chem - CBSE Guess
... Ans. The copper vessel will be corroded and a green layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 will be deposited on the copper vessel. Q. Explain what corrosion of iron means.? 1 Ans see page 1 Q. Why is sodium or potassium metals are kept immersed in kerosene oil?. 1 Ans.Sodium and potassium met ...
... Ans. The copper vessel will be corroded and a green layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 will be deposited on the copper vessel. Q. Explain what corrosion of iron means.? 1 Ans see page 1 Q. Why is sodium or potassium metals are kept immersed in kerosene oil?. 1 Ans.Sodium and potassium met ...
Chemistry and electronic properties of metal
... core of the molecule. Oxygen-related levels are 1–3 eV below the centroid of the HOMO. This is in contrast with a previous report that attributed the HOMO to the p bonding of the anhydride group.34 The determination of filled and empty states of a molecular solid via electron spectroscopies can be a ...
... core of the molecule. Oxygen-related levels are 1–3 eV below the centroid of the HOMO. This is in contrast with a previous report that attributed the HOMO to the p bonding of the anhydride group.34 The determination of filled and empty states of a molecular solid via electron spectroscopies can be a ...
File
... Amphoteric- substance that can act as both an acid and a base, e.g. water. Acid -Base Theories Svante Arrhenius- acids yield H+ ions and bases yield OH- ions. Johannes Brønsted - Thomas Lowry - acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. ...
... Amphoteric- substance that can act as both an acid and a base, e.g. water. Acid -Base Theories Svante Arrhenius- acids yield H+ ions and bases yield OH- ions. Johannes Brønsted - Thomas Lowry - acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. ...
LESSON 23: Exploding Bags
... acids and bases and use two common household substances to observe a chemical reaction. OBSERVATION & RESEARCH To describe certain chemical compounds, chemists use the terms “acid” and “base.” You can determine whether a solution is an acid or a base by determining the concentration of hydrogen ions ...
... acids and bases and use two common household substances to observe a chemical reaction. OBSERVATION & RESEARCH To describe certain chemical compounds, chemists use the terms “acid” and “base.” You can determine whether a solution is an acid or a base by determining the concentration of hydrogen ions ...
Chemistry in Society - Cathkin High School
... Crude oil is a raw material from which naphtha is obtained by fractional distillation. Naphtha is a feedstock that can be cracked to produce ethene. Batch and Continuous Processes In a batch process the chemicals are loaded into the reaction vessel. The reaction is monitored and at the end of the re ...
... Crude oil is a raw material from which naphtha is obtained by fractional distillation. Naphtha is a feedstock that can be cracked to produce ethene. Batch and Continuous Processes In a batch process the chemicals are loaded into the reaction vessel. The reaction is monitored and at the end of the re ...
Complete Solution Manual
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
H2 Chemistry Syllabus (9729)
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O Level, students have been i ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O Level, students have been i ...
Unit 3 Homework Booklet
... Two chemicals A and B react in solution to form C. The reaction has an activation energy of 150 kJ mol-1. If hydrogen ions are used as a catalyst the activation energy is 50 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the reaction is -125 kJ mol-1. Present this information as a potential energy diagram using ...
... Two chemicals A and B react in solution to form C. The reaction has an activation energy of 150 kJ mol-1. If hydrogen ions are used as a catalyst the activation energy is 50 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the reaction is -125 kJ mol-1. Present this information as a potential energy diagram using ...
1. You should review balancing equations and identifying types of
... 1. You should review balancing equations and identifying types of reactions from the worksheets. In addition you should be able to write balanced chemical equations for reactions. Try to write, balance, and identify the types of the following reactions: a. the decomposition of ammonium nitrate to ni ...
... 1. You should review balancing equations and identifying types of reactions from the worksheets. In addition you should be able to write balanced chemical equations for reactions. Try to write, balance, and identify the types of the following reactions: a. the decomposition of ammonium nitrate to ni ...
File
... Describe a chemical test to show that the fat is unsaturated. name of reagent ................................................................................................................ result of test .............................................................................................. ...
... Describe a chemical test to show that the fat is unsaturated. name of reagent ................................................................................................................ result of test .............................................................................................. ...
Full answers
... As 1.0 L of water is present, the initial concentrations of the ions are [Na+(aq)] = 0.086 M, [Cl-(aq)] = 0.086 M and [Ag+(aq)] = 0.029 mol. The Na+(aq) will form any precipitate with the ions present: [Na+(aq)] = 0.086 M. The ionic product for the precipitation of AgCl(s) is given by: Qsp = [Ag+(aq ...
... As 1.0 L of water is present, the initial concentrations of the ions are [Na+(aq)] = 0.086 M, [Cl-(aq)] = 0.086 M and [Ag+(aq)] = 0.029 mol. The Na+(aq) will form any precipitate with the ions present: [Na+(aq)] = 0.086 M. The ionic product for the precipitation of AgCl(s) is given by: Qsp = [Ag+(aq ...
Final competitions (29.03.2008) Competing equilibria Complex
... moles, which is equal to 2,17·10−3 mola × 419,8 g/mol = 0,911 g of KI3. It was given in the text that 0,950g of salt A was used for titration, so the salt A is salt hydrate containing 0,950g − 0,911 g = 0,039 g of water which is equal to n(H2O) = 0,039 g / 18,02 g/mol = 2,17·10−3 moles of H2O. In co ...
... moles, which is equal to 2,17·10−3 mola × 419,8 g/mol = 0,911 g of KI3. It was given in the text that 0,950g of salt A was used for titration, so the salt A is salt hydrate containing 0,950g − 0,911 g = 0,039 g of water which is equal to n(H2O) = 0,039 g / 18,02 g/mol = 2,17·10−3 moles of H2O. In co ...
Document
... Which statement is true if 12 moles of CO and 12 moles of Fe2O3 are allowed to react? 3CO(g) + Fe2O3(s) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) a. The limiting reactant is CO and 8.0 mol Fe will be formed. b. The limiting reactant is Fe2O3 and 24 mol Fe will be formed. c. The limiting reactant is CO and 3.0 mol CO2 will ...
... Which statement is true if 12 moles of CO and 12 moles of Fe2O3 are allowed to react? 3CO(g) + Fe2O3(s) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) a. The limiting reactant is CO and 8.0 mol Fe will be formed. b. The limiting reactant is Fe2O3 and 24 mol Fe will be formed. c. The limiting reactant is CO and 3.0 mol CO2 will ...
Complete Solution Manual
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
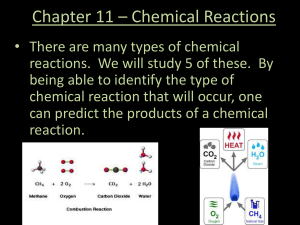
Chapter 11 * Chemical Reactions
... reactions. We will study 5 of these. By being able to identify the type of chemical reaction that will occur, one can predict the products of a chemical reaction. ...
... reactions. We will study 5 of these. By being able to identify the type of chemical reaction that will occur, one can predict the products of a chemical reaction. ...
physical setting chemistry
... and particle size. These properties can be used to (1) separate the substances (2) chemically combine the substances (3) determine the freezing point of the mixture (4) predict the electrical conductivity of the mixture P.S./Chem.–Jan. ’15 ...
... and particle size. These properties can be used to (1) separate the substances (2) chemically combine the substances (3) determine the freezing point of the mixture (4) predict the electrical conductivity of the mixture P.S./Chem.–Jan. ’15 ...
PPT - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... not appear in the overall stoichiometry of the reaction. If a mechanism has several elementary steps, then the overall rate is determined by t he slowest step, called the rate-determining step. ...
... not appear in the overall stoichiometry of the reaction. If a mechanism has several elementary steps, then the overall rate is determined by t he slowest step, called the rate-determining step. ...
kinetics and equilibrium
... • Misconceptions about Entropy • This view of the second law of thermodynamics is very popular, and it has been misused. Some argue that the second law of thermodynamics means that a system can never become more orderly. Not true. It just means that in order to become more orderly (for entropy to d ...
... • Misconceptions about Entropy • This view of the second law of thermodynamics is very popular, and it has been misused. Some argue that the second law of thermodynamics means that a system can never become more orderly. Not true. It just means that in order to become more orderly (for entropy to d ...
Chemistry - Ysgol Bro Pedr
... would have been the next step. We can now write the fully balanced equation: 2Na(s) ...
... would have been the next step. We can now write the fully balanced equation: 2Na(s) ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.