Just a Few Things 2012
... Catalyst lowers activation energy for both forward and reverse reaction speed up reaction do not change position of equilibrium ...
... Catalyst lowers activation energy for both forward and reverse reaction speed up reaction do not change position of equilibrium ...
chemeqohnotes18f2005
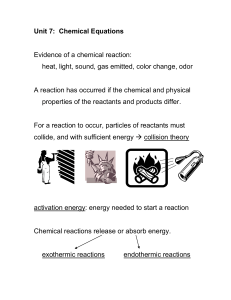
... For a reaction to occur, particles of reactants must collide, and with sufficient energy collision theory ...
... For a reaction to occur, particles of reactants must collide, and with sufficient energy collision theory ...
Advanced Chemical Reactions
... ◦ Solid gas increases entropy Gibbs free energy – max amt of E that can be used in another process ...
... ◦ Solid gas increases entropy Gibbs free energy – max amt of E that can be used in another process ...
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
... Be familiar with the names and symbols of the 1st 20 elements in the Periodic Table (ie. H, He, B, Be …….to Ca). Compounds have very different properties to the elements from which they are formed. It is often difficult to break compounds up into their elements (because the atoms are chemically join ...
... Be familiar with the names and symbols of the 1st 20 elements in the Periodic Table (ie. H, He, B, Be …….to Ca). Compounds have very different properties to the elements from which they are formed. It is often difficult to break compounds up into their elements (because the atoms are chemically join ...
Exam 3 Review Key
... d) Oxidizing agent: Ag+; reducing agent: O3 Pt(s)|O3(g), O2(g)|OH-(aq)|| Ag+(aq)|Ag(s); -0.44V (this is for basic conditions, used because this is how the reaction is given in the Standard Potentials Table in the book’s appendix. In acid, the cell would have the same set-up, only there would be H+ ...
... d) Oxidizing agent: Ag+; reducing agent: O3 Pt(s)|O3(g), O2(g)|OH-(aq)|| Ag+(aq)|Ag(s); -0.44V (this is for basic conditions, used because this is how the reaction is given in the Standard Potentials Table in the book’s appendix. In acid, the cell would have the same set-up, only there would be H+ ...
AHSGE Review
... Conservation applies to mass and matter as well. LaVoisier proved the law completing his reactions on a balance with a bell jar to contain the gases. ...
... Conservation applies to mass and matter as well. LaVoisier proved the law completing his reactions on a balance with a bell jar to contain the gases. ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
Curriculum Plan
... collision theory, Explain the concept of activation energy and activated complex, Define entropy, Describe an increase in the entropy of the universe as a driving force (2nd law of thermodynamics), Create and recognize an energy diagram for an exothermic or endothermic reaction, including EA, Ho, e ...
... collision theory, Explain the concept of activation energy and activated complex, Define entropy, Describe an increase in the entropy of the universe as a driving force (2nd law of thermodynamics), Create and recognize an energy diagram for an exothermic or endothermic reaction, including EA, Ho, e ...
physical and chemical change
... A physical property is a property of a substance that can be observed without changing the substance into another substance. For example, the melting point of a solid is a physical property. Color, hardness, shape and texture are other physical properties. A chemical property is a property of a subs ...
... A physical property is a property of a substance that can be observed without changing the substance into another substance. For example, the melting point of a solid is a physical property. Color, hardness, shape and texture are other physical properties. A chemical property is a property of a subs ...
Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. The smaller the atom, the closer the ...
... boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. The smaller the atom, the closer the ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.