Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... translocations to give rise to thousands of nanochromosomes), followed by their at least thousand-fold amplification (see figures 2 and 3 for the diagrammatic representation of the processes involved in MAC differentiation). Asexual cell divisions occur by fission (b). MIC undergoes mitosis and MAC ami ...
... translocations to give rise to thousands of nanochromosomes), followed by their at least thousand-fold amplification (see figures 2 and 3 for the diagrammatic representation of the processes involved in MAC differentiation). Asexual cell divisions occur by fission (b). MIC undergoes mitosis and MAC ami ...
1.5MB - Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
... – We now recognize this inheritance as being carried by variation in DNA ...
... – We now recognize this inheritance as being carried by variation in DNA ...
Using mouse genetics to understand human disease
... – We now recognize this inheritance as being carried by variation in DNA ...
... – We now recognize this inheritance as being carried by variation in DNA ...
Hongbin (H.-B.) Zhang, Ph.D. - Department of Soil and Crop Sciences
... • Re-established the molecular basis of biology and genetics: The DNA “Jigsaw Puzzle” Structure Model. Discovered and established the “Jigsaw Puzzle” DNA structure model as the new molecular basis of biology. This DNA structure model has been tested using a large number of plant, animal and microbe ...
... • Re-established the molecular basis of biology and genetics: The DNA “Jigsaw Puzzle” Structure Model. Discovered and established the “Jigsaw Puzzle” DNA structure model as the new molecular basis of biology. This DNA structure model has been tested using a large number of plant, animal and microbe ...
What are genetic disorders?
... Inheritance Patterns of Monogenic Disorders - From the Genetic Interest Group in the U.K. Genetics - From the Medical Encyclopedia at MEDLINEplus. ...
... Inheritance Patterns of Monogenic Disorders - From the Genetic Interest Group in the U.K. Genetics - From the Medical Encyclopedia at MEDLINEplus. ...
Full text - Caister Academic Press
... and Petrov, 2010; Hildebrand et al., 2010; Rocha and Feil, 2010). Lind and Andersson (2008) compared the genomes of 2 Salmonella typhimurium mutants and showed a bias toward mutations from GC to AT. Rocha and Danchin (2002) suggested that GC content variation may be related to the higher energy cost ...
... and Petrov, 2010; Hildebrand et al., 2010; Rocha and Feil, 2010). Lind and Andersson (2008) compared the genomes of 2 Salmonella typhimurium mutants and showed a bias toward mutations from GC to AT. Rocha and Danchin (2002) suggested that GC content variation may be related to the higher energy cost ...
Evolution of DNA by celluLar automata HC Lee Department of
... • Reality is complex, but models don't have to be • Von Neumann machines - a machine capable of reproduction; the basis of life is information – Stanislaw Ulam: build the machine on paper, as a collection of cells on a lattice ...
... • Reality is complex, but models don't have to be • Von Neumann machines - a machine capable of reproduction; the basis of life is information – Stanislaw Ulam: build the machine on paper, as a collection of cells on a lattice ...
Genomics - FSU Biology - Florida State University
... type of periodic compositional bias. These principles can help discriminate structural genes in two ways: 1) based on the local “non-randomness” of a stretch, and 2) based on the known codon usage of a particular life form. The first, the non-randomness test, does not tell us anything about the part ...
... type of periodic compositional bias. These principles can help discriminate structural genes in two ways: 1) based on the local “non-randomness” of a stretch, and 2) based on the known codon usage of a particular life form. The first, the non-randomness test, does not tell us anything about the part ...
DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing: the IGS
... with a dilute bleach solution after every round of extractions, dedicated equipment and filtered tips were used for all extraction procedures, and extraction blanks were extracted along with samples. The quantity and purity of genomic DNA was determined using a NanodropTM Spectrophotometer (NanoDrop ...
... with a dilute bleach solution after every round of extractions, dedicated equipment and filtered tips were used for all extraction procedures, and extraction blanks were extracted along with samples. The quantity and purity of genomic DNA was determined using a NanodropTM Spectrophotometer (NanoDrop ...
