I PUC Chemistry Mock Paper
... 21. Write any three differences between sigma and pi bond. 22. Based on molecular orbital theory, Write the electronic configuration of Lithium molecule and calculate bond order. 23. Balance the following equation by half reaction method. MnO4– (aq) + I– (aq) -------------------> MnO2(s) + I2 (s) ( ...
... 21. Write any three differences between sigma and pi bond. 22. Based on molecular orbital theory, Write the electronic configuration of Lithium molecule and calculate bond order. 23. Balance the following equation by half reaction method. MnO4– (aq) + I– (aq) -------------------> MnO2(s) + I2 (s) ( ...
Reactions and Equations
... a chemical reaction by an equation, the equation must show equal numbers of atoms of each reactant and each product on both sides of the arrow. • Such an equation is called a balanced chemical equation. ...
... a chemical reaction by an equation, the equation must show equal numbers of atoms of each reactant and each product on both sides of the arrow. • Such an equation is called a balanced chemical equation. ...
Using mass to calculate molecular formula
... Benzene consists of 7.69% H and 92.31%C. Converting this to a formula gives CH. This is the simplest integer ratio. In fact a molecule of benzene has the formula C6H6. Empirical formula CH – simplest whole number ratio. Molecular formula C6H6 – actual number of atoms in the molecule. Percentages of ...
... Benzene consists of 7.69% H and 92.31%C. Converting this to a formula gives CH. This is the simplest integer ratio. In fact a molecule of benzene has the formula C6H6. Empirical formula CH – simplest whole number ratio. Molecular formula C6H6 – actual number of atoms in the molecule. Percentages of ...
NEW METHOD OF ELECTROSTATIC ACCELERATING AND
... It can also be used to create an efficient accumullatorcollider of accelerated deuterium and tritium ions for neutron generation in vacuum collisions of two merging beams for energy generation by means of sub-critical nuclear reactor driven by an accelerator [2-6] and for the transmutation of radioa ...
... It can also be used to create an efficient accumullatorcollider of accelerated deuterium and tritium ions for neutron generation in vacuum collisions of two merging beams for energy generation by means of sub-critical nuclear reactor driven by an accelerator [2-6] and for the transmutation of radioa ...
4 • Reactions In Aqueous Solution
... equation for the reaction of washing soda, Na2CO3 and vinegar, HC2H3O2. ...
... equation for the reaction of washing soda, Na2CO3 and vinegar, HC2H3O2. ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... 14.Draw the Lewis structure, illustrating the molecular geometry of the following molecules. (SR#2, p.207) a. SO2 b. CI4 c. Bl3 ...
... 14.Draw the Lewis structure, illustrating the molecular geometry of the following molecules. (SR#2, p.207) a. SO2 b. CI4 c. Bl3 ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... 22.5 mL of 0.383 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 20.0 mL of a KOH solution. Calculate the molarity of the KOH solution. H2SO4 + 2 KOH d K2SO4 + 2 H2O M KOH = (0.0225 L H2SO4)(0.383 mol H2SO4/L H2SO4)(2 mol KOH/ 1 mol H2SO4)/ (0.0200 mL KOH) = ...
... 22.5 mL of 0.383 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 20.0 mL of a KOH solution. Calculate the molarity of the KOH solution. H2SO4 + 2 KOH d K2SO4 + 2 H2O M KOH = (0.0225 L H2SO4)(0.383 mol H2SO4/L H2SO4)(2 mol KOH/ 1 mol H2SO4)/ (0.0200 mL KOH) = ...
All That Matters - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... with other substances. Will it burn? Does it dissolve in water? Does it produce bubbles of gas dropped into acid? All of these things allow us to tell the difference between water and alcohol, for example, and many other substances with the use of only one or two of our senses. List at least five of ...
... with other substances. Will it burn? Does it dissolve in water? Does it produce bubbles of gas dropped into acid? All of these things allow us to tell the difference between water and alcohol, for example, and many other substances with the use of only one or two of our senses. List at least five of ...
experiment 10 - Faculty Web Pages
... Consider this generalized reaction between two ionic compounds: AB + CD AD + CB where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ ...
