GCSE Chemistry Specification Specification for exams from 2014 2014
... Scientific investigations often seek to identify links between two or more variables. These links may be: – causal, in that a change in one variable causes a change in another − due to association, in that changes in one variable and a second variable are linked by a third variable − due to chance o ...
... Scientific investigations often seek to identify links between two or more variables. These links may be: – causal, in that a change in one variable causes a change in another − due to association, in that changes in one variable and a second variable are linked by a third variable − due to chance o ...
Thermochemistry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
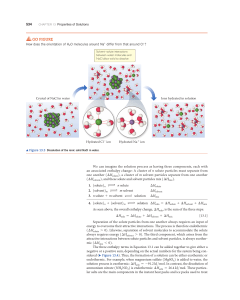
... universe is constant. In other words, energy can be neither destroyed nor created. This idea can be expressed by the following equation: ∆Euniverse = 0 Energy can, however, be transferred from one substance to another. It can also be converted into various forms. In order to interpret energy changes ...
... universe is constant. In other words, energy can be neither destroyed nor created. This idea can be expressed by the following equation: ∆Euniverse = 0 Energy can, however, be transferred from one substance to another. It can also be converted into various forms. In order to interpret energy changes ...
View/Open
... enthalpy. Therefore the amount of heat change during a reaction at constant temperature and pressure may also be called enthalpy change. Its value depends upon the number of moles of the reactants which have reacted in the given chemical reaction. Thus, Heat of reaction may be defined as the amount ...
... enthalpy. Therefore the amount of heat change during a reaction at constant temperature and pressure may also be called enthalpy change. Its value depends upon the number of moles of the reactants which have reacted in the given chemical reaction. Thus, Heat of reaction may be defined as the amount ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry
... 5.3.3. III.5.3.3 Purification of contaminated alum with recrystallization ............. 54 5.4. III.5.4 Distillation, sublimation .............................................................................. 54 5.4.1. III.5.4.1 Experimental task: Fractional distillation of a methanol-water mixture ...
... 5.3.3. III.5.3.3 Purification of contaminated alum with recrystallization ............. 54 5.4. III.5.4 Distillation, sublimation .............................................................................. 54 5.4.1. III.5.4.1 Experimental task: Fractional distillation of a methanol-water mixture ...
AP Chemistry - Siva Kodali
... MAY HAVE CHANGED OR DISAPPEARED BETWEEN WHEN THIS WORK WAS WRITTEN AND WHEN IT IS READ. For general information on our other products and services, please contact our Customer Care Department within the U.S. at 800-762-2974, outside the U.S. at 317-572-3993, or fax 317-572-4002. For technical suppor ...
... MAY HAVE CHANGED OR DISAPPEARED BETWEEN WHEN THIS WORK WAS WRITTEN AND WHEN IT IS READ. For general information on our other products and services, please contact our Customer Care Department within the U.S. at 800-762-2974, outside the U.S. at 317-572-3993, or fax 317-572-4002. For technical suppor ...
Ch20 Lesson20_3
... To use this method, start with the skeleton equation for the redox reaction. Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) → Fe(s) + CO2(g) (unbalanced) In a blast furnace, air is blown through a combination of iron ore and coke. The carbon monoxide produced from the oxidation of coke reduces the Fe3+ ions to metallic iron. ...
... To use this method, start with the skeleton equation for the redox reaction. Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) → Fe(s) + CO2(g) (unbalanced) In a blast furnace, air is blown through a combination of iron ore and coke. The carbon monoxide produced from the oxidation of coke reduces the Fe3+ ions to metallic iron. ...
Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Chemistry Syllabus code 9701
... handle information, distinguishing the relevant from the extraneous ...
... handle information, distinguishing the relevant from the extraneous ...
Surface and sub-surface reactions during low temperature
... Plasma processes generate reactive radicals and ions in the gas phase that function to modify or coat polymers, or activate nonreactive surfaces to promote film nucleation.1,2,16,17 However, plasma-generated radicals and ultraviolet radiation can also act to break down and degrade polymers. Recent i ...
... Plasma processes generate reactive radicals and ions in the gas phase that function to modify or coat polymers, or activate nonreactive surfaces to promote film nucleation.1,2,16,17 However, plasma-generated radicals and ultraviolet radiation can also act to break down and degrade polymers. Recent i ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.