Ch19CT
... side, a voltage drop so the voltage change is -V2. Then we go through R1 from the low V side to the high V side (since we are moving against the current flow I1): a voltage rise so the change is +I1R1. Finally, we go through R2, in the same direction as the current I2, so we have a voltage drop and ...
... side, a voltage drop so the voltage change is -V2. Then we go through R1 from the low V side to the high V side (since we are moving against the current flow I1): a voltage rise so the change is +I1R1. Finally, we go through R2, in the same direction as the current I2, so we have a voltage drop and ...
Op amp - schoolphysics
... hence derive an expression for V2 in terms of V1 and the values of the circuit components. The current, I, through a certain device varies with applied potential difference, V according to the relation I= IoekV where Io and k are constants. If R2 is replaced by this device, write down an expression ...
... hence derive an expression for V2 in terms of V1 and the values of the circuit components. The current, I, through a certain device varies with applied potential difference, V according to the relation I= IoekV where Io and k are constants. If R2 is replaced by this device, write down an expression ...
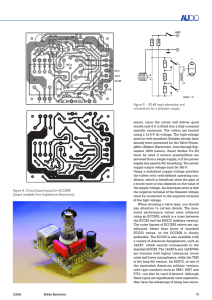
Figure 8. Circuit board layout for ECC808 (board available from
... 12AX7. The ECC83 and ECC808 are identical electrically, but the noise characteristics of the ECC808 are better by a factor of three, it is less sensitive to hum and it is significantly less microphonic. Its noise characteristics roughly match those of the ECC83S. In addition, it has a screen between ...
... 12AX7. The ECC83 and ECC808 are identical electrically, but the noise characteristics of the ECC808 are better by a factor of three, it is less sensitive to hum and it is significantly less microphonic. Its noise characteristics roughly match those of the ECC83S. In addition, it has a screen between ...
ECE 201 Exam #2 Review
... sources (just like superposition). (b) If there are only dependent sources, then must use a test voltage or current source in order to calculate RTh (or ZTh) = VTest/Itest (c) If there are both independent and dependent sources, then compute RTh (or ZTh) from VOC/ISC. ECE201 Exam #2 Review ...
... sources (just like superposition). (b) If there are only dependent sources, then must use a test voltage or current source in order to calculate RTh (or ZTh) = VTest/Itest (c) If there are both independent and dependent sources, then compute RTh (or ZTh) from VOC/ISC. ECE201 Exam #2 Review ...
Document
... The frequency of the mains voltage is 50 Hz. The current i1 splits at the node to form the currents i2 and i3. All the current waveforms are sinusoidal; however i1 and i2 have a phase angle between them of 90 degrees. The amplitudes of the currents i1 and i2 are √3 Amps and 1 Amp respectively. ...
... The frequency of the mains voltage is 50 Hz. The current i1 splits at the node to form the currents i2 and i3. All the current waveforms are sinusoidal; however i1 and i2 have a phase angle between them of 90 degrees. The amplitudes of the currents i1 and i2 are √3 Amps and 1 Amp respectively. ...
Slide 1
... The CLR serves two purposes in the ESP Power Supply. 1. As the name suggests the primary purpose is to limit the surge current that can be delivered to the ESP as a result of sparks and Arcs that will occur. The value of the CLR is expressed as Inductance in Milli-Henris or Percent Impedance. The ty ...
... The CLR serves two purposes in the ESP Power Supply. 1. As the name suggests the primary purpose is to limit the surge current that can be delivered to the ESP as a result of sparks and Arcs that will occur. The value of the CLR is expressed as Inductance in Milli-Henris or Percent Impedance. The ty ...
Longitudinal Voltages, Induced by Parallel Overhead Transmission
... Abstract— Longitudinal voltage values, induced by magnetic fields currents in parallel overhead transmission line are determined usually by derivative of Carson’ integral equations. These equations application have broad “dead space” conditionally the spacing of transmission lines and ground conduct ...
... Abstract— Longitudinal voltage values, induced by magnetic fields currents in parallel overhead transmission line are determined usually by derivative of Carson’ integral equations. These equations application have broad “dead space” conditionally the spacing of transmission lines and ground conduct ...
Ohm`s Law
... change in current is proportional to the voltage, the data should be in a straight line and it should go through zero. In these two examples how close is the y-intercept to zero? Is there a proportional relationship between voltage and current? If so, write the equation for each run in the form pote ...
... change in current is proportional to the voltage, the data should be in a straight line and it should go through zero. In these two examples how close is the y-intercept to zero? Is there a proportional relationship between voltage and current? If so, write the equation for each run in the form pote ...
ENT161LAB3 - UniMAP Portal
... The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source. If one path is drawing 1 amp and the other is drawing 1 amp then the total is 2 amps at the source. If there are 4 branches in this same 2 amp circuit, then one path may draw 1/4A (.25A), the next 1/4 ...
... The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source. If one path is drawing 1 amp and the other is drawing 1 amp then the total is 2 amps at the source. If there are 4 branches in this same 2 amp circuit, then one path may draw 1/4A (.25A), the next 1/4 ...
June 2011 - Vicphysics
... Time constant = RC = 5 x 106 x 10 x -6 = 50 sec 2. D Voltage = peak voltage = 3600 x 1.414 =5091 V. Time constant is much longer than time scale of graph so no variation would be detected. 3. B Power used = V2/R = 5000 x 5000 / (5 x 106) = 5 W. Best is 10W. 4. A Only the input voltage affects the ou ...
... Time constant = RC = 5 x 106 x 10 x -6 = 50 sec 2. D Voltage = peak voltage = 3600 x 1.414 =5091 V. Time constant is much longer than time scale of graph so no variation would be detected. 3. B Power used = V2/R = 5000 x 5000 / (5 x 106) = 5 W. Best is 10W. 4. A Only the input voltage affects the ou ...
Josephson voltage standard

A Josephson voltage standard is a complex system that uses a superconductive integrated circuit chip operating at 4 K to generate stable voltages that depend only on an applied frequency and fundamental constants. It is an intrinsic standard in the sense that it does not depend on any physical artifact. It is the most accurate method to generate or measure voltage and, by international agreement, is the basis for voltage standards around the World.