... Consider this generalized reaction between two ionic compounds: AB + CD AD + CB where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ ...
EXAM # 1
... the electrode. Crystalline Membrane Electrode, Liquid Membrane Electrode or Enzyme electrodes are common examples ...
... the electrode. Crystalline Membrane Electrode, Liquid Membrane Electrode or Enzyme electrodes are common examples ...
Chemical Reaction
... Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
... Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
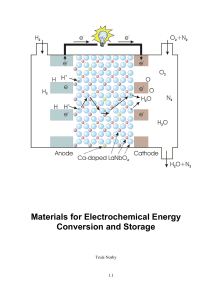
Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage
... A fuel cell is a galvanic cell in which the chemicals (fuel and oxidant) are continuously supplied to the electrodes. The fuel can be of fossil origin or come from renewable energy. With fossil origin we think primarily of gases produced from natural gas, oil, or coal. They comprise hydrogen, CO, me ...
... A fuel cell is a galvanic cell in which the chemicals (fuel and oxidant) are continuously supplied to the electrodes. The fuel can be of fossil origin or come from renewable energy. With fossil origin we think primarily of gases produced from natural gas, oil, or coal. They comprise hydrogen, CO, me ...
FORM 1 GEOGRAPHY REVISION GRID
... State that during a chemical change a new substance is made Recall the differences between a chemical and a physical change ...
... State that during a chemical change a new substance is made Recall the differences between a chemical and a physical change ...
1 Chemistry 201 Name Assignment 2 1. Consider the following
... Al2S3 + 6 H2O 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2S If 24.3 g of Al2S3 were reacted with an excess of H2O, then: a) What is the theoretical yield of Al(OH)3? b) What is the theoretical yield of H2S? 2. What mass of O2 is required for the complete combustion of 6.19 g of propane (C3H8) to produce CO2 and H2O? 3. An exce ...
... Al2S3 + 6 H2O 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2S If 24.3 g of Al2S3 were reacted with an excess of H2O, then: a) What is the theoretical yield of Al(OH)3? b) What is the theoretical yield of H2S? 2. What mass of O2 is required for the complete combustion of 6.19 g of propane (C3H8) to produce CO2 and H2O? 3. An exce ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Conversion Factor: Allows for the conversion from one unit of measure to another Covalent Bond: Bond formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. Deposition: Phase change from a gas to a solid Dipole-Dipole: Permanent IMF present in polar molecules Direct Relationship: Relationship between two ...
... Conversion Factor: Allows for the conversion from one unit of measure to another Covalent Bond: Bond formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. Deposition: Phase change from a gas to a solid Dipole-Dipole: Permanent IMF present in polar molecules Direct Relationship: Relationship between two ...
Periodic Table - personals.okan.edu.tr
... • - Chlorine react with water and hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid are produced : • Cl2(g) + H2O(l) HCl(aq) + HOCl(aq) • - Hypochlorous acid is an important desinfectant and used in swimming pools(Chlorine is added into the water). • - Halogenes react with plenty of metals to form metallic ...
... • - Chlorine react with water and hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid are produced : • Cl2(g) + H2O(l) HCl(aq) + HOCl(aq) • - Hypochlorous acid is an important desinfectant and used in swimming pools(Chlorine is added into the water). • - Halogenes react with plenty of metals to form metallic ...
CHEM 462 Inorganic/Organometallic Chemistry Fall 2016 Midterm
... “better” interaction? Explain your reasoning and why the solid state structure is the same or different from your conclusion. ...
... “better” interaction? Explain your reasoning and why the solid state structure is the same or different from your conclusion. ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Reactions and Solution
... 1. All soluble ionic compounds, including the soluble strong bases: These substances dissociate (separate) into their ions in water. 1. We will explore the general solubility guidelines for ionic compounds in lab. You will be expected to memorize a list of these to be handed out later. ...
... 1. All soluble ionic compounds, including the soluble strong bases: These substances dissociate (separate) into their ions in water. 1. We will explore the general solubility guidelines for ionic compounds in lab. You will be expected to memorize a list of these to be handed out later. ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.