Atoms, electrons and the periodic table
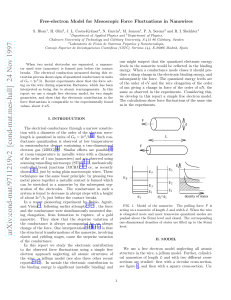
... binding energy appears as kinetic energy of the emitted electron. What seemed peculiar, however, was that the energy of the ejected electrons did not depend on the intensity of the light as classical physics would predict. Instead, the energy of the photoelectrons (as they are called) varies with th ...
... binding energy appears as kinetic energy of the emitted electron. What seemed peculiar, however, was that the energy of the ejected electrons did not depend on the intensity of the light as classical physics would predict. Instead, the energy of the photoelectrons (as they are called) varies with th ...
name chemistry final review
... a. 200.0 g C3H6 and 200.0 g of O2 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2 O2 is the LR, C3H6 is in excess. There is 141.5g of C3H6 left over and 75.08g H2O and 183.4g CO2 produced. b. 45.9 g CuSO4 and 67.3 g of Fe(C2H3O2)3 3 CuSO4 + 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 → 3 Cu(C2H3O2)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 CuSO4 is the LR, Fe(C2H3O2)3 is in ...
... a. 200.0 g C3H6 and 200.0 g of O2 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2 O2 is the LR, C3H6 is in excess. There is 141.5g of C3H6 left over and 75.08g H2O and 183.4g CO2 produced. b. 45.9 g CuSO4 and 67.3 g of Fe(C2H3O2)3 3 CuSO4 + 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 → 3 Cu(C2H3O2)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 CuSO4 is the LR, Fe(C2H3O2)3 is in ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a single proton (+)! ...
... For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a single proton (+)! ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 28. What is the density of 325g of a substance with a volume of 492mL? 29. Define accuracy and precision. 30. Complete the following calculations with the correct number of significant figures: a. 1.23kg + 4.082kg b. 16.04s – 5s c. 0.070cm x 1.08cm 31. What is the lowest temperature on the Kelvin sc ...
... 28. What is the density of 325g of a substance with a volume of 492mL? 29. Define accuracy and precision. 30. Complete the following calculations with the correct number of significant figures: a. 1.23kg + 4.082kg b. 16.04s – 5s c. 0.070cm x 1.08cm 31. What is the lowest temperature on the Kelvin sc ...
isuintroduction
... A mole contains approximately 6.022 x 1023 particles, no matter what the volume, pressure, or temperature is.(2) For instance, 1 mol (which is the abbreviation of the mole) of a gas at 3000 K (K is the abbreviation of the Kelvin temperature scale) contains 6.02 x 1023 particles, while 1 mol of the ...
... A mole contains approximately 6.022 x 1023 particles, no matter what the volume, pressure, or temperature is.(2) For instance, 1 mol (which is the abbreviation of the mole) of a gas at 3000 K (K is the abbreviation of the Kelvin temperature scale) contains 6.02 x 1023 particles, while 1 mol of the ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
Chapter 7
... for an insulator, while for a semiconductor e B ≥ e−20 ' 10−9 . The factor 10−35 even when multiplied by 1023 cm−3 gives n ' 0 for an insulator. With 0.1eV ≤ EG <2.0eV the carrier concentration satisfies 1022 cm−3 > n > ...
... for an insulator, while for a semiconductor e B ≥ e−20 ' 10−9 . The factor 10−35 even when multiplied by 1023 cm−3 gives n ' 0 for an insulator. With 0.1eV ≤ EG <2.0eV the carrier concentration satisfies 1022 cm−3 > n > ...
Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • A number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol in a formula. ...
... • A number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol in a formula. ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT AP Chemistry is a
... 9. How many Energy levels do strontium and iodine have? ________ 10. Which element is located in Period 4, group 2? ________________ 11. Name an element that has similar properties to sodium. __________ 12. State a property of cobalt._______________________________________ 13. Cobalt has a total of ...
... 9. How many Energy levels do strontium and iodine have? ________ 10. Which element is located in Period 4, group 2? ________________ 11. Name an element that has similar properties to sodium. __________ 12. State a property of cobalt._______________________________________ 13. Cobalt has a total of ...
Electron energy level statistics in graphene quantum dots
... To conclude, it seems that disorder due to randomness of the edges is, in principle, enough to reproduce the experimentally observed level distribution which makes the term “chaotic Dirac billiard” quite reasonable. One may need the local on-site disorder and some disorder in the hopping integrals t ...
... To conclude, it seems that disorder due to randomness of the edges is, in principle, enough to reproduce the experimentally observed level distribution which makes the term “chaotic Dirac billiard” quite reasonable. One may need the local on-site disorder and some disorder in the hopping integrals t ...
Skill Sheet 19-B Chemical Formulas
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
Document
... Prediction – e– should emit light at whatever frequency f it orbits nucleus d sin θ = mλ ...
... Prediction – e– should emit light at whatever frequency f it orbits nucleus d sin θ = mλ ...
OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... The structures produced by forming bonds are either giant or simple The possible combinations of structure and bonding are giant ionic, simple covalent, giant covalent and giant metallic Simple covalent is sometimes called simple molecular Giant covalent is sometimes called giant molecular or macrom ...
... The structures produced by forming bonds are either giant or simple The possible combinations of structure and bonding are giant ionic, simple covalent, giant covalent and giant metallic Simple covalent is sometimes called simple molecular Giant covalent is sometimes called giant molecular or macrom ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.