ece2201_lab4
... allowing you to see whether the output is changing or not. Again, fake the logic control “switch” with a length of wire. L21. Observe the output voltage on the oscilloscope with the “switch” in each position. Record which state of the VCTL logic signal correspond with which input being routed to the ...
... allowing you to see whether the output is changing or not. Again, fake the logic control “switch” with a length of wire. L21. Observe the output voltage on the oscilloscope with the “switch” in each position. Record which state of the VCTL logic signal correspond with which input being routed to the ...
DAC
... The clear pulse resets the counter to the zero. The counter then records in the binary form the number of pulses from clock line. The clock is a source of pulses equally spaced in time. Since the number of pulses counted increases as the input linearly with time, the binary word representing this co ...
... The clear pulse resets the counter to the zero. The counter then records in the binary form the number of pulses from clock line. The clock is a source of pulses equally spaced in time. Since the number of pulses counted increases as the input linearly with time, the binary word representing this co ...
V a
... •The formula for power applies to devices that provide power such as a battery as well as to devices that consume or dissipate power such as resistors, light bulbs and electric motors. ...
... •The formula for power applies to devices that provide power such as a battery as well as to devices that consume or dissipate power such as resistors, light bulbs and electric motors. ...
Coupling of disturbances and how to avoid it
... possible, i.e. by using twisted-pair cable. Then, the capacitance from the source of disturbance to the both signal wires will become equal. Further, using shielded cable and increasing the distance (d) will improve the situation by lowering the capacitances. In case of earth-fault, a fault current ...
... possible, i.e. by using twisted-pair cable. Then, the capacitance from the source of disturbance to the both signal wires will become equal. Further, using shielded cable and increasing the distance (d) will improve the situation by lowering the capacitances. In case of earth-fault, a fault current ...
Unit 4 - Section 13.8 2011 Relating V to I
... From our houses, we know that some machines (e.g., stoves and clothes dryers) require more potential difference that some other machines (e.g., night lights, battery rechargers). What effect does a higher potential have on current flowing through the wires of each machine? Purpose To determine ...
... From our houses, we know that some machines (e.g., stoves and clothes dryers) require more potential difference that some other machines (e.g., night lights, battery rechargers). What effect does a higher potential have on current flowing through the wires of each machine? Purpose To determine ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE POWER LAB AND LAB TUTOR
... manipulation become very much easy and less time consuming. ...
... manipulation become very much easy and less time consuming. ...
Low-Noise, Regulated, Negative Charge-Pump Power Supplies for GaAsFET Bias _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... Good layout is important, primarily for good noise performance. 1) Mount all components as close together as possible. 2) Keep traces short to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance. This includes connections to FB. ...
... Good layout is important, primarily for good noise performance. 1) Mount all components as close together as possible. 2) Keep traces short to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance. This includes connections to FB. ...
UNIT VII FET AMPLIFIERS 7.0 INTRODUCTION Field Effect
... between drain and source to change. As this resistance is connected across RE, so effective RE also changes according to change in the drain to source resistance. When output signal level increases, the drain to source resistance rd increases, increasing effective RE. Increase in RE causes the gain ...
... between drain and source to change. As this resistance is connected across RE, so effective RE also changes according to change in the drain to source resistance. When output signal level increases, the drain to source resistance rd increases, increasing effective RE. Increase in RE causes the gain ...
MAX3262 1Gbps, High-Speed Limiting Amplifier with Chatter
... The MAX3262 is an integrated limiting amplifier intended for high-frequency fiber-optic applications. The circuit connects to typical transimpedance amplifiers found within a fiber-optic link. The linear signal output from a transimpedance amplifier can contain significant amounts of noise, and may ...
... The MAX3262 is an integrated limiting amplifier intended for high-frequency fiber-optic applications. The circuit connects to typical transimpedance amplifiers found within a fiber-optic link. The linear signal output from a transimpedance amplifier can contain significant amounts of noise, and may ...
DS90LV047A 3V LVDS Quad CMOS Differential Line Driver DS90L V047A
... current for a range of loads (a voltage mode driver on the other hand supplies a constant voltage for a range of loads). Current is switched through the load in one direction to produce a logic state and in the other direction to produce the other logic state. The output current is typically 3.1 mA, ...
... current for a range of loads (a voltage mode driver on the other hand supplies a constant voltage for a range of loads). Current is switched through the load in one direction to produce a logic state and in the other direction to produce the other logic state. The output current is typically 3.1 mA, ...
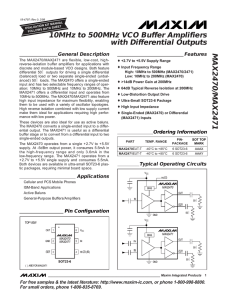
MAX2470/MAX2471 10MHz to 500MHz VCO Buffer Amplifiers with Differential Outputs General Description
... (balanced) load or two separate single-ended (unbalanced) 50Ω loads. The MAX2470 offers a single-ended input and has two selectable frequency ranges of operation: 10MHz to 500MHz and 10MHz to 200MHz. The MAX2471 offers a differential input and operates from 10MHz to 500MHz. The MAX2470/MAX2471 also ...
... (balanced) load or two separate single-ended (unbalanced) 50Ω loads. The MAX2470 offers a single-ended input and has two selectable frequency ranges of operation: 10MHz to 500MHz and 10MHz to 200MHz. The MAX2471 offers a differential input and operates from 10MHz to 500MHz. The MAX2470/MAX2471 also ...
OP193 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... emitter follower Q1, while Q2 provides current sink capability. When Q2 saturates, the output is pulled to within 5 mV of ground without an external pull-down resistor. The totem-pole output stage will supply a minimum of 5 mA to an external load, even when operating from a single 3.0 V power supply ...
... emitter follower Q1, while Q2 provides current sink capability. When Q2 saturates, the output is pulled to within 5 mV of ground without an external pull-down resistor. The totem-pole output stage will supply a minimum of 5 mA to an external load, even when operating from a single 3.0 V power supply ...
FAB3103 2.3 Watt Class-D Audio Amplifier with Integrated
... The input section includes an 80KHz low-pass filter for removing out-of-band noise from audio sources, such as sigma delta DACs. ...
... The input section includes an 80KHz low-pass filter for removing out-of-band noise from audio sources, such as sigma delta DACs. ...
Electronics Lab Manual
... for the proper functioning of an amplifier. In the circuit diagram, an NPN transistor is connected as a common emitter ac amplifier. R1 and R2 are employed for the voltage divider bias of the transistor. Voltage divider bias provides good stabilisation independent of the variations of β. The input s ...
... for the proper functioning of an amplifier. In the circuit diagram, an NPN transistor is connected as a common emitter ac amplifier. R1 and R2 are employed for the voltage divider bias of the transistor. Voltage divider bias provides good stabilisation independent of the variations of β. The input s ...
Valve RF amplifier

A valve RF amplifier (UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs.