CHE 1401 - Summer 2012 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... B) A negative ΔH corresponds to an exothermic process. C) ΔE = Efinal - Einitial D) Energy lost by the system must be gained by the surroundings. E) 1 cal = 4.184 J (exactly) 9) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat requir ...
... B) A negative ΔH corresponds to an exothermic process. C) ΔE = Efinal - Einitial D) Energy lost by the system must be gained by the surroundings. E) 1 cal = 4.184 J (exactly) 9) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat requir ...
LESSON 23: Exploding Bags
... chemical reaction are called reactants. The new substance(s) that are produced as a result of the reaction are called products. In this experiment, adding baking soda to vinegar starts a chemical reaction. The reaction produces sodium acetate and carbonic acid. The carbonic acid is unstable and inst ...
... chemical reaction are called reactants. The new substance(s) that are produced as a result of the reaction are called products. In this experiment, adding baking soda to vinegar starts a chemical reaction. The reaction produces sodium acetate and carbonic acid. The carbonic acid is unstable and inst ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... 2) Which one of the following conditions would always result in an increase in the internal energy of a system? A) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system gains heat and does work on the su ...
... 2) Which one of the following conditions would always result in an increase in the internal energy of a system? A) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system gains heat and does work on the su ...
Chemical Equations - Salem Community Schools
... Is the equation balanced now? Two sodium atoms are on each side. How many oxygen atoms are on each side? You should be able to find four on each side. How about hydrogen atoms? Now two are on each side. Because one carbon atom is still on each side, the entire equation is balanced; it now represents ...
... Is the equation balanced now? Two sodium atoms are on each side. How many oxygen atoms are on each side? You should be able to find four on each side. How about hydrogen atoms? Now two are on each side. Because one carbon atom is still on each side, the entire equation is balanced; it now represents ...
2009 - NESACS
... crucial in creating C-12 but for a split second, 2 He−4 particles fuse to make Be-8 which is then struck by a third α particle, creating C-12. This improbable sequence is called the triple-alpha process because the net effect is to combine 3 α particles (He nuclei) to form a C-12 nucleus. This resul ...
... crucial in creating C-12 but for a split second, 2 He−4 particles fuse to make Be-8 which is then struck by a third α particle, creating C-12. This improbable sequence is called the triple-alpha process because the net effect is to combine 3 α particles (He nuclei) to form a C-12 nucleus. This resul ...
Hydrogen Bonding
... △S: Change in entropy (measure of the energy lost to disorder in system) △G: Change in free energy ...
... △S: Change in entropy (measure of the energy lost to disorder in system) △G: Change in free energy ...
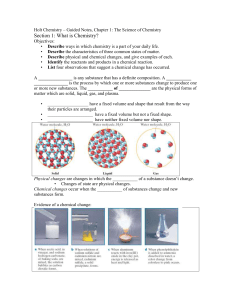
Holt Chemistry – Guided Notes, Chapter 1
... • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a chemical change has occurred. A _______________ is any substance that has a definite composition. A ___________ _______________ i ...
... • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a chemical change has occurred. A _______________ is any substance that has a definite composition. A ___________ _______________ i ...
Section 4.6: Double Displacement Reactions
... 7. Silver ions are the only metal ions that can be precipitated from a solution containing the C2H3O2− ions. Therefore, a solution such as NaC2H3O2(aq) can be used to precipitate silver ions from a mixture of dissolved metal ions. 8. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Most of the limescale that forms ...
... 7. Silver ions are the only metal ions that can be precipitated from a solution containing the C2H3O2− ions. Therefore, a solution such as NaC2H3O2(aq) can be used to precipitate silver ions from a mixture of dissolved metal ions. 8. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Most of the limescale that forms ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... Chapter 1 “Introduction: Matter and Measurement” Assignments Classification and Properties of Matter: Exercises: p.31: #11,15,16 11. Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture; if a mixture, indicate whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous: a) rice pudding b) seawater c) magn ...
... Chapter 1 “Introduction: Matter and Measurement” Assignments Classification and Properties of Matter: Exercises: p.31: #11,15,16 11. Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture; if a mixture, indicate whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous: a) rice pudding b) seawater c) magn ...
Stage 2 Chemistry Intended Student Learning 2014
... Topic 1: Elemental and Environmental Chemistry This topic deals with some of the underlying principles of chemistry (‘elemental chemistry’) and then considers the chemistry of the environment. The elemental chemistry component of the topic focuses on the periodic table and the concept of electroneg ...
... Topic 1: Elemental and Environmental Chemistry This topic deals with some of the underlying principles of chemistry (‘elemental chemistry’) and then considers the chemistry of the environment. The elemental chemistry component of the topic focuses on the periodic table and the concept of electroneg ...
Chemistry I Syllabus 2011-2012
... Essential Questions: 1. What specific properties of materials allow them to be classified as metals or nonmetals? 2. How is the relative mass of atoms determined? What does that indicate about the way in which they react? 3. What evidence is there for the existence of electrons and the nucleus? 4. H ...
... Essential Questions: 1. What specific properties of materials allow them to be classified as metals or nonmetals? 2. How is the relative mass of atoms determined? What does that indicate about the way in which they react? 3. What evidence is there for the existence of electrons and the nucleus? 4. H ...
Notes Unit 5-4
... a) _ Al + _ Pb(NO3)2 ---> _ Pb + _ Al(NO3)3 b) _ C3H8 + _ O2 ---> _ CO2 + _ H2O 2. A reaction yield 25%, how many grams of CO2 produced if the expected amount is 80g? ...
... a) _ Al + _ Pb(NO3)2 ---> _ Pb + _ Al(NO3)3 b) _ C3H8 + _ O2 ---> _ CO2 + _ H2O 2. A reaction yield 25%, how many grams of CO2 produced if the expected amount is 80g? ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.