Slide 1
... Acidic proton on a hydroxyl group bonded or coordinated to a central atom on which there is an oxo (=O) group ...
... Acidic proton on a hydroxyl group bonded or coordinated to a central atom on which there is an oxo (=O) group ...
50 frequently forgotten facts answer key
... 27) Network solids are substances that do not have distinct molecules or ions that can separate with heating. To melt a network solid, covalent bonds have to be broken. This takes tremendous energy, meaning that network solids have extremely high melting points. They are insoluble in water, and are ...
... 27) Network solids are substances that do not have distinct molecules or ions that can separate with heating. To melt a network solid, covalent bonds have to be broken. This takes tremendous energy, meaning that network solids have extremely high melting points. They are insoluble in water, and are ...
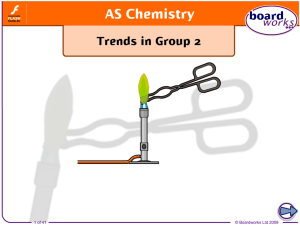
Groups 2 and 7
... When heated, the group 2 metal carbonates decompose to form the metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas. Splitting compounds using heat is called thermal decomposition. MCO3(s) MO(s) + CO2(g) ...
... When heated, the group 2 metal carbonates decompose to form the metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas. Splitting compounds using heat is called thermal decomposition. MCO3(s) MO(s) + CO2(g) ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts Answer Key
... 17) When metal atoms form ions, they lose all their valence electrons, and their dot diagrams are the metal symbol, in brackets, with no dots and the + charge on the upper right, outside the brackets. [P.T.] a) What is the electron configuration of a K+1 ion? _2-8-8-1, lose 1 e- t make +1 = 2-8-8__ ...
... 17) When metal atoms form ions, they lose all their valence electrons, and their dot diagrams are the metal symbol, in brackets, with no dots and the + charge on the upper right, outside the brackets. [P.T.] a) What is the electron configuration of a K+1 ion? _2-8-8-1, lose 1 e- t make +1 = 2-8-8__ ...
File
... results are listed below.• dissolves in water • is an electrolyte • melts at a high temperature Based on these results, the solid substance could be A) Cu B) CuBr2 C) C D) C6H12O6 86. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are A) transferred from one atom to another B) captured by the nucleus C) m ...
... results are listed below.• dissolves in water • is an electrolyte • melts at a high temperature Based on these results, the solid substance could be A) Cu B) CuBr2 C) C D) C6H12O6 86. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are A) transferred from one atom to another B) captured by the nucleus C) m ...
File
... Periodic Table and Ion Formation • Atoms gain and lose electrons to form bonds. When atoms become electrically charged particles, they are called ions. Metals lose electrons and become positive ions (called cations). Some metals (multivalent) lose electrons in different ways. For example, i ...
... Periodic Table and Ion Formation • Atoms gain and lose electrons to form bonds. When atoms become electrically charged particles, they are called ions. Metals lose electrons and become positive ions (called cations). Some metals (multivalent) lose electrons in different ways. For example, i ...
SCH 3U - othsmath
... 2) Going down a group, a new energy level is added with each subsequent atom, ensuring the valence electrons are moved further and further from the nucleus. This increases the shielding provided by non-valence electrons, decreases the ENC (even though the number of protons in the nucleus is increasi ...
... 2) Going down a group, a new energy level is added with each subsequent atom, ensuring the valence electrons are moved further and further from the nucleus. This increases the shielding provided by non-valence electrons, decreases the ENC (even though the number of protons in the nucleus is increasi ...
Powerpoint
... is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface. is always tangent to an equipotential surface. always bisects an equipotential surface. makes an angle to an equipotential surface that depends on the amount of charge. ...
... is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface. is always tangent to an equipotential surface. always bisects an equipotential surface. makes an angle to an equipotential surface that depends on the amount of charge. ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam CHAPTER 8 TEST
... student reported a value of 38 percent. The correct value for the percentage of water in the hydrate is 51 percent. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this difference? (A) Strong initial heating caused some of the hydrate sample to spatter out of the crucible. (B) The dehydrat ...
... student reported a value of 38 percent. The correct value for the percentage of water in the hydrate is 51 percent. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this difference? (A) Strong initial heating caused some of the hydrate sample to spatter out of the crucible. (B) The dehydrat ...
Chapter 20 – The Representative Elements
... Elements of Group 5A overwhelmingly form covalent compounds. Whereas nitrogen can form a maximum of four covalent bonds, other elements in the group can form more than four covalent bonds by utilizing one or more of the nd orbitals. Nitrogen and phosphorus form simple anion with “-3” charge when rea ...
... Elements of Group 5A overwhelmingly form covalent compounds. Whereas nitrogen can form a maximum of four covalent bonds, other elements in the group can form more than four covalent bonds by utilizing one or more of the nd orbitals. Nitrogen and phosphorus form simple anion with “-3” charge when rea ...
