K c
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
Chapter 19 Reaction Rates And Equilibrium
... Predict the direction the equilibrium will shift if: a) N2 is added? b) H2 is removed? c) NH3 is added? d) NH3 is removed? ...
... Predict the direction the equilibrium will shift if: a) N2 is added? b) H2 is removed? c) NH3 is added? d) NH3 is removed? ...
Chapter 7 Review
... 4.00 mol of ammonia gas are introduced into a 2.00 L container and heated. At equilibrium, 2.50 mol of ammonia remain in the container. a) Use an ICE table to determine the equilibrium concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen gas. (3) b) Plot the concentrations of these gases on the graph as the syst ...
... 4.00 mol of ammonia gas are introduced into a 2.00 L container and heated. At equilibrium, 2.50 mol of ammonia remain in the container. a) Use an ICE table to determine the equilibrium concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen gas. (3) b) Plot the concentrations of these gases on the graph as the syst ...
Calculating Enthalpy Changes
... small, this tells us that the equilibrium lies far to the right (products) or left (reactants), respectively. If the equilibrium constant is somewhere between 0.001 and 1000, then significant concentrations of both reactants and products will be present at equilibrium. We can calculate the equilibri ...
... small, this tells us that the equilibrium lies far to the right (products) or left (reactants), respectively. If the equilibrium constant is somewhere between 0.001 and 1000, then significant concentrations of both reactants and products will be present at equilibrium. We can calculate the equilibri ...
Second Semester Extra Review
... c) heat 4. What factors determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or not? 5. Calculate the Gibb’s free energy if the entropy is 0.555 kJ/mol K and enthalpy is 56.9 kJ/mol at 25C. Is this reaction spontaneous? 6. What factors affect rate of a reaction? 7. What are the two conditions to have an eff ...
... c) heat 4. What factors determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or not? 5. Calculate the Gibb’s free energy if the entropy is 0.555 kJ/mol K and enthalpy is 56.9 kJ/mol at 25C. Is this reaction spontaneous? 6. What factors affect rate of a reaction? 7. What are the two conditions to have an eff ...
Presentation by class of 2013
... Some reactions will only go to completion if: A) the activation energy (Ea) is low enough B) the products are more stable than the reactants Some reactions don’t happen at all because either: A) activation energy is too high B) products are less stable than the reactants Sometimes the reactants ...
... Some reactions will only go to completion if: A) the activation energy (Ea) is low enough B) the products are more stable than the reactants Some reactions don’t happen at all because either: A) activation energy is too high B) products are less stable than the reactants Sometimes the reactants ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... The equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction 2NO2 (g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) is 158 at 1000K. What is the equilibrium pressure of O2 if the PNO2 = 0.400 atm and PNO = 0.270 atm? ...
... The equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction 2NO2 (g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) is 158 at 1000K. What is the equilibrium pressure of O2 if the PNO2 = 0.400 atm and PNO = 0.270 atm? ...
Chemical equilibrium
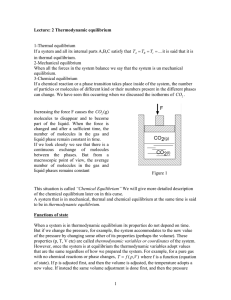
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.