Genetic Enhancement
... for some other gene. For instance, in Africa, there is an uncommonly high number of people who carry the sickle-cell gene. When two parents carrying this gene have offspring, that child will have sickle-cell anemia. However, sickle-cells bestow resistance to malaria. So, if we try to remove the gene ...
... for some other gene. For instance, in Africa, there is an uncommonly high number of people who carry the sickle-cell gene. When two parents carrying this gene have offspring, that child will have sickle-cell anemia. However, sickle-cells bestow resistance to malaria. So, if we try to remove the gene ...
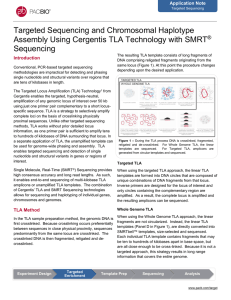
Application Note: Targeted sequencing and chromosomal haplotype
... with ~4 segments per read. The schematic in Figure 3 illustrates the general structure of the reads and how they mapped to the reference. Mapped reads generated with the Targeted TLA to BRCA1 fully cover the BRCA1 region (Figure 4), with heterozygous SNPs clearly visible from the TLA data (Figure 5) ...
... with ~4 segments per read. The schematic in Figure 3 illustrates the general structure of the reads and how they mapped to the reference. Mapped reads generated with the Targeted TLA to BRCA1 fully cover the BRCA1 region (Figure 4), with heterozygous SNPs clearly visible from the TLA data (Figure 5) ...
Separating derived from ancestral features of mouse and human
... almost as many protein-coding genes as humans [13–15]. Nevertheless, the reduction of the human gene count from an initial 32 000 in the draft human genome publication [3] to its current level of approx. 19 000 shows the many inherent difficulties in gene predictions as well as the great progress th ...
... almost as many protein-coding genes as humans [13–15]. Nevertheless, the reduction of the human gene count from an initial 32 000 in the draft human genome publication [3] to its current level of approx. 19 000 shows the many inherent difficulties in gene predictions as well as the great progress th ...
A THREE-GENERATION APPROACH IN BIODEMOGRAPHY IS
... Development encompasses all gametogenesis and meiosis processes starting during the grandmother’s fetal period and continuing during the mother’s gestation. We briefly describe two oogenesis-associated epigenetic processes: erasure of parental imprints (and subsequent epigenetic maternalization) and ...
... Development encompasses all gametogenesis and meiosis processes starting during the grandmother’s fetal period and continuing during the mother’s gestation. We briefly describe two oogenesis-associated epigenetic processes: erasure of parental imprints (and subsequent epigenetic maternalization) and ...
Isolation and identification of viral DNA from
... included in the total nucleic acid amount. • The amount of DNA decreases as time increases since the lysozyme activity acts longer on the corresponding bacterial targets. • The final yield of the samples are over 30 ng, which is a sufficient amount for future genomic amplifications ...
... included in the total nucleic acid amount. • The amount of DNA decreases as time increases since the lysozyme activity acts longer on the corresponding bacterial targets. • The final yield of the samples are over 30 ng, which is a sufficient amount for future genomic amplifications ...
RGC Collaborator Factsheet
... as part of this project; Mayo Clinic and University of Kiel have contributed DNA samples from nearly 2,500 consented PSC patients and many more including primary biliary cirrhosis, healthy volunteers and inflammatory bowel disease (which is strongly associated with and has a high co-occurrence rate i ...
... as part of this project; Mayo Clinic and University of Kiel have contributed DNA samples from nearly 2,500 consented PSC patients and many more including primary biliary cirrhosis, healthy volunteers and inflammatory bowel disease (which is strongly associated with and has a high co-occurrence rate i ...
This presentation is for educational purposes only and - GEC-KO
... screening recommendations see the point of care tool • For a recent article see Edwards JG, Feldman G, Goldberg J et al. Expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicinepoints to consider: a joint statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetrician ...
... screening recommendations see the point of care tool • For a recent article see Edwards JG, Feldman G, Goldberg J et al. Expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicinepoints to consider: a joint statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetrician ...