OKEMOS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... __P___ dissolving a solid in a liquid 4) What are the indications that a chemical change (reaction) has occurred? Light, heat, color, gas, precipitate 5) a. Define a chemical change: when one substance is converted into an entirely new substance b. How do properties of compounds compare to the prope ...
... __P___ dissolving a solid in a liquid 4) What are the indications that a chemical change (reaction) has occurred? Light, heat, color, gas, precipitate 5) a. Define a chemical change: when one substance is converted into an entirely new substance b. How do properties of compounds compare to the prope ...
examination review
... Strong bases are bases that produce a high concentration of OH-(aq) ions in aqueous solution. As with strong acids, there are also relatively few common strong bases. Soluble hydroxides and soluble carbonates will produce strong bases. Since most hydroxides have low solubilities, very few hydroxides ...
... Strong bases are bases that produce a high concentration of OH-(aq) ions in aqueous solution. As with strong acids, there are also relatively few common strong bases. Soluble hydroxides and soluble carbonates will produce strong bases. Since most hydroxides have low solubilities, very few hydroxides ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint
... More than 100 elements are known, but only about two dozen are commonly found in living organisms. Elements are represented by one- or two-letter symbols. For example, C stands for carbon, H for hydrogen, Na for sodium, and Hg for mercury (shown). ...
... More than 100 elements are known, but only about two dozen are commonly found in living organisms. Elements are represented by one- or two-letter symbols. For example, C stands for carbon, H for hydrogen, Na for sodium, and Hg for mercury (shown). ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... Dissociation pressure of Ag / Ag Br: Ag Ag Br Br2 , C Ag Æ Ag+ + e- ...
... Dissociation pressure of Ag / Ag Br: Ag Ag Br Br2 , C Ag Æ Ag+ + e- ...
Mathematical Modeling of the Formation of Calcareous
... the influence of physics and chemistry of seawater, cathodic protection, and surface preparation on the formation of calcareous deposits through electrochemical experiments in natural seawater 512 and in artificial seawater. 13-~4 However, there are very few papers regarding mathematical modeling of ...
... the influence of physics and chemistry of seawater, cathodic protection, and surface preparation on the formation of calcareous deposits through electrochemical experiments in natural seawater 512 and in artificial seawater. 13-~4 However, there are very few papers regarding mathematical modeling of ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed
... When two atoms that differ in electronegativity bond, they do not share the electron pair equally and they form a polar covalent bond. o The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar covalent because oxygen has a much higher electronegativity than does hydrogen. o Compounds with a polar c ...
... When two atoms that differ in electronegativity bond, they do not share the electron pair equally and they form a polar covalent bond. o The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar covalent because oxygen has a much higher electronegativity than does hydrogen. o Compounds with a polar c ...
B.Sc.-Chemistry
... Electronic structure, oxidation states and ionic radii and lanthanide contraction, complex formation, occurrence and isolation, ceric ammonium sulphate and its analytical uses. B. Chemistry of Actinides Electronic configuration, oxidation states and magnetic properties, chemistry of separation of Np ...
... Electronic structure, oxidation states and ionic radii and lanthanide contraction, complex formation, occurrence and isolation, ceric ammonium sulphate and its analytical uses. B. Chemistry of Actinides Electronic configuration, oxidation states and magnetic properties, chemistry of separation of Np ...
Chapter 2 - My Teacher Site
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can interact with other atoms in such a way that completes their valence shell, either by: • Sharing valence electrons • Transferring valence electrons • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bon ...
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can interact with other atoms in such a way that completes their valence shell, either by: • Sharing valence electrons • Transferring valence electrons • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bon ...
Final Exam Review
... basis of this information, the heat of solution, H of sulfuric acid is which of the following? [HINT: Calculate the energy absorbed by the water, using the calorimetry equation (q = mTC), where C = 1.00 cal/g ºC. Then calculate the moles of sulfuric acid dissolved. Knowing that energy is conserved ...
... basis of this information, the heat of solution, H of sulfuric acid is which of the following? [HINT: Calculate the energy absorbed by the water, using the calorimetry equation (q = mTC), where C = 1.00 cal/g ºC. Then calculate the moles of sulfuric acid dissolved. Knowing that energy is conserved ...
02_Lecture_Presentation
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Check: We can check our result by confirming that both the elements and the electric charge are balanced. Each side has one Ca, one C, and three O, and the net charge on each side equals 0. Comment: If none of the ions in an ionic equation is removed from solution or changed in some way, then they a ...
... Check: We can check our result by confirming that both the elements and the electric charge are balanced. Each side has one Ca, one C, and three O, and the net charge on each side equals 0. Comment: If none of the ions in an ionic equation is removed from solution or changed in some way, then they a ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.