change the subscripts of polyatomic ions; if you change the subscripts you change the identity of these ions. When indicating the presence ...
... Refer to the Periodic Chart of Ions for a list of ions. The charge for polyatomic ions is for the whole group of atoms not just for the atom written last. DO NOT change the subscripts of polyatomic ions; if you change the subscripts you change the identity of these ions. When indicating the presence ...
... In fact, as early as 1862 H. Letheby of the College of London Hospital, by anodic oxidation of aniline in sulphuric acid, obtained a partly conductive material which was probably polyaniline. In the early 1970s, it was found that the inorganic explosive polymer, poly(sulphur nitride) (SN)x, was supe ...
Final Review 2006
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
Document
... Atoms can be represented as shown in this example: Mass number 23 Na Atomic number 11 The relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons are: Name of particle Mass Proton 1 Neutron 1 Electron Very small The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is called its mass number. Atoms of the s ...
... Atoms can be represented as shown in this example: Mass number 23 Na Atomic number 11 The relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons are: Name of particle Mass Proton 1 Neutron 1 Electron Very small The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is called its mass number. Atoms of the s ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... 1. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scientists to conclude that an atom’s (1) positive charge is evenly distributed throughout its volume (2) negative charge is mainly concentrated in its nucleus (3) mass is evenly distributed throughout its volume (4) volume is mainly unoc ...
... 1. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scientists to conclude that an atom’s (1) positive charge is evenly distributed throughout its volume (2) negative charge is mainly concentrated in its nucleus (3) mass is evenly distributed throughout its volume (4) volume is mainly unoc ...
AS specification - word format File
... e use chemical equations to calculate reacting masses and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar mass f use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar volume of gases, eg calculation of the mass or volum ...
... e use chemical equations to calculate reacting masses and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar mass f use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar volume of gases, eg calculation of the mass or volum ...
Topic 4 Chemistry of the Elements of the Main Group
... Hydrogen forms ionic hydrides with the reactive s-block metals (groups 1 and 2) and forms covalent hydrides with the p-group metals, e.g. Al and Sn (group 13 and 14). Electronegativity = 2.1. The value is intermediate in the electronegativity scale that spans from 0.7 to 4.0. H can form hydrides ( ...
... Hydrogen forms ionic hydrides with the reactive s-block metals (groups 1 and 2) and forms covalent hydrides with the p-group metals, e.g. Al and Sn (group 13 and 14). Electronegativity = 2.1. The value is intermediate in the electronegativity scale that spans from 0.7 to 4.0. H can form hydrides ( ...
Summary - Clydebank High School
... Section (d) - Bonding, structure and properties of the first 20 elements. 1. Metallic bonding is an electrostatic attraction between the ................................charged nucleus and the delocalised outer .................................................. 2. Atoms of non-metal elements bond to ...
... Section (d) - Bonding, structure and properties of the first 20 elements. 1. Metallic bonding is an electrostatic attraction between the ................................charged nucleus and the delocalised outer .................................................. 2. Atoms of non-metal elements bond to ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.