Enabling Loss of Heterozygosity Studies Using Fluidigm Digital Arrays
... The 12.765 Digital Array (Figure 1) is an integrated fluidic circuit (IFC), which partitions a single sample into 765 individual 6nL reactions. The ratio of any two sequences in a DNA sample can be calculated using real-time qPCR curves or end point images of positive chambers for one assay versus a ...
... The 12.765 Digital Array (Figure 1) is an integrated fluidic circuit (IFC), which partitions a single sample into 765 individual 6nL reactions. The ratio of any two sequences in a DNA sample can be calculated using real-time qPCR curves or end point images of positive chambers for one assay versus a ...
Genome sequence analysis of Ebola virus in
... gene that comprises 36% of the total genome. These data suggest that the L gene is conserved, with only two non-synonymous SNPs. One amino acid change is seen from UK2 to UK1 and UK3 (A to T at 17,848) and one amino acid change from UK3 to UK1 and UK2 (T to A at 16,894) (combined, UK3 differs in one ...
... gene that comprises 36% of the total genome. These data suggest that the L gene is conserved, with only two non-synonymous SNPs. One amino acid change is seen from UK2 to UK1 and UK3 (A to T at 17,848) and one amino acid change from UK3 to UK1 and UK2 (T to A at 16,894) (combined, UK3 differs in one ...
Chapter 13
... repeated sequences that have no direct function. These regions are called noncoding sequences. ...
... repeated sequences that have no direct function. These regions are called noncoding sequences. ...
Genome changes
... • A physical map expresses the distance between genetic markers, usually as the number of base pairs along the DNA • It is constructed by cutting a DNA molecule into many short fragments and arranging them in order by identifying overlaps ...
... • A physical map expresses the distance between genetic markers, usually as the number of base pairs along the DNA • It is constructed by cutting a DNA molecule into many short fragments and arranging them in order by identifying overlaps ...
Lecture 1: October 25, 2001 1.1 Biological Background
... structure of DNA and immediately inferred its method of replication. In February 2001, due to a joint venture of the Human Genome Project and a commercial company Celera, the first draft of the human genome was published. ...
... structure of DNA and immediately inferred its method of replication. In February 2001, due to a joint venture of the Human Genome Project and a commercial company Celera, the first draft of the human genome was published. ...
PopGen 5: Mutation pressure
... the L. monocytogenes genome much longer than the above metabolism island, as its GC content is much closer to the native value. Because this is such a slow process, the signal of old transfer events can be detected in a genome. This is useful to help detect regions of genomes, and the involved genes ...
... the L. monocytogenes genome much longer than the above metabolism island, as its GC content is much closer to the native value. Because this is such a slow process, the signal of old transfer events can be detected in a genome. This is useful to help detect regions of genomes, and the involved genes ...
Improving coverage of poorly sequenced regions in clinical exomes
... We have previously reported an orthogonal sequencing approach for clinical whole exome sequencing in which results of two next-generation sequencing platforms are combined for rapid variant confirmation. This both reduces the Sanger sequencing confirmation burden by ~95% and increases overall assay ...
... We have previously reported an orthogonal sequencing approach for clinical whole exome sequencing in which results of two next-generation sequencing platforms are combined for rapid variant confirmation. This both reduces the Sanger sequencing confirmation burden by ~95% and increases overall assay ...
Whole genome sequencing

Whole genome sequencing (also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing) is a laboratory process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast.Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA profiling, which only determines the likelihood that genetic material came from a particular individual or group, and does not contain additional information on genetic relationships, origin or susceptibility to specific diseases. Also unlike full genome sequencing, SNP genotyping covers less than 0.1% of the genome. Almost all truly complete genomes are of microbes; the term ""full genome"" is thus sometimes used loosely to mean ""greater than 95%"". The remainder of this article focuses on nearly complete human genomes.High-throughput genome sequencing technologies have largely been used as a research tool and are currently being introduced in the clinics. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data will be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response.