chapter 4 review_package
... i. How many grams of aluminum oxide, Al2O3, would be expected to form in the reaction of 15.0g Al with 18.43g of oxygen gas? ...
... i. How many grams of aluminum oxide, Al2O3, would be expected to form in the reaction of 15.0g Al with 18.43g of oxygen gas? ...
Changes of State
... But the increased concentration of molecules in the vapor phase then increases the rate at which molecules reenter the liquid phase. the increased concentration (of molecules) (in the vapor phase) (then) increases the rate molecules reenter the liquid phase at the rate. ...
... But the increased concentration of molecules in the vapor phase then increases the rate at which molecules reenter the liquid phase. the increased concentration (of molecules) (in the vapor phase) (then) increases the rate molecules reenter the liquid phase at the rate. ...
AP Chemistry
... 2. breaking bonds takes energy chemical system gains bond energy; surroundings lose energy (heat, etc.) 3. forming bonds releases energy chemical system loses energy, surroundings gain energy 4. change in energy called “change in enthalpy”—H a. when energy required to break bonds > energy relea ...
... 2. breaking bonds takes energy chemical system gains bond energy; surroundings lose energy (heat, etc.) 3. forming bonds releases energy chemical system loses energy, surroundings gain energy 4. change in energy called “change in enthalpy”—H a. when energy required to break bonds > energy relea ...
1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
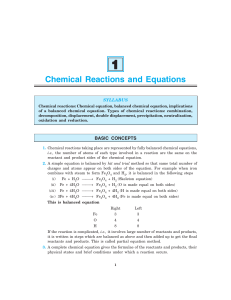
... If the reaction is complicated, i.e., it involves large number of reactants and products, it is written in steps which are balanced as above and then added up to get the final reactants and products. This is called partial equation method. 3. A complete chemical equation gives the formulae of the re ...
... If the reaction is complicated, i.e., it involves large number of reactants and products, it is written in steps which are balanced as above and then added up to get the final reactants and products. This is called partial equation method. 3. A complete chemical equation gives the formulae of the re ...
Ch 5 HEAT IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chemical reactions and the
... We can easily measure the change in enthalpy of a chemical reaction. This is called: ∆Hrxn, or enthalpy (heat) of reaction and is equal to heat absorbed or released in a chemical rxn (assuming constant pressure) ∆ Hrxn = Hproducts - Hreactants Endothermic reactions have a positive ∆ H, meaning the H ...
... We can easily measure the change in enthalpy of a chemical reaction. This is called: ∆Hrxn, or enthalpy (heat) of reaction and is equal to heat absorbed or released in a chemical rxn (assuming constant pressure) ∆ Hrxn = Hproducts - Hreactants Endothermic reactions have a positive ∆ H, meaning the H ...
Chemistry
... (iii) Base dissociation constants, Kb (iv) The ionic product of water, Kw (v) pH: choice of indicators (vi) Buffer solutions Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) explain, in terms of rates of the forward and reverse reactions, what is meant by a reversible reaction and dynamic equilib ...
... (iii) Base dissociation constants, Kb (iv) The ionic product of water, Kw (v) pH: choice of indicators (vi) Buffer solutions Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) explain, in terms of rates of the forward and reverse reactions, what is meant by a reversible reaction and dynamic equilib ...
enzymatic hydrolysis of sunflower oil in sc co2
... To compare between reactions in high-pressure batch and continuous system, enzymecatalyzed hydrolysis of sunflower oil was also performed in high-pressure flat-shape membrane reactor. Polysulfone and nylon membranes served as a separation unit to retain the biocatalyst in the reactor. In the high-p ...
... To compare between reactions in high-pressure batch and continuous system, enzymecatalyzed hydrolysis of sunflower oil was also performed in high-pressure flat-shape membrane reactor. Polysulfone and nylon membranes served as a separation unit to retain the biocatalyst in the reactor. In the high-p ...
answers to part a of the canadian chemistry
... answer in MB, compared with only 37% in AB). It requires students to choose the atom with the smallest atomic radius, which means that they need to know (1) that periods that are lower in the periodic table have larger atoms in them (because larger atoms have more electrons and some of these will be ...
... answer in MB, compared with only 37% in AB). It requires students to choose the atom with the smallest atomic radius, which means that they need to know (1) that periods that are lower in the periodic table have larger atoms in them (because larger atoms have more electrons and some of these will be ...
Which notation represents an atom of sodium
... d) nuclear fusion b For which compound is the process of dissolving in water exothermic? 22) ____ a) NaCl b) NaOH c) NH4Cl d) NH4NO3 b 23) ____ Which quantities must be equal for a chemical reaction at equilibrium? a) the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions b) the rates of the f ...
... d) nuclear fusion b For which compound is the process of dissolving in water exothermic? 22) ____ a) NaCl b) NaOH c) NH4Cl d) NH4NO3 b 23) ____ Which quantities must be equal for a chemical reaction at equilibrium? a) the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions b) the rates of the f ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.