THE FREE ENERGIES OF FORMATION OF AQUEOUS d
... restricted, until recently, to the use of first law data. In the last few years a beginning has been made in the application of the second law; i.e., of free energy data (1, 2). The development of this field is limited by the paucity of available free energy data. We have therefore undertaken the sy ...
... restricted, until recently, to the use of first law data. In the last few years a beginning has been made in the application of the second law; i.e., of free energy data (1, 2). The development of this field is limited by the paucity of available free energy data. We have therefore undertaken the sy ...
Useful Rocks - Prairie Rose School Division No. 8
... • Three-quarters of the salt we use comes from rock salt. • As the earth’s surface changed stretches of sea-water became landlocked. • Evaporation of this water along with further geological changes led to deposits of rock salt in many countries including the UK. ...
... • Three-quarters of the salt we use comes from rock salt. • As the earth’s surface changed stretches of sea-water became landlocked. • Evaporation of this water along with further geological changes led to deposits of rock salt in many countries including the UK. ...
Useful Rocks - We can`t sign you in
... • Three-quarters of the salt we use comes from rock salt. • As the earth’s surface changed stretches of sea-water became landlocked. • Evaporation of this water along with further geological changes led to deposits of rock salt in many countries including the UK. ...
... • Three-quarters of the salt we use comes from rock salt. • As the earth’s surface changed stretches of sea-water became landlocked. • Evaporation of this water along with further geological changes led to deposits of rock salt in many countries including the UK. ...
REDOX ZONATION IN THE PHANEROZOIC ANOXIC OCEAN Part I
... various "black" shales or sapropels in the general geologic record [Demaison and Moore, 1980] and particularly in the Paleozoic [Berry and Wilde, 1978] and in the Mesozoic [eg. Arthur and Schlanger, 1979; Arthur, Schlanger and Jenkyns, 1987; Brass et al., 1982; Hallan, 1981, 1986; Jenkyns, 1980; Rya ...
... various "black" shales or sapropels in the general geologic record [Demaison and Moore, 1980] and particularly in the Paleozoic [Berry and Wilde, 1978] and in the Mesozoic [eg. Arthur and Schlanger, 1979; Arthur, Schlanger and Jenkyns, 1987; Brass et al., 1982; Hallan, 1981, 1986; Jenkyns, 1980; Rya ...
CHAPTER TWO ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isotopes of hydrogen have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons in the nucleus. Because we are talking about atoms, this implies a neutral charge which dictates 1 electron present for all hydro ...
... neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isotopes of hydrogen have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons in the nucleus. Because we are talking about atoms, this implies a neutral charge which dictates 1 electron present for all hydro ...
Energy Matters - Perth Grammar
... Powdered silver metal behaves as a heterogeneous catalyst in the decomposition of ‘5 volume’ hydrogen peroxide solution to give water and oxygen as the only products. Note: Concentrations of peroxide solutions are quoted by ‘volume number’ with higher numbers relating to solutions of greater concent ...
... Powdered silver metal behaves as a heterogeneous catalyst in the decomposition of ‘5 volume’ hydrogen peroxide solution to give water and oxygen as the only products. Note: Concentrations of peroxide solutions are quoted by ‘volume number’ with higher numbers relating to solutions of greater concent ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... Characteristics of Chemical Equations • The following 3 requirements will aid you in writing and reading chemical equations correctly: 1. The equation must represent known facts. 2. The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. 3. The Law of conservation of mass must ...
... Characteristics of Chemical Equations • The following 3 requirements will aid you in writing and reading chemical equations correctly: 1. The equation must represent known facts. 2. The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. 3. The Law of conservation of mass must ...
Ch 13 kinetics
... More than a balanced chemical equation, a reaction mechanism ________________________________________ . Provides a detailed picture of how a reaction occurs. Elementary step: Any process that occurs ____________________________________________________________________ Makes either ___________________ ...
... More than a balanced chemical equation, a reaction mechanism ________________________________________ . Provides a detailed picture of how a reaction occurs. Elementary step: Any process that occurs ____________________________________________________________________ Makes either ___________________ ...
Introductory Electricity - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... 2. Find the electric potential at the point (0, 2). 3. Find the electric potential at the point (1, 2). 4. Find the electric potential energy of this configuration. Exercise 4 − The Electric Potential, Part II 1. Recall that the potential is defined as the integral of the electric field. What is th ...
... 2. Find the electric potential at the point (0, 2). 3. Find the electric potential at the point (1, 2). 4. Find the electric potential energy of this configuration. Exercise 4 − The Electric Potential, Part II 1. Recall that the potential is defined as the integral of the electric field. What is th ...
I 1 Chemical Reaction Cross Sections I and Rate Constants
... absorption of light when the concentration of the light absorbing species is expressed in number of molecules per unit volume. From eqn. (14) [or (13)] we see that to each impact parameter b there corresponds a particular scattering angle 0 if p, v , and the equation for the potential, V(r), are giv ...
