4_ Chemical reactions
... 4.6 Classification of Chemical Reactions There is no comprehensive classification scheme that would accommodate all known chemical reactions. One approach is to classify reactions into four types: combination, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reacti ...
... 4.6 Classification of Chemical Reactions There is no comprehensive classification scheme that would accommodate all known chemical reactions. One approach is to classify reactions into four types: combination, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reacti ...
1-Three states of matter . A: density, volume and weight B: solid
... Non-polar molecular crystals are very soft and are soluble in non-polar solvents. Non-polar molecular crystals are formed from symmetrical molecules with covalent bonds between atoms with small electronegativity differences. ...
... Non-polar molecular crystals are very soft and are soluble in non-polar solvents. Non-polar molecular crystals are formed from symmetrical molecules with covalent bonds between atoms with small electronegativity differences. ...
Summary - Clydebank High School
... 7. With some chemical reactions light energy can be used to increase the number of particles with the necessary activation energy. One such reaction is ........................................................... in which green plants use light energy to make starch. 8. From a balanced chemical equat ...
... 7. With some chemical reactions light energy can be used to increase the number of particles with the necessary activation energy. One such reaction is ........................................................... in which green plants use light energy to make starch. 8. From a balanced chemical equat ...
The Sabatier Principle Illustrated by Catalytic H2
... Initially, the curve is nearly linear and then drops off slightly as the H2O2 is used up (see inset). This is the reason that the activity is only measured initially where there is plenty of H2O2 so that the only limit to reaction is the properties of the surfaces. The reduced rate for copper after a ...
... Initially, the curve is nearly linear and then drops off slightly as the H2O2 is used up (see inset). This is the reason that the activity is only measured initially where there is plenty of H2O2 so that the only limit to reaction is the properties of the surfaces. The reduced rate for copper after a ...
On the Modeling of the Production and Drift of Carriers in
... point tip is several orders of magnitude smaller than the measured values (with a peak of about 100 μA [5]). This result shows that an additional mechanism of electron transfer into the liquid (other than the ones described above) is required in the simulation in order to reach the measured currents ...
... point tip is several orders of magnitude smaller than the measured values (with a peak of about 100 μA [5]). This result shows that an additional mechanism of electron transfer into the liquid (other than the ones described above) is required in the simulation in order to reach the measured currents ...
INDIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY
... The stoichiometry of the title reaction is expressed by the Equation, MnO 4 + 2C6H5HP(O)OH + 4H+ Mn(III) + 2C6H5PO(OH)2 + 2H2O. The kinetics and the rapid scan of the reaction mixture suggest the formation of the complexes by C6H5HP(O)OH(C1, K1) and C6H5HP(O)O (C2, K2) with MnO4 ion. The equilib ...
... The stoichiometry of the title reaction is expressed by the Equation, MnO 4 + 2C6H5HP(O)OH + 4H+ Mn(III) + 2C6H5PO(OH)2 + 2H2O. The kinetics and the rapid scan of the reaction mixture suggest the formation of the complexes by C6H5HP(O)OH(C1, K1) and C6H5HP(O)O (C2, K2) with MnO4 ion. The equilib ...
2. CHEMICAL ACTIVITY of the METALS 3. PATTERNS of the
... • brass, a mixture of z).................... and ................... • aa)...................................., with a very low melting point, is an alloy of ab).................................. and .................................... and is used in ac)..................................... and ... ...
... • brass, a mixture of z).................... and ................... • aa)...................................., with a very low melting point, is an alloy of ab).................................. and .................................... and is used in ac)..................................... and ... ...
uplift luna ap chemistry
... CnH2n+1OH; Do not be fooled—this looks like a hydroxide ion, but is not! It does not make this hydrocarbon an alkaline or basic compound. Do not name these as a hydroxide! C2H6 is ethane while C2H5OH is ethanol. NAMING BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS How do I know it is ionic? The chemical formula will begin ...
... CnH2n+1OH; Do not be fooled—this looks like a hydroxide ion, but is not! It does not make this hydrocarbon an alkaline or basic compound. Do not name these as a hydroxide! C2H6 is ethane while C2H5OH is ethanol. NAMING BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS How do I know it is ionic? The chemical formula will begin ...
112 ex iii lec outline f 04
... 1 In naming salts, the cation is written before the anion 2 Within a complex ion , the ligands are named before the metal ion 3 Ligands are listed in alphabetical order 4 Prefixes that give the number of ligands are not considered indetermining the alphabetical order 5 The names of anionic ligands e ...
