RES8_chemcontentchecklist
... Explain in terms of van der Waals’ forces the variations in the boiling points of alkanes with different carbon-chain length and branching. Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion o ...
... Explain in terms of van der Waals’ forces the variations in the boiling points of alkanes with different carbon-chain length and branching. Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion o ...
The Working Cell: Energy from Sunlight
... Carbon cycle – process by which carbon moves from inorganic to organic & back to inorganic. ...
... Carbon cycle – process by which carbon moves from inorganic to organic & back to inorganic. ...
Single crystal structure determination using synchrotron X
... TFE/dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (60/40 v/v%) mixed solvent (700 μ L) and heated at 100°C (Fig. 2). The time-dependent NMR monitoring of the reaction solution revealed that the self-assembly completed after 24 h. The formation of a giant product was first indicated by the broadness of the 1H NMR signal ...
... TFE/dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (60/40 v/v%) mixed solvent (700 μ L) and heated at 100°C (Fig. 2). The time-dependent NMR monitoring of the reaction solution revealed that the self-assembly completed after 24 h. The formation of a giant product was first indicated by the broadness of the 1H NMR signal ...
Programme
... new class of photochemical reactions of benzophenones and related compounds is documented in this Thesis. Their photobehaviour in aqueous solvent media varied dramatically from their well-known behaviour in organic solvents and suggests unique and unprecedented mechanistic pathways. The aqueous phot ...
... new class of photochemical reactions of benzophenones and related compounds is documented in this Thesis. Their photobehaviour in aqueous solvent media varied dramatically from their well-known behaviour in organic solvents and suggests unique and unprecedented mechanistic pathways. The aqueous phot ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... – Solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) – Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
... – Solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) – Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
Study Guide for Lab Quiz
... 1) Dehydration of alcohols are catalyzed by acids. Explain why the acid is necessary in order for the dehydration to take place at a useful rate. 2) It acid-catalyzed dehydration occurs via an SN1 mechanism, which type of alcohols dehydrate most rapidly, 1°, 2°, or 3°. 3) Acid catalyzed dehydration ...
... 1) Dehydration of alcohols are catalyzed by acids. Explain why the acid is necessary in order for the dehydration to take place at a useful rate. 2) It acid-catalyzed dehydration occurs via an SN1 mechanism, which type of alcohols dehydrate most rapidly, 1°, 2°, or 3°. 3) Acid catalyzed dehydration ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... The technician made up aqueous solutions of the unknown compounds and did some tests to confirm their identity. Describe the tests you would do to show that these chemicals are correctly named. In each case give the reagent(s) you would use and then what you would see. (a) The test and result for po ...
... The technician made up aqueous solutions of the unknown compounds and did some tests to confirm their identity. Describe the tests you would do to show that these chemicals are correctly named. In each case give the reagent(s) you would use and then what you would see. (a) The test and result for po ...
2 - FacultyWeb
... electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom In living cells, the electronegative partners of hydrogen are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms • Hydrogen bonds are common between dipoles such as water • Hydrogen bonds also act as intramolecular bonds, holding a large molecul ...
... electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom In living cells, the electronegative partners of hydrogen are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms • Hydrogen bonds are common between dipoles such as water • Hydrogen bonds also act as intramolecular bonds, holding a large molecul ...
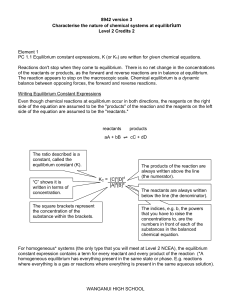
Rate and Equilibrium
... Distribution of gas and the effect of temperature: All gases are in random motion. This is caused by the collision of gaseous particles in air. The collisions are occurs randomly. Collisions may result in a loss or gain of kinetic energy and an uneven distribution of speed amount gaseous particles. ...
... Distribution of gas and the effect of temperature: All gases are in random motion. This is caused by the collision of gaseous particles in air. The collisions are occurs randomly. Collisions may result in a loss or gain of kinetic energy and an uneven distribution of speed amount gaseous particles. ...
Reactions In Aqueous Solution
... elementary substance (free element) is zero. Ex: Cl2 and P4 = 0 (2) Monatomic ions have oxidation numbers equal to their charge. Ex: Na+1 and Cl-1 (3) O-2 except for peroxides (O2-1) where O-1 Ex: Na2O2 (O-1) and Na2O (O-2) (4) H+1 except for hydrides (H-1) Ex: HCl (H+) and NaH (H-) (5) The sum of t ...
... elementary substance (free element) is zero. Ex: Cl2 and P4 = 0 (2) Monatomic ions have oxidation numbers equal to their charge. Ex: Na+1 and Cl-1 (3) O-2 except for peroxides (O2-1) where O-1 Ex: Na2O2 (O-1) and Na2O (O-2) (4) H+1 except for hydrides (H-1) Ex: HCl (H+) and NaH (H-) (5) The sum of t ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Car ...
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Car ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... Determines the chemical properties of the atom During chemical processes, interactions occur between the outermost electrons of each atom The electron properties of the atom will define the type(s) of interaction ...
... Determines the chemical properties of the atom During chemical processes, interactions occur between the outermost electrons of each atom The electron properties of the atom will define the type(s) of interaction ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
The Grignard Reagent
... – Once reaction 1 has started it should keep going on its own. If the reaction slows you may need to add a little heat to continue the reflux. – Be careful not to overheat the reaction. Remember ether boils at 35°C. Do not confuse the reaction starting with the ether boiling. You will see a cloudine ...
... – Once reaction 1 has started it should keep going on its own. If the reaction slows you may need to add a little heat to continue the reflux. – Be careful not to overheat the reaction. Remember ether boils at 35°C. Do not confuse the reaction starting with the ether boiling. You will see a cloudine ...
CH1 Student Revision Guides pdf
... The first graph shows that as the nuclear charge increases, the molar first ionisation energy does not increase uniformly. The second graph seems to indicate that the electrons in an atom exist in distinct energy levels. For sodium, shown above, there is one electron on its own which is the easiest ...
... The first graph shows that as the nuclear charge increases, the molar first ionisation energy does not increase uniformly. The second graph seems to indicate that the electrons in an atom exist in distinct energy levels. For sodium, shown above, there is one electron on its own which is the easiest ...