Chemistry Final Test 1999-2000 - Nashoba Valley Technical High
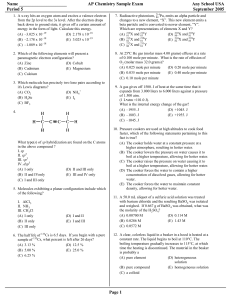
... 17) Which of the following represents a pair of isotopes? A. 1H1+ and 11Na1+ B. 54Cr and 54Mn C. 31P3- and 80Br1D. 32S and 35S 18) The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Which of the following lists these types of radiation from lest dangerous to most dangerous? A. alp ...
... 17) Which of the following represents a pair of isotopes? A. 1H1+ and 11Na1+ B. 54Cr and 54Mn C. 31P3- and 80Br1D. 32S and 35S 18) The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Which of the following lists these types of radiation from lest dangerous to most dangerous? A. alp ...
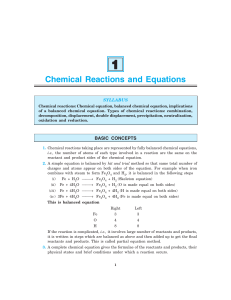
1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
... (ii) Addition of colourless lead nitrate solution to potassium iodide solution gives yellow coloured precipitate (lead iodide). So there is a change of colour. (iii) Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid to zinc granules gives a gas (H2) with effervescence. Q. 4. How do you show that respiration is a ...
... (ii) Addition of colourless lead nitrate solution to potassium iodide solution gives yellow coloured precipitate (lead iodide). So there is a change of colour. (iii) Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid to zinc granules gives a gas (H2) with effervescence. Q. 4. How do you show that respiration is a ...
+ H 2 O(l) - Cloudfront.net
... added to water. (NaOH) • NH3 is a base. In water it accepts an H+ ion from HOH, leaving an OH- in solution. – NH3 is a weak electrolyte – About 1% ionizes to form NH4+/OH- ...
... added to water. (NaOH) • NH3 is a base. In water it accepts an H+ ion from HOH, leaving an OH- in solution. – NH3 is a weak electrolyte – About 1% ionizes to form NH4+/OH- ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... An experiment is set up to determine the molecular mass of a water-soluble, nonvolatile, non-electrolyte. The equipment listed above is availeable to use. No other equipment is available. (a) Briefly list the steps needed to carry out this experiment. (b) What experimental data needs to be collected ...
... An experiment is set up to determine the molecular mass of a water-soluble, nonvolatile, non-electrolyte. The equipment listed above is availeable to use. No other equipment is available. (a) Briefly list the steps needed to carry out this experiment. (b) What experimental data needs to be collected ...
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
... A 1.00 mol sample of CO2 is heated to 1000K with excess graphite in a container of volume 40.0 L. At this temperature, Kc is 2.11x10-2 for the reaction: C(graphite) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) a) b) ...
... A 1.00 mol sample of CO2 is heated to 1000K with excess graphite in a container of volume 40.0 L. At this temperature, Kc is 2.11x10-2 for the reaction: C(graphite) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) a) b) ...
A Classification of AP Chemistry Reactions
... There are four types of redox with oxygen compounds, classified by the oxidizing agent: oxidizing acids (HNO3 and H2SO4), manganese compounds (MnO4- and MnO2), chromium compounds (Cr2O72-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Oxidizing acids Oxidizing acids are strong acids with anions that can be reduced ...
... There are four types of redox with oxygen compounds, classified by the oxidizing agent: oxidizing acids (HNO3 and H2SO4), manganese compounds (MnO4- and MnO2), chromium compounds (Cr2O72-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Oxidizing acids Oxidizing acids are strong acids with anions that can be reduced ...
Review Packet - Newton.k12.ma.us
... with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams and pounds. 7. Hydrates are compounds formed by the union of water with some other substance, generally forming a neutral body, as certain crystallized salts. 8. The concen ...
... with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams and pounds. 7. Hydrates are compounds formed by the union of water with some other substance, generally forming a neutral body, as certain crystallized salts. 8. The concen ...
2007 local exam - American Chemical Society
... 17. A sample of C2H6 gas initially at 50 ˚C and 720 mmHg is heated to 100 ˚C in a container of constant volume. What is the new pressure (in mmHg)? ...
... 17. A sample of C2H6 gas initially at 50 ˚C and 720 mmHg is heated to 100 ˚C in a container of constant volume. What is the new pressure (in mmHg)? ...
Formulation - Good Hope School
... 26. Sodium hydroxide reacts with acids. Which of the following solutions would give the highest initial rate? A. 60 cm3 of 1.5 M NaOH(aq) and 60 cm3 of 1.5 M HCl(aq) at 30C. B. 20 cm3 of 2.0 M NaOH(aq) and 20 cm3 of 2.0 M HCl(aq) at 30C. C. 50 cm3 of 2.0 M NaOH(aq) and 50 cm3 of 2.0 M HCl(aq) at 2 ...
... 26. Sodium hydroxide reacts with acids. Which of the following solutions would give the highest initial rate? A. 60 cm3 of 1.5 M NaOH(aq) and 60 cm3 of 1.5 M HCl(aq) at 30C. B. 20 cm3 of 2.0 M NaOH(aq) and 20 cm3 of 2.0 M HCl(aq) at 30C. C. 50 cm3 of 2.0 M NaOH(aq) and 50 cm3 of 2.0 M HCl(aq) at 2 ...
BONUS: Which line in the above graph represents G for the reaction
... which change will cause an increase in the pressure of CO2(g) when equilibrium is re-established? (A) ...
... which change will cause an increase in the pressure of CO2(g) when equilibrium is re-established? (A) ...
Mole Equation Homework Hint: Start equations with the numbers
... Hint: Start equations with the numbers given, and pay close attention to what the question is asking you to find. Usually, the first step in most stoichiometry problems (calculation of quantities in chemical equations) is to convert the given numbers to moles. SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
... Hint: Start equations with the numbers given, and pay close attention to what the question is asking you to find. Usually, the first step in most stoichiometry problems (calculation of quantities in chemical equations) is to convert the given numbers to moles. SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.