... 1 In naming salts, the cation is written before the anion 2 Within a complex ion , the ligands are named before the metal ion 3 Ligands are listed in alphabetical order 4 Prefixes that give the number of ligands are not considered indetermining the alphabetical order 5 The names of anionic ligands e ...
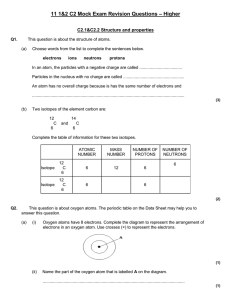
Year 11 C2 Mock Exam Revision Questions
... Phosphorus and fluorine form a covalent compound, phosphorus trifluoride. Complete the sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of .......................... ...
... Phosphorus and fluorine form a covalent compound, phosphorus trifluoride. Complete the sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of .......................... ...
Ministry of Education and Science of the Ukraine
... the solution concentration: mass and volume percents, molar fraction, molarity, molality. Electrolytic dissociation, electrolytes. Strong and weak electrolytes. The degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Ostwald’s dilution law. 5. Acid-base equilibrium in biological liquids. General prope ...
... the solution concentration: mass and volume percents, molar fraction, molarity, molality. Electrolytic dissociation, electrolytes. Strong and weak electrolytes. The degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Ostwald’s dilution law. 5. Acid-base equilibrium in biological liquids. General prope ...
Chemistry workbook
... solid sodium carbonate is stirred into a solution of iron (III) nitrate to yield sodium nitrate solution and iron (III) carbonate precipitate ...
... solid sodium carbonate is stirred into a solution of iron (III) nitrate to yield sodium nitrate solution and iron (III) carbonate precipitate ...
chapter 21 chemistry of the main-group elements i
... (M) First we note that sodium carbonate ionizes virtually completely when dissolved in H2O and thus is described as highly soluble in water. This is made evident by the fact that there is no Ksp value for Na2CO3. By contrast, the existence of Ksp values for MgCO3 and Li2CO3 shows that these compound ...
... (M) First we note that sodium carbonate ionizes virtually completely when dissolved in H2O and thus is described as highly soluble in water. This is made evident by the fact that there is no Ksp value for Na2CO3. By contrast, the existence of Ksp values for MgCO3 and Li2CO3 shows that these compound ...
2002 local exam - Virginia Section
... 66. Boron trichloride, BCl3, is a planar molecule while NCl3 is pyramidal can best be explained by: (A) nitrogen is more electronegative than boron (B) the nitrogen atom in NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons and the boron atom in BCl3 does not. (C) the nitrogen atom is smaller than the boron ...
... 66. Boron trichloride, BCl3, is a planar molecule while NCl3 is pyramidal can best be explained by: (A) nitrogen is more electronegative than boron (B) the nitrogen atom in NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons and the boron atom in BCl3 does not. (C) the nitrogen atom is smaller than the boron ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous
... Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ionizes into H+ and anions. H2SO4(aq) 2 H+(aq) + SO42−(aq) ...
... Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ionizes into H+ and anions. H2SO4(aq) 2 H+(aq) + SO42−(aq) ...
3 - Study Hungary
... A: the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number by 4. B: the atomic number decreases by 4 and the mass number by 2. C: the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn’t change. D: the loss of a neutron decreases the mass number by 1 and the charge by 1. E: the loss of a proton dec ...
... A: the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number by 4. B: the atomic number decreases by 4 and the mass number by 2. C: the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn’t change. D: the loss of a neutron decreases the mass number by 1 and the charge by 1. E: the loss of a proton dec ...
chemistry
... A beaker contains a liquid sample of a molecular substance. Both the beaker and the liquid are at 194 K. The graph below represents the relationship between temperature and time as the beaker and its contents are cooled for 12 minutes in a refrigerated chamber. Cooling Curve for a Substance ...
... A beaker contains a liquid sample of a molecular substance. Both the beaker and the liquid are at 194 K. The graph below represents the relationship between temperature and time as the beaker and its contents are cooled for 12 minutes in a refrigerated chamber. Cooling Curve for a Substance ...
投影片 1
... system of charges (U) Potential energy of a system of charges: work done to assemble charge configuration Potential: work to move test charge from infinity to (x,y,z) ...
... system of charges (U) Potential energy of a system of charges: work done to assemble charge configuration Potential: work to move test charge from infinity to (x,y,z) ...
1 • Introduction The Scientific Method (1 of 20) 1
... sodium metal + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen gas Na° + H 2 O → NaOH + H2 ...
... sodium metal + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen gas Na° + H 2 O → NaOH + H2 ...
KEY - Unit 10 - Practice Questions
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.