2.0 Chem 20 Final Review
... ▫ Hydrogen nucleus (proton) is simultaneously attracted to two pairs of electrons; one closer (in the same molecule) and one further away (a lone pair on the next molecule) Why do you need a strongly electronegative atom? It pulls the hydrogen’s ...
... ▫ Hydrogen nucleus (proton) is simultaneously attracted to two pairs of electrons; one closer (in the same molecule) and one further away (a lone pair on the next molecule) Why do you need a strongly electronegative atom? It pulls the hydrogen’s ...
physical setting chemistry
... physical reaction (2) generates its own energy from a nonspontaneous physical reaction (3) requires an outside energy source for a spontaneous chemical reaction to occur (4) requires an outside energy source for a nonspontaneous chemical reaction to occur ...
... physical reaction (2) generates its own energy from a nonspontaneous physical reaction (3) requires an outside energy source for a spontaneous chemical reaction to occur (4) requires an outside energy source for a nonspontaneous chemical reaction to occur ...
Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... Solid aluminum carbide, Al4C3, reacts with water to produce methane gas and solid aluminum hydroxide. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. ...
... Solid aluminum carbide, Al4C3, reacts with water to produce methane gas and solid aluminum hydroxide. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. ...
METO 637
... • The nitrate radical was first observed in 1881. It is formed by the reaction: NO2 + O3 → NO3 + O2 • It can be stored as Nitrogen Pentoxide N2O5 • During the day the NO3 radical is rapidly photolyzed, the product being either NO or NO2. • Although the OH radical is usually the main agent of attack ...
... • The nitrate radical was first observed in 1881. It is formed by the reaction: NO2 + O3 → NO3 + O2 • It can be stored as Nitrogen Pentoxide N2O5 • During the day the NO3 radical is rapidly photolyzed, the product being either NO or NO2. • Although the OH radical is usually the main agent of attack ...
Chapter 6 - Sites @ Suffolk University
... : When hydrogen molecules and oxygen molecules react to form water molecules, the atoms form different bonds to make new molecules. The total number of atoms remains the same because the same atoms are present before and after the reaction. But this equation as we have written it is an unbalanced eq ...
... : When hydrogen molecules and oxygen molecules react to form water molecules, the atoms form different bonds to make new molecules. The total number of atoms remains the same because the same atoms are present before and after the reaction. But this equation as we have written it is an unbalanced eq ...
Periodic Trends in Monoatomic Chemisorbate
... was chosen so to enable positive potentials to be accessed, at which strong halide chemisorption occurs. The halide concentration was typically 10 mM, although varying this over the range 5-100 mM yielded similar results. Representative potential-dependent sets of SER spectra for chloride and bromid ...
... was chosen so to enable positive potentials to be accessed, at which strong halide chemisorption occurs. The halide concentration was typically 10 mM, although varying this over the range 5-100 mM yielded similar results. Representative potential-dependent sets of SER spectra for chloride and bromid ...
Document
... Mass of starting atoms is Mass of desired product is CuO = 63.5 + 16 = 79.5 CuSO4 = 63.5 + 32 + 64 = 159.5 H2SO4 = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98 Total = 177.5 ...
... Mass of starting atoms is Mass of desired product is CuO = 63.5 + 16 = 79.5 CuSO4 = 63.5 + 32 + 64 = 159.5 H2SO4 = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98 Total = 177.5 ...
Harrisburg Area Community College 2013/2014
... the precision of data and results without having to specifically identify all devices used and the exact procedures. The reader merely looks at the number to see how well it was measured. An illustration of how this works follows: Two students are asked to count the amount of money in a bag that’s i ...
... the precision of data and results without having to specifically identify all devices used and the exact procedures. The reader merely looks at the number to see how well it was measured. An illustration of how this works follows: Two students are asked to count the amount of money in a bag that’s i ...
Chapter 4
... the molarity desired for a particular solution. Dilution with water does not alter the numbers of moles of solute present. Moles of solute before dilution = moles of solute after dilution M1V1 = M2V2 Return to TOC ...
... the molarity desired for a particular solution. Dilution with water does not alter the numbers of moles of solute present. Moles of solute before dilution = moles of solute after dilution M1V1 = M2V2 Return to TOC ...
Naming Binary Molecular Compounds
... • Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound. • Use molar mass to convert between mass in grams and amount in moles of a chemical compound. • Calculate the # of molecules, formula units, or ions in a given molar amount of a chemical compound. •Calculate the % composition of a giv ...
... • Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound. • Use molar mass to convert between mass in grams and amount in moles of a chemical compound. • Calculate the # of molecules, formula units, or ions in a given molar amount of a chemical compound. •Calculate the % composition of a giv ...
chapter 7-Chemical Bonding
... • Na+ sodium ion, Ca2+, Al3+ -- cations • Cl- chloride ion, O2-, N3- -- anions ...
... • Na+ sodium ion, Ca2+, Al3+ -- cations • Cl- chloride ion, O2-, N3- -- anions ...
KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM
... a. During a certain unit of time, the rate at which the product is made is equal to the rate at which the Product is broken down b. This results in the mass of each substance remaining constant at ...
... a. During a certain unit of time, the rate at which the product is made is equal to the rate at which the Product is broken down b. This results in the mass of each substance remaining constant at ...
b - PianetaChimica
... with hydrogen gas to prevent reaction with air. Fiona also learnt that even a small amount of dissolved oxygen could affect the titration. To her unknown iron(III) solution, she added saturated sodium carbonate solution, forming a rusty yellow precipitate, followed by dilute hydrochloric acid soluti ...
... with hydrogen gas to prevent reaction with air. Fiona also learnt that even a small amount of dissolved oxygen could affect the titration. To her unknown iron(III) solution, she added saturated sodium carbonate solution, forming a rusty yellow precipitate, followed by dilute hydrochloric acid soluti ...
134_2010_1897_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... according to Watson [3], ∆G can be calculated for each reaction. For reaction (1), ∆G(1) = 2.303∙RT (log{[HA]∙[HCO3-]}/{[A-]∙pCO2}– log K(1)) = -437 cal/mol, and composed constant K(1) = 4.359E-05 (Kc1/Ka). For reaction (2), ∆G(2) = 2.303∙RT (log [HCO3-]2 /{[CO32-]∙pCO2}– log K(2)) = -427 cal/mol, ...
... according to Watson [3], ∆G can be calculated for each reaction. For reaction (1), ∆G(1) = 2.303∙RT (log{[HA]∙[HCO3-]}/{[A-]∙pCO2}– log K(1)) = -437 cal/mol, and composed constant K(1) = 4.359E-05 (Kc1/Ka). For reaction (2), ∆G(2) = 2.303∙RT (log [HCO3-]2 /{[CO32-]∙pCO2}– log K(2)) = -427 cal/mol, ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... stable configuration. It can gain these electrons, for example, by combining with four hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom has one electron in its outer shell and requires one electron to reach a stable configuration. The carbon atom shares one electron with each hydrogen atom, forming four covalent ...
... stable configuration. It can gain these electrons, for example, by combining with four hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom has one electron in its outer shell and requires one electron to reach a stable configuration. The carbon atom shares one electron with each hydrogen atom, forming four covalent ...
Chapter 5 Chemical Equilibrium 1 State whether each of the
... pressure is decreased? Why? The equilibrium will shift to the left to increase the pressure, since thee are 1.5 moles of gas on the left and only 1 mole of gas on the right. 11. Graphite is the standard state of carbon. Why do diamonds exist at 25cC and 1 atm? Diamond is thermodynamically unstable, ...
... pressure is decreased? Why? The equilibrium will shift to the left to increase the pressure, since thee are 1.5 moles of gas on the left and only 1 mole of gas on the right. 11. Graphite is the standard state of carbon. Why do diamonds exist at 25cC and 1 atm? Diamond is thermodynamically unstable, ...
Electrons
... • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
... • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
homework_#1_10
... Interpret the balanced equation in terms of relative numbers of moles, volumes of gases at STP and masses of reactants and products. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2 (g) ...
... Interpret the balanced equation in terms of relative numbers of moles, volumes of gases at STP and masses of reactants and products. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2 (g) ...
COMMUNICATIONS
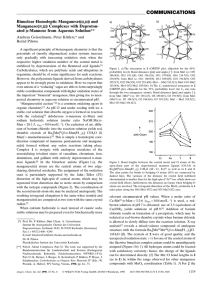
... in the range of pH 9 to 12 the pH dependence corresponds to an addition of about one proton to the reduced form (dilution is much larger in the voltammetric investigation than for other experiments; thus, protolysis reactions are more important). ...
... in the range of pH 9 to 12 the pH dependence corresponds to an addition of about one proton to the reduced form (dilution is much larger in the voltammetric investigation than for other experiments; thus, protolysis reactions are more important). ...
Document
... i) State the observations made whenever the lid was lifted during the early stages of the ...
... i) State the observations made whenever the lid was lifted during the early stages of the ...
CLASS X carbon and its compound
... The process of rapid burning of carbon or its compounds in air/oxygen, with the release of a large amount of energy and formation of carbon dioxide and water is called combustion. Coal and petroleum are formed when organic matter (plants and animals) got buried deep inside the earth and then decompo ...
... The process of rapid burning of carbon or its compounds in air/oxygen, with the release of a large amount of energy and formation of carbon dioxide and water is called combustion. Coal and petroleum are formed when organic matter (plants and animals) got buried deep inside the earth and then decompo ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.