... absorption of light when the concentration of the light absorbing species is expressed in number of molecules per unit volume. From eqn. (14) [or (13)] we see that to each impact parameter b there corresponds a particular scattering angle 0 if p, v , and the equation for the potential, V(r), are giv ...
CHAPTER TWO ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS For Review 1. a
... neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isotopes of hydrogen have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons in the nucleus. Because we are talking about atoms, this implies a neutral charge which dictates 1 electron present for all hydro ...
... neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isotopes of hydrogen have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons in the nucleus. Because we are talking about atoms, this implies a neutral charge which dictates 1 electron present for all hydro ...
Document
... temperature to 500°C. How can the reaction counteract the change you have made? How can it cool itself down again? • To cool down, it needs to absorb the extra heat that you have just put in. In the case we are looking at, the back reaction absorbs heat. The position of equilibrium therefore moves t ...
... temperature to 500°C. How can the reaction counteract the change you have made? How can it cool itself down again? • To cool down, it needs to absorb the extra heat that you have just put in. In the case we are looking at, the back reaction absorbs heat. The position of equilibrium therefore moves t ...
Review #7: Solutions, Acids and Bases 1. Definitions: a) Solution: a
... not have H+ ions. Because there are no H+ ions, these substances are not acids. However, when these substances are dissolved in water, the water allows the substances to ionize and form H+ ions. After these substances have dissolved in water and ionized to form H+ ions, they are then considered to b ...
... not have H+ ions. Because there are no H+ ions, these substances are not acids. However, when these substances are dissolved in water, the water allows the substances to ionize and form H+ ions. After these substances have dissolved in water and ionized to form H+ ions, they are then considered to b ...
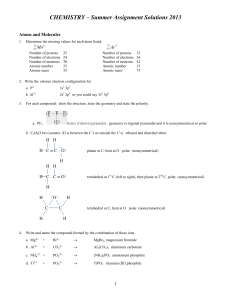
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, the carbonic acid that is formed immediately breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. What mass of sodium carbonate would have been originally present if 5.0 L of carbon dioxide was produced? [hint - molar volume of a gas is 22.414 L/mol] Na2CO3 ...
... When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, the carbonic acid that is formed immediately breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. What mass of sodium carbonate would have been originally present if 5.0 L of carbon dioxide was produced? [hint - molar volume of a gas is 22.414 L/mol] Na2CO3 ...
Slide 1 - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... • The high field desorbs the hydrogen on the silicon surface and enables exposed silicon to oxidize in air (the oxidation rate is enhanced by the presence of the accelerating field). • That is, the negatively biased tip induces a high electric field which ionizes the water molecules from the ambient ...
... • The high field desorbs the hydrogen on the silicon surface and enables exposed silicon to oxidize in air (the oxidation rate is enhanced by the presence of the accelerating field). • That is, the negatively biased tip induces a high electric field which ionizes the water molecules from the ambient ...
File
... _______17. How many moles are there in 3.40 grams of ammonia, NH 3 ? A) 57.8 B) 2.00 C) 5.00 D) 0.461 E) 0.200 _______18. 0.150 mole of propanone has a mass of 8.7 grams. What is the molar mass of propanone? (in grams/mol) A) 1.3 B) 17 C) 58 D) 8.7 _______19. Which of the following contains 3.01 x 1 ...
... _______17. How many moles are there in 3.40 grams of ammonia, NH 3 ? A) 57.8 B) 2.00 C) 5.00 D) 0.461 E) 0.200 _______18. 0.150 mole of propanone has a mass of 8.7 grams. What is the molar mass of propanone? (in grams/mol) A) 1.3 B) 17 C) 58 D) 8.7 _______19. Which of the following contains 3.01 x 1 ...
Document
... The standard enthalpy of formation, DHf°, is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of the substance from its elements in their reference forms and in their standard states. DHf° for an element in its reference and standard state is zero. For example, the standard enthalpy of formation f ...
... The standard enthalpy of formation, DHf°, is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of the substance from its elements in their reference forms and in their standard states. DHf° for an element in its reference and standard state is zero. For example, the standard enthalpy of formation f ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Academic Success Center Science Tutoring Area *
... remove the denominator of the fraction to have the final balanced equation with whole number coefficients ...
... remove the denominator of the fraction to have the final balanced equation with whole number coefficients ...
View PDF
... ____ 24. In the equation 2Al(s) + 3Fe(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) → 3Fe(s) + 2Al(NO 3 ) 3 (aq), iron has been replaced by a. nitrate. c. aluminum. b. water. d. nitrogen. ____ 25. If a certain metal is placed in an ionic solution containing another metal and no reaction occurs, then the metal originally in the sol ...
... ____ 24. In the equation 2Al(s) + 3Fe(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) → 3Fe(s) + 2Al(NO 3 ) 3 (aq), iron has been replaced by a. nitrate. c. aluminum. b. water. d. nitrogen. ____ 25. If a certain metal is placed in an ionic solution containing another metal and no reaction occurs, then the metal originally in the